RNN从理论到实战【实战篇】
来源:投稿 作者:175
编辑:学姐
昨天的文章中,我们学习了RNN的理论部分,本文来看如何实现它,包括堆叠RNN和双向RNN。从而理解它们的原理。最后看一个应用到词性标注任务的实战。
RNNCell
首先实现单时间步RNN计算类,这是一个公共类:
class RNNCell(Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size: int, bias: bool = True, nonlinearity: str = 'tanh') -> None:
'''
RNN单时间步的抽象
:param input_size: 输入x的特征数
:param hidden_size: 隐藏状态的特征数
:param bias: 线性层是否包含偏置
:param nonlinearity: 非线性激活函数 tanh | relu
'''
super(RNNCell, self).__init__()
# 输入x的线性变换
self.input_trans = Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=bias)
# 隐藏状态的线性变换
self.hidden_trans = Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=bias)
if nonlinearity == 'tanh':
self.activation = F.tanh
else:
self.activation = F.relu
def forward(self, x: Tensor, h: Tensor) -> Tensor:
'''
单个RNN的前向传播
:param x: 形状 [batch_size, input_size]
:param h: 形状 [batch_size, hidden_size]
:return:
'''
# [batch_size, input_size] x [input_size, hidden_size] + [batch_size, hidden_size] x [hidden_size, hidden_size]
# = [batch_size, hidden_size]
h_next = self.activation(self.input_trans(x) + self.hidden_trans(h))
return h_next
激活函数支持tanh和relu,这只是单时间步的RNN计算,RNN模型就是基于它来实现的。
RNN
下面来实现简单RNN。
class RNN(Module):
def __init__(self, input_size: int, hidden_size: int, batch_first: bool = False, num_layers: int = 1,
nonlinearity: str = 'tanh',
bias: bool = True, dropout: float = 0) -> None:
'''
:param input_size: 输入x的特征数
:param hidden_size: 隐藏状态的特征数
:param batch_first:
:param num_layers: 层数
:param nonlinearity: 非线性激活函数 tanh | relu
:param bias: 线性层是否包含偏置
:param dropout: 用于多层堆叠RNN,默认为0代表不使用dropout
'''
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.batch_first = batch_first
# 支持多层
self.cells = ModuleList([RNNCell(input_size, hidden_size, bias, nonlinearity)] +
[RNNCell(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias, nonlinearity) for _ in range(num_layers - 1)])
self.dropout = dropout
if dropout:
# Dropout层
self.dropout_layer = Dropout(dropout)
从参数可以看到,我们支持多层RNN,同时在多层RNN之间经过了一层Dropout。
def forward(self, input: Tensor, h_0: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
'''
RNN的前向传播
:param input: 形状 [n_steps, batch_size, input_size] 若batch_first=False
:param h_0: 形状 [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
:return:
output: (n_steps, batch_size, hidden_size)若batch_first=False 或
(batch_size, n_steps, hidden_size)若batch_first=True
h_n: (num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
'''
is_batched = input.ndim == 3
batch_dim = 0 if self.batch_first else 1
if not is_batched:
# 转换为批大小为1的输入
input = input.unsqueeze(batch_dim)
if h_0 is not None:
h_0 = h_0.unsqueeze(1)
if self.batch_first:
batch_size, n_steps, _ = input.shape
input = input.transpose((1, 0, 2)) # 将batch放到中间维度
else:
n_steps, batch_size, _ = input.shape
if h_0 is None:
h = [Tensor.zeros((batch_size, self.hidden_size), device=input.device) for _ in range(self.num_layers)]
else:
h = h_0
h = list(F.unbind(h)) # 按层数拆分h
output = []
for t in range(n_steps):
inp = input[t]
for layer in range(self.num_layers):
h[layer] = self.cells[layer](inp, h[layer])
inp = h[layer]
if self.dropout and layer != self.num_layers - 1:
inp = self.dropout_layer(inp)
# 收集最终层的输出
output.append(h[-1])
output = F.stack(output)
if self.batch_first:
output = output.transpose((1, 0, 2))
h_n = F.stack(h)
return output, h_n
为了简化实现,将batch维度放到维度1。
由于包含多层,每层含有不同的隐藏状态,所以需要按层数来拆分h。
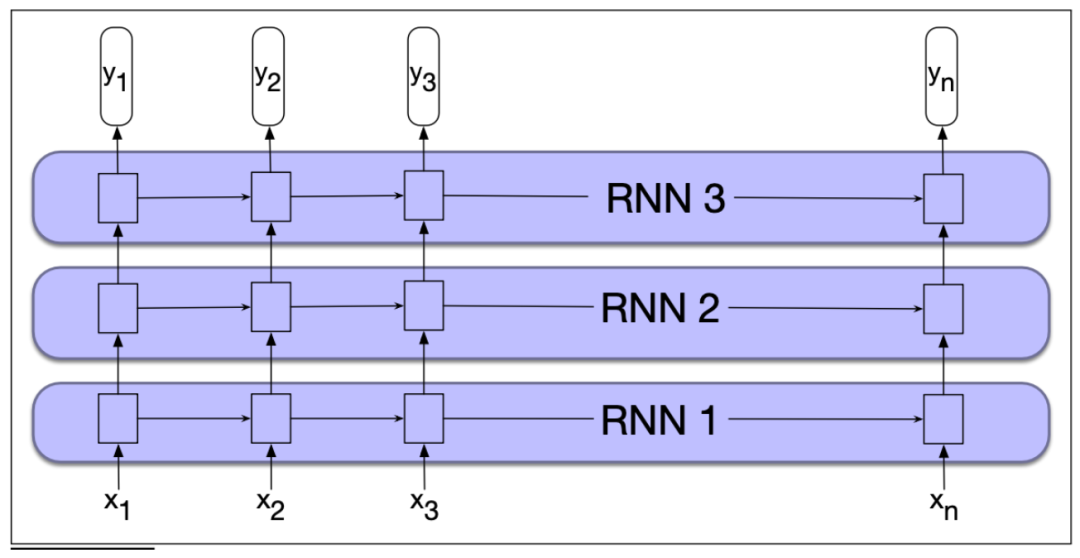
多层的情况下,需要在合适的位置增加Dropout。比如上图的例子中,在RNN1和RNN2以及RNN2和RNN3的连接处增加Dropout。
双向RNN

双向RNN其实就是多了另一个反方向处理的RNN,因此我们首先增加新的用于处理反序输入的RNN:
# 支持多层
self.cells = ModuleList([RNNCell(input_size, hidden_size, bias, nonlinearity)] +
[RNNCell(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias, nonlinearity) for _ in range(num_layers - 1)])
if self.bidirectional:
# 支持双向
self.back_cells = copy.deepcopy(self.cells)
最简单的方法,就是将输入逆序,然后依照正向过程重新,重新跑一遍反向RNN过程。但这样会有重复代码,因此我们把RNN沿着某个方向的运算过程抽成一个函数。
def forward(self, input: Tensor, h_0: Tensor) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
'''
RNN的前向传播
:param input: 形状 [n_steps, batch_size, input_size] 若batch_first=False
:param h_0: 形状 [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
:return:
num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1
output: (n_steps, batch_size, num_directions * hidden_size)若batch_first=False 或
(batch_size, n_steps, num_directions * hidden_size)若batch_first=True
包含每个时间步最后一层(多层RNN)的输出h_t
h_n: (num_directions * num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) 包含最终隐藏状态
'''
is_batched = input.ndim == 3
batch_dim = 0 if self.batch_first else 1
if not is_batched:
# 转换为批大小为1的输入
input = input.unsqueeze(batch_dim)
if h_0 is not None:
h_0 = h_0.unsqueeze(1)
if self.batch_first:
batch_size, n_steps, _ = input.shape
input = input.transpose((1, 0, 2)) # 将batch放到中间维度
else:
n_steps, batch_size, _ = input.shape
if h_0 is None:
num_directions = 2 if self.bidirectional else 1
h = Tensor.zeros((self.num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size), dtype=input.dtype,
device=input.device)
else:
h = h_0
hs = list(F.unbind(h)) # 按层数拆分h
if not self.bidirectional:
# 如果是单向的
output, h_n = one_directional_op(input, self.cells, n_steps, hs, self.num_layers, self.dropout_layer,
self.batch_first)
else:
output_f, h_n_f = one_directional_op(input, self.cells, n_steps, hs[:self.num_layers], self.num_layers,
self.dropout_layer, self.batch_first)
output_b, h_n_b = one_directional_op(F.flip(input, 0), self.back_cells, n_steps, hs[self.num_layers:],self.num_layers, self.dropout_layer, self.batch_first, reverse=True)
output = F.cat([output_f, output_b], 2)
h_n = F.cat([h_n_f, h_n_b], 0)
return output, h_n
我们这里输出的维度和PyTorch保持一致。那么其中的one_directional_op是怎么实现的呢?
def one_directional_op(input, cells, n_steps, hs, num_layers, dropout, batch_first, reverse=False):
'''
单向RNN运算
Args:
input: [n_steps, batch_size, input_size]
cells:
n_steps:
hs:
num_layers:
dropout:
batch_first:
reverse:
Returns:
'''
output = []
for t in range(n_steps):
inp = input[t]
for layer in range(num_layers):
hs[layer] = cells[layer](inp, hs[layer])
inp = hs[layer]
if dropout and layer != num_layers - 1:
inp = dropout(inp)
# 收集最终层的输出
output.append(hs[-1])
output = F.stack(output)
if reverse:
output = F.flip(output, 0) #
if batch_first:
output = output.transpose((1, 0, 2))
h_n = F.stack(hs)
return output, h_n
这里要注意的是output = F.flip(output, 0)将输出按时间步维度逆序,使得时间步t=0上,是看了整个序列的结果。
最后我们通过词性标注任务实战来应用我们的RNN。
词性标注实战
词性标注任务可以看成是多类别文本分类问题,我们使用NLTK提供的宾州树库(Penn Treebank)样例数据,首先加载词性标注语料库:
def load_treebank():
from nltk.corpus import treebank
sents, postags = zip(*(zip(*sent) for sent in treebank.tagged_sents()))
vocab = Vocabulary.build(sents, reserved_tokens=["<pad>"])
tag_vocab = Vocabulary.build(postags)
train_data = [(vocab.to_ids(sentence), tag_vocab.to_ids(tags)) for sentence, tags in
zip(sents[:3000], postags[:3000])]
test_data = [(vocab.to_ids(sentence), tag_vocab.to_ids(tags)) for sentence, tags in
zip(sents[3000:], postags[3000:])]
return train_data, test_data, vocab, tag_vocab
我们采用前3000句作为训练数据,其余的作为测试数据。然后实现我们的数据集类:
class RNNDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = np.asarray(data)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, i):
return self.data[i]
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(examples):
inputs = [Tensor(ex[0]) for ex in examples]
targets = [Tensor(ex[1]) for ex in examples]
inputs = pad_sequence(inputs)
targets = pad_sequence(targets)
mask = inputs.data != 0
return inputs, targets, Tensor(mask)
为了对齐批次内数据的长度,需要对输入序列和输出序列进行补齐,同时用mask记录了哪些是经过补齐的标记。
然后基于我们上面实现的RNN来实现该词性标注分类模型,这里同样也叫RNN:
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size: int, embedding_dim: int, hidden_dim: int, output_dim: int, n_layers: int,
dropout: float, bidirectional: bool = False):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
# 调用我们模型库中的RNN
self.rnn = nn.RNN(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, batch_first=True, num_layers=n_layers, dropout=dropout, bidirectional=bidirectional)
num_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1
self.output = nn.Linear(num_directions * hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, input: Tensor, hidden: Tensor = None) -> Tensor:
embeded = self.embedding(input)
output, _ = self.rnn(embeded, hidden) # pos tag任务利用的是包含所有时间步的output
outputs = self.output(output)
log_probs = F.log_softmax(outputs, axis=-1)
return log_probs
这里在序列标注任务中,需要使用序列全部状态的隐藏层,存储在变量output中。
最后,在训练和预测阶段,需要使用mask来保证仅对有效标记求损失、对正确预测结果以及总的标记计数。
训练代码如下:
embedding_dim = 128
hidden_dim = 128
batch_size = 32
num_epoch = 10
n_layers = 2
dropout = 0.2
# 加载数据
train_data, test_data, vocab, pos_vocab = load_treebank()
train_dataset = RNNDataset(train_data)
test_dataset = RNNDataset(test_data)
train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn, shuffle=True)
test_data_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, collate_fn=test_dataset.collate_fn, shuffle=False)
num_class = len(pos_vocab)
# 加载模型
device = cuda.get_device("cuda:0" if cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = RNN(len(vocab), embedding_dim, hidden_dim, num_class, n_layers, dropout, bidirectional=True)
model.to(device)
# 训练过程
nll_loss = NLLLoss()
optimizer = SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
model.train() # 确保应用了dropout
for epoch in range(num_epoch):
total_loss = 0
for batch in tqdm(train_data_loader, desc=f"Training Epoch {epoch}"):
inputs, targets, mask = [x.to(device) for x in batch]
log_probs = model(inputs)
loss = nll_loss(log_probs[mask], targets[mask]) # 通过bool选择,mask部分不需要计算
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
print(f"Loss: {total_loss:.2f}")
# 测试过程
acc = 0
total = 0
model.eval() # 不需要dropout
for batch in tqdm(test_data_loader, desc=f"Testing"):
inputs, targets, mask = [x.to(device) for x in batch]
with no_grad():
output = model(inputs)
acc += (output.argmax(axis=-1).data == targets.data)[mask.data].sum().item()
total += mask.sum().item()
# 输出在测试集上的准确率
print(f"Acc: {acc / total:.2f}")
我们通过model.train()来model.eval()来控制需不需要进行Dropout。最终,在双向RNN中训练了10个批次,结果为:
Training Epoch 9: 94it [02:00, 1.29s/it]
Loss: 103.25
Testing: 29it [00:05, 5.02it/s]
Acc: 0.70
由于电脑上没有GPU,因此速度较慢,就只训练了10个批次,看起来效果还不错,测试集上的准确率达到了70%。
完整代码
https://github.com/nlp-greyfoss/metagrad
参考
Speech and Language Processing
自然语言处理:基于预训练模型的方法
https://nn.labml.ai/lstm/index.html
关注下方《学姐带你玩AI》🚀🚀🚀
220+篇AI必读论文免费领取
码字不易,欢迎大家点赞评论收藏!
