leetcode--各种数据结构相关的题
数据结构
- 1.数组
- (1)找到所有数组中消失的数字(448)
- (2)旋转图像(48)
- (3)搜索二维矩阵 II(240)
- (4)最多能完成排序的块(769)
- 2.栈和队列
- (1)用栈实现队列(232)
- (2)最小栈(155)
- (3)有效的括号(20)
- 3.单调栈
- (1)每日温度
- 4.优先队列
- (1)合并K个升序链表(23)
- 5.双端队列
- (1)滑动窗口最大值(239)
- 6.哈希表
- (1)两数之和(1)
- (2)最长连续序列(128)
- (3)直线上最多的点数
- 7.前缀和与积分图
- (1)区域和检索 - 数组不可变(303)
- (2)二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变(304)
- (3)和为 K 的子数组(560)
- 8.练习
- (1)重塑矩阵(566)
- (2)用队列实现栈(225)
- (3)下一个更大元素 II(503)
- (4)存在重复元素(217)
- (5)数组的度
- (6)最长和谐子序列(594)
- (7)寻找重复数(287)
- (8)优势洗牌(870)
1.数组
(1)找到所有数组中消失的数字(448)
给你一个含 n 个整数的数组 nums ,其中 nums[i] 在区间 [1, n] 内。请你找出所有在 [1, n] 范围内但没有出现在 nums 中的数字,并以数组的形式返回结果。
输入:nums = [4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
输出:[5,6]
输入:nums = [1,1]
输出:[2]
//时间空间复杂度都为O(n)
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.findDisappearedNumbers(arr));
}
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
boolean[] find=new boolean[n+1];//数组中出现的数将该数对应的数组位置置为true
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
find[nums[i]]=true;
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if (!find[i]){
list.add(i);
}
}
return list;
}
}
//空间复杂度为O(1)
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.findDisappearedNumbers(arr));
}
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
//遍历数组 每遇到一个数x 就让nums[x-1]增加n
//当我们遍历到某个位置时 其中的数可能已经被增加过了 因此需要对n取模
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
int x=(nums[i]-1)%n;
nums[x]+=n;
}
//遍历nums 若nums[i]未大于n 就说明没有遇到过数i+1
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
if (nums[i]<=n){
list.add(i+1);
}
}
return list;
}
}
(2)旋转图像(48)
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
你必须在 原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
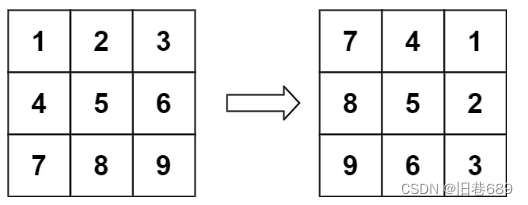
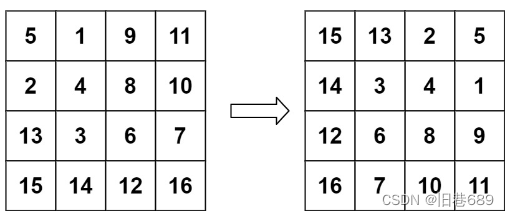
对应位置交换位置,结束条件可以考虑i和j同时向内缩进,也就是一圈一圈考虑
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr={{5,1,9,11},
{2,4,8,10},
{13,3,6,7},
{15,14,12,16}};
Solution solution=new Solution();
solution.rotate(arr);
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for (int j=0;j< arr[0].length;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int rowMin=0;//从第0行开始 起始行
int colMin=0;//从第0列开始 起始列
int rowMax= matrix.length-1;//第一圈可以用到的的最大行数是总行数-1
int colMax=matrix[0].length-1;//第一圈可以用到的的最大列数是总列数-1
//旋转完一圈开始下一圈 循环退出条件是 起始行>最大行 起始列>最大列
while (rowMin<=rowMax&&colMin<=colMax){
RotateOneCircle(matrix,rowMin,colMin,rowMax,colMax);
//缩进
rowMin++;
colMin++;
rowMax--;
colMax--;
}
}
//旋转一圈的方法
private void RotateOneCircle(int[][] arr, int rowMin, int colMin, int rowMax, int colMax) {
int temp=0;//辅助数
//遍历旋转这一圈
for (int j=0;j<colMax-colMin;j++){
temp=arr[rowMin][colMin+j];
arr[rowMin][colMin+j]=arr[rowMax-j][colMin];
arr[rowMax-j][colMin]=arr[rowMax][colMax-j];
arr[rowMax][colMax-j]=arr[rowMin+j][colMax];
arr[rowMin+j][colMax]=temp;
}
}
}
(3)搜索二维矩阵 II(240)
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target 。该矩阵具有以下特性:
每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
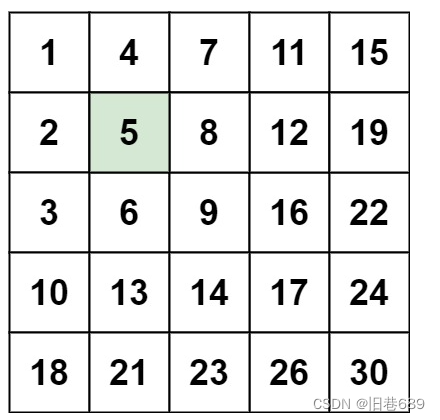
输入:matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
输出:true
从数组的右上角开始遍历,如果target大于当前元素,则用当前元素下方的元素再次比较;如果target小于当前元素,
则用当前元素左边的元素再次比较;以此类推,知道找到target或者到达边界
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr={{1,4,7,11,15},
{2,5,8,12,19},
{3,6,9,16,22},
{10,13,14,17,24},
{18,21,23,26,30}};
int target=5;
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.searchMatrix(arr,5));
}
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m= matrix.length;
int n=matrix[0].length-1;//表示列
int i=0;//表示行
while (i<m&&n>=0){
if (target>matrix[i][n]){//target大于当前元素 比较下方元素
i++;
} else if (target<matrix[i][n]) {//target小于当前元素 比较左方元素
n--;
}else {//找到target
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
(4)最多能完成排序的块(769)
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 arr ,它表示在 [0, n - 1] 范围内的整数的排列。
我们将 arr 分割成若干 块 (即分区),并对每个块单独排序。将它们连接起来后,使得连接的结果和按升序排序后的原数组相同。
返回数组能分成的最多块数量。
输入: arr = [4,3,2,1,0]
输出: 1
解释:
将数组分成2块或者更多块,都无法得到所需的结果。
例如,分成 [4, 3], [2, 1, 0] 的结果是 [3, 4, 0, 1, 2],这不是有序的数组。
输入: arr = [1,0,2,3,4]
输出: 4
解释:
我们可以把它分成两块,例如 [1, 0], [2, 3, 4]。
然而,分成 [1, 0], [2], [3], [4] 可以得到最多的块数。
对每个块单独排序后,结果为 [0, 1], [2], [3], [4]
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,0,2,3,4};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.maxChunksToSorted(arr));
}
public int maxChunksToSorted(int[] arr) {
int n=arr.length;
if (arr.length==1){
return 1;
}
int maxCount=0;//可以分成的最大块数
int preMax=0;//当前最大值
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
preMax=Math.max(preMax,arr[i]);
//如果当前最大值等于当前的i值
if (preMax==i){
maxCount++;//可以分块数+1
}
}
return maxCount;
}
}
2.栈和队列
(1)用栈实现队列(232)
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
public class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1=new Stack<>();
stack2=new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
while (!stack2.isEmpty()){
stack1.push(stack2.pop());
}
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()){
while (!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()){
while (!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
if (stack1.empty()&& stack2.empty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class QueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue queue=new MyQueue();
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.push(3);
//System.out.println("pop():"+queue.pop());
System.out.println("peak():"+queue.peek());
System.out.println("empty():"+queue.empty());
queue.push(4);
System.out.println("====================");
System.out.println("pop():"+queue.pop());
System.out.println("peak():"+queue.peek());
System.out.println("empty():"+queue.empty());
}
}
(2)最小栈(155)
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
实现 MinStack 类:
MinStack() 初始化堆栈对象。
void push(int val) 将元素val推入堆栈。
void pop() 删除堆栈顶部的元素。
int top() 获取堆栈顶部的元素。
int getMin() 获取堆栈中的最小元素。
public class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> stack;//普通栈
Stack<Integer> minStack;//返回最小值的栈
public MinStack() {
stack=new Stack<>();
minStack=new Stack<>();
minStack.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
//最小值栈保存当前元素加进来后 栈中的最小值
minStack.push(Math.min(minStack.peek(),val));
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
//当前元素出栈时 最小值栈对应的位置也要出栈
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
public class MinStackTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MinStack stack=new MinStack();
stack.push(-3);
stack.push(1);
stack.push(23);
System.out.println(stack.getMin());
}
}
(3)有效的括号(20)
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,‘)’,‘{’,‘}’,‘[’,‘]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="()[]{}";
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.isValid(s));
}
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n=s.length();
//长度为奇数直接返回false
if (n%2!=0){
return false;
}
Stack<Character> stack=new Stack<>();
Map<Character,Character> map=new HashMap<>();
//将右括号和左括号分别以 key 和 value 存储
map.put(')','(');
map.put('}','{');
map.put(']','[');
//遍历字符串匹配括号
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
char ch=s.charAt(i);
if (map.containsKey(ch)){//如果ch是map集合里的key 也就是右括号
//先判断stack是否为空或者栈顶元素是否与ch匹配
if (stack.isEmpty()||stack.peek()!=map.get(ch)){
return false;
}
//如果匹配
stack.pop();//弹出栈顶括号
}else {//如果ch是左括号
stack.push(ch);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
3.单调栈
(1)每日温度
给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
输入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
输出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
输入: temperatures = [30,40,50,60]
输出: [1,1,1,0]
输入: temperatures = [30,60,90]
输出: [1,1,0]
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73};
Solution solution=new Solution();
int[] tem = solution.dailyTemperatures(arr);
for (int i=0;i< tem.length;i++){
System.out.print(tem[i]+" ");
}
}
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int n = temperatures.length;
if (n==1){
return new int[1];
}
int[] arr=new int[n];
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
//当栈不为空并且栈顶温度小于当前温度时
while (!stack.isEmpty()&&temperatures[i]>temperatures[stack.peek()]){
arr[stack.peek()]=i-stack.pop();
}
//当上边两个条件不全满足时 将当前元素的下标入栈
stack.push(i);
}
return arr;
}
}
4.优先队列
(1)合并K个升序链表(23)
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
//顺序遍历合并每一个链表
public class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode list=null;//需要返回的链表
//遍历每一个链表 然后与list合并
for (int i=0;i< lists.length;i++){
list=mergeTwoLists(lists[i],list);
}
return list;
}
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode a,ListNode b){
if (a==null||b==null){
return a!=null?a:b;
}
ListNode head=new ListNode(0);//设置一个头节点 返回的时候返回他的next节点
ListNode tail=head;//记录下一个插入位置的前一个位置
ListNode preA=a;//a链表的当前节点
ListNode preB=b;//b链表的当前节点
while (preA!=null&&preB!=null){
if (preA.val<preB.val){
tail.next=preA;
preA=preA.next;
}else {
tail.next=preB;
preB=preB.next;
}
tail=tail.next;
}
tail.next=preA!=null?preA:preB;
return head.next;
}
}
//采用分治合并
public class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
return merge(lists,0,lists.length-1);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists,int left,int right){
if (left==right){
return lists[left];
}
if (left>right){
return null;
}
int mid=(left+right)>>1;//因为lists.length<500 所以这里不用担心越界 可以使用left+right
return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, left, mid),merge(lists, mid+1, right));
}
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode a,ListNode b){
if (a==null||b==null){
return a!=null?a:b;
}
ListNode head=new ListNode(0);//设置一个头节点 返回的时候返回他的next节点
ListNode tail=head;//记录下一个插入位置的前一个位置
ListNode preA=a;//a链表的当前节点
ListNode preB=b;//b链表的当前节点
while (preA!=null&&preB!=null){
if (preA.val<preB.val){
tail.next=preA;
preA=preA.next;
}else {
tail.next=preB;
preB=preB.next;
}
tail=tail.next;
}
tail.next=preA!=null?preA:preB;
return head.next;
}
}
5.双端队列
(1)滑动窗口最大值(239)
给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3
输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7]
解释:
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
输入:nums = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
//优先队列
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7};
int k=3;
Solution solution=new Solution();
int[] ints = solution.maxSlidingWindow(arr, k);
for (int i:ints) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n= nums.length;
int[] res=new int[n-k+1];
//定义一个大根堆
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
if (o1[0]!=o2[0]){//如果元素值不相等 按照元素值降序排序
return o2[0]-o1[0];
}
//如果元素值相等 按照索引值降序排序
return o2[1]-o1[1];
}
});
//将数组前k个元素加入大根堆
for (int i=0;i<k;i++){
heap.add(new int[]{nums[i],i});
}
res[0]=heap.peek()[0];
//开始滑动窗口
for (int i=k;i<n;i++){
heap.add(new int[]{nums[i],i});//当前元素加入大根堆
//如果此时最大值不在窗口内 就将堆顶元素移除 直到堆顶元素最大值在当前窗口内
//此时堆顶元素就是当前窗口内的最大值
while (heap.peek()[1]<=i-k){
heap.poll();//弹出堆顶元素
}
res[i-k+1]=heap.peek()[0];
}
return res;
}
}
6.哈希表
哈希表又称为散列表,使用O(n)的空间复杂度存储数据,通过hash函数映射位置,从而实现近似O(1)的时间
复杂度的插入、删除、查找等操作
(1)两数之和(1)
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
//暴力遍历
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={2,7,11,15};
int k=9;
Solution solution=new Solution();
int[] ints = solution.twoSum(arr, k);
for (int i:ints) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n= nums.length;
for (int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
for (int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if (nums[j]==target-nums[i]){
return new int[]{i,j};
}
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}
//使用hash表
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={2,7,11,15};
int k=9;
Solution solution=new Solution();
int[] ints = solution.twoSum(arr, k);
for (int i:ints) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n= nums.length;
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
//如果map里存在一个key使它和当前值相加等于target 直接返回他们的下标
if (map.containsKey(target-nums[i])){
return new int[]{map.get(target-nums[i]),i};
}
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
(2)最长连续序列(128)
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
输出:4
解释:最长数字连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
输入:nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1]
输出:9
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={100,4,200,1,3,2};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.longestConsecutive(arr));
}
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
if (n==0){
return 0;
} else if (n==1) {
return 1;
}
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
int longestLen=0;//最长序列长度
//将数组中元素加入set集合中 并去重
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
set.add(nums[i]);
}
//遍历数组中每一个元素
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
//当一个元素在数组中不存在前驱元素时 从这个元素出发才可以得到当前最长序列
//如果存在前驱元素 那么从前驱元素开始 得到的序列长度一定大于从当前这个元素开始的序列长度
if (!set.contains(nums[i]-1)){
int curLen=1;//当前长度
int curNum=nums[i];//当前元素
//当当前元素存在后继元素时 当前长度+1
while (set.contains(curNum+1)){
curLen++;
curNum++;
}
longestLen=Math.max(longestLen,curLen);
}
}
return longestLen;
}
}
(3)直线上最多的点数
给你一个数组 points ,其中 points[i] = [xi, yi] 表示 X-Y 平面上的一个点。求最多有多少个点在同一条直线上。
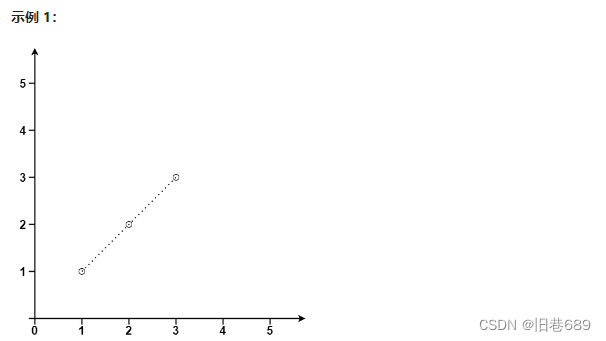
输入:points = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]]
输出:3
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr={{1,1},{3,2},{5,3},{4,1},{2,3},{1,4}};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.maxPoints(arr));
}
public int maxPoints(int[][] points) {
int n=points.length;
if (n<=2){
return n;
}
int maxPoint=0;//最多有多少个点在同一条直线上
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
//当共线点的数量 > n/2时 或者 共线点的数量 >= 当前点i之后所剩的点的数量时 就直接退出循环
if (maxPoint>=n-i||maxPoint>n/2){
break;
}
//用map集合来存储每个不同直线上共线点的个数
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for (int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
int x=points[j][0]-points[i][0];
int y=points[j][1]-points[i][1];
//当x=0或者y=0时 将不为0的一方设置为1
if (x==0){
y=1;
} else if (y==0) {
x=1;
}else {
//假设y始终为正数
if (y<0){
x=-x;
y=-y;
}
//求x和y的最大公倍数
int gcdXY=gcd(Math.abs(x),Math.abs(y));
//化简x和y
x/=gcdXY;
y/=gcdXY;
}
//将x和y用一个正数表示 作为集合的key
int key=y+20001*x;
if (map.containsKey(key)){//当集合中存在key时 点数+1
map.put(key,map.get(key)+1);
}else {//集合中不存在key时 将这个key加入集合
map.put(key,1);
}
}
int preMax=0;//当前i所在的最大点数
//遍历当前的map集合 求出当前的最大值
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry: map.entrySet()){
preMax=Math.max(preMax, entry.getValue()+1);
}
//将每一次的当前最大值与最大值做比较 求总的最大值
maxPoint=Math.max(preMax,maxPoint);
}
return maxPoint;
}
private int gcd(int x,int y){
return y!=0?gcd(y,x%y):x;
}
}
7.前缀和与积分图
(1)区域和检索 - 数组不可变(303)
给定一个整数数组 nums,处理以下类型的多个查询:
计算索引 left 和 right (包含 left 和 right)之间的 nums 元素的 和 ,其中 left <= right
实现 NumArray 类:
NumArray(int[] nums) 使用数组 nums 初始化对象
int sumRange(int i, int j) 返回数组 nums 中索引 left 和 right 之间的元素的 总和 ,包含 left 和 right 两点(也就是 nums[left] + nums[left + 1] + … + nums[right] )
//暴力
public class NumArray {
int[] arr;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
this.arr=nums;
}
public int sumRange(int left, int right) {
int sum=0;
for (int i=left;i<=right;i++){
sum+=arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
//前缀和
public class NumArray {
int[] arr;//前缀和数组
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
arr=new int[n+1];//前缀和数组的arr[0]=0 这样可以避免i=0的特殊判断
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i+1]=arr[i]+nums[i];
}
}
public int sumRange(int left, int right) {
//left~right这个区间元素的和是 0~right的前缀和减去0~left-1的前缀和的值
return arr[right+1]-arr[left];
}
}
(2)二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变(304)
给定一个二维矩阵 matrix,以下类型的多个请求:
计算其子矩形范围内元素的总和,该子矩阵的 左上角 为 (row1, col1) ,右下角 为 (row2, col2) 。
实现 NumMatrix 类:
NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) 给定整数矩阵 matrix 进行初始化
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) 返回 左上角 (row1, col1) 、右下角 (row2, col2) 所描述的子矩阵的元素 总和 。
//使用一维前缀和
public class NumMatrix {
int arr[][];
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m= matrix.length;//行
int n=matrix[0].length;//列
arr=new int[m][n+1];
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
//计算出每一行的前缀和
for (int j=0;j<n;j++){
arr[i][j+1]=arr[i][j]+matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int sum=0;
for (int i=row1;i<=row2;i++){
sum+=arr[i][col2+1]-arr[i][col1];
}
return sum;
}
}
//使用二维前缀和
public class NumMatrix {
int arr[][];
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m= matrix.length;//行
int n=matrix[0].length;//列
arr=new int[m+1][n+1];
//计算出第一行的所有列的前缀和
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
for (int j=0;j<n;j++){
arr[i+1][j+1]=arr[i][j+1]+arr[i+1][j]-arr[i][j]+matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return arr[row2+1][col2+1]-arr[row1][col2+1]-arr[row2+1][col1]+arr[row1][col1];
}
}
(3)和为 K 的子数组(560)
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你统计并返回 该数组中和为 k 的连续子数组的个数 。
输入:nums = [1,1,1], k = 2
输出:2
输入:nums = [1,2,3], k = 3
输出:2
//暴力枚举
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3};
int k=3;
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.subarraySum(arr,k));
}
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int n= nums.length;
int count=0;//连续子数组的个数
//依次遍历每个元素 分别以每个元素结尾向前寻找 看能否找到连续子数组的和为k
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
int sum=0;//连续子数组的和
for (int j=i;j>=0;j--){
sum+=nums[j];
if (sum==k){
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
//前缀和+哈希表优化
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3};
int k=3;
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.subarraySum(arr,k));
}
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int n= nums.length;
int count=0;//连续子数组的个数
int pre=0;//前缀和
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put(pre,1);
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
pre+=nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(pre-k)){
count+=map.get(pre-k);
}
map.put(pre,map.getOrDefault(pre,0)+1);
}
return count;
}
}
8.练习
(1)重塑矩阵(566)
在 MATLAB 中,有一个非常有用的函数 reshape ,它可以将一个 m x n 矩阵重塑为另一个大小不同(r x c)的新矩阵,但保留其原始数据。
给你一个由二维数组 mat 表示的 m x n 矩阵,以及两个正整数 r 和 c ,分别表示想要的重构的矩阵的行数和列数。
重构后的矩阵需要将原始矩阵的所有元素以相同的 行遍历顺序 填充。
如果具有给定参数的 reshape 操作是可行且合理的,则输出新的重塑矩阵;否则,输出原始矩阵。
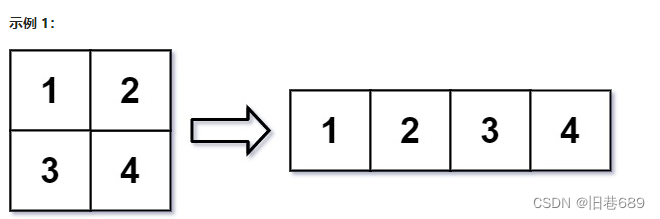
输入:mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 1, c = 4
输出:[[1,2,3,4]]
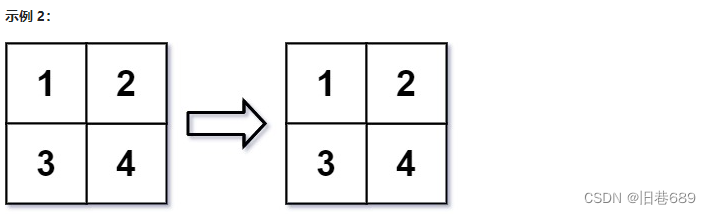
输入:mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 2, c = 4
输出:[[1,2],[3,4]]
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr={{1,2},{3,4}};
int r=1;
int c=4;
Solution solution=new Solution();
int[][] ints = solution.matrixReshape(arr, r, c);
System.out.println("行:"+ints.length+" "+"列:"+ints[0].length);
}
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] mat, int r, int c) {
int m= mat.length;
int n=mat[0].length;
if (r*c!=m*n){
return mat;
}
int[][] arr=new int[r][c];
Queue<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<>();
//将数组元素入队列
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
for (int j=0;j<n;j++){
queue.add(mat[i][j]);
}
}
//将队列的元素插入新的数组
for (int i=0;i<r;i++){
for (int j=0;j<c;j++){
arr[i][j]=queue.poll();
}
}
return arr;
}
}
(2)用队列实现栈(225)
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
public class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue;
Queue<Integer> auxQueue;//辅助栈
public MyStack() {
queue=new LinkedList<>();
auxQueue=new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
//首先将queue里剩余的元素弹入auxQueue中 为了保证元素顺序
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
auxQueue.add(queue.poll());
}
//将auxQueue中元素按照顺序弹入queue中
while (!auxQueue.isEmpty()){
queue.add(auxQueue.poll());
}
queue.add(x);
}
public int pop() {
//首先将queue里剩余的元素弹入auxQueue中 为了保证元素顺序
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
auxQueue.add(queue.poll());
}
//在每一次操作前 先将auxQueue中的元素弹入queue中
while (!auxQueue.isEmpty()){
queue.add(auxQueue.poll());
}
while (queue.size()>1){
auxQueue.add(queue.poll());
}
return queue.poll();
}
public int top() {
//首先将queue里剩余的元素弹入auxQueue中 为了保证元素顺序
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
auxQueue.add(queue.poll());
}
//在每一次操作前 先将auxQueue中的元素弹入queue中
while (!auxQueue.isEmpty()){
queue.add(auxQueue.poll());
}
while (queue.size()>1){
auxQueue.add(queue.poll());
}
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
while (queue.isEmpty()&&auxQueue.isEmpty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
(3)下一个更大元素 II(503)
给定一个循环数组 nums ( nums[nums.length - 1] 的下一个元素是 nums[0] ),返回 nums 中每个元素的 下一个更大元素 。
数字 x 的 下一个更大的元素 是按数组遍历顺序,这个数字之后的第一个比它更大的数,这意味着你应该循环地搜索它的下一个更大的数。如果不存在,则输出 -1 。
输入: nums = [1,2,1]
输出: [2,-1,2]
解释: 第一个 1 的下一个更大的数是 2;
数字 2 找不到下一个更大的数;
第二个 1 的下一个最大的数需要循环搜索,结果也是 2。
输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,3]
输出: [2,3,4,-1,4]
//小根堆+循环数组
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,1};
Solution solution=new Solution();
int[] ints = solution.nextGreaterElements(arr);
for (int i:ints){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
if (n==1){
return new int[]{-1};
}
int[] arr=new int[n];
//先将数组中所有位置初始化为-1
Arrays.fill(arr,-1);
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
if (o1[0]==o2[0]){
return o1[1]-o2[1];
}
return o1[0]-o2[0];
}
});
for (int i=0;i<n*2-1;i++){
//当小根堆不为空并且堆顶元素小于当前元素时 堆顶元素对应位置放当前元素
while (!heap.isEmpty()&&heap.peek()[0]<nums[i%n]){
arr[heap.poll()[1]]=nums[i%n];
}
//当前元素入堆
heap.add(new int[]{nums[i%n],i%n});
}
return arr;
}
}
//单调栈+循环数组
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,1};
Solution solution=new Solution();
int[] ints = solution.nextGreaterElements(arr);
for (int i:ints){
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
if (n==1){
return new int[]{-1};
}
int[] arr=new int[n];
//先将数组中所有位置初始化为-1
Arrays.fill(arr,-1);
//单调栈中保存数组元素下标
Deque<Integer> stack=new LinkedList<>();
for (int i=0;i<n*2-1;i++){
//当栈不为空并且当前元素大于栈顶下标所对应的元素时 将栈顶元素对应位置赋值为当前元素
while (!stack.isEmpty()&&nums[stack.peek()]<nums[i%n]){
arr[stack.poll()]=nums[i%n];
}
//当前元素下标入栈
stack.push(i%n);
}
return arr;
}
}
(4)存在重复元素(217)
给你一个整数数组 nums 。如果任一值在数组中出现 至少两次 ,返回 true ;如果数组中每个元素互不相同,返回 false 。
输入:nums = [1,2,3,1]
输出:true
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4]
输出:false
输入:nums = [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2]
输出:true
//排序
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,1};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.containsDuplicate(arr));
}
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
if (n==1){
return false;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
if (nums[i]==nums[i+1]){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
//集合
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,1};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.containsDuplicate(arr));
}
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
if (n==1){
return false;
}
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
//当集合中存在某个值时 证明这个值算上当前值至少出现了两次 直接返回true
if (set.contains(nums[i])){
return true;
}
set.add(nums[i]);
}
return false;
}
}
(5)数组的度
给定一个非空且只包含非负数的整数数组 nums,数组的 度 的定义是指数组里任一元素出现频数的最大值。
你的任务是在 nums 中找到与 nums 拥有相同大小的度的最短连续子数组,返回其长度。
输入:nums = [1,2,2,3,1]
输出:2
解释:
输入数组的度是 2 ,因为元素 1 和 2 的出现频数最大,均为 2 。
连续子数组里面拥有相同度的有如下所示:
[1, 2, 2, 3, 1], [1, 2, 2, 3], [2, 2, 3, 1], [1, 2, 2], [2, 2, 3], [2, 2]
最短连续子数组 [2, 2] 的长度为 2 ,所以返回 2 。
输入:nums = [1,2,2,3,1,4,2]
输出:6
解释:
数组的度是 3 ,因为元素 2 重复出现 3 次。
所以 [2,2,3,1,4,2] 是最短子数组,因此返回 6 。
//哈希表
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,2,3,1};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.findShortestSubArray(arr));
}
public int findShortestSubArray(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
if (n==1){
return 1;
}
int maxCount=0;//出现最大的频数
int minLen=0;//出现频数最多且子数组长度最短的长度
//哈希表 用来存储元素 和 其出现的次数以及第一次出现和最后一次出现的位置
Map<Integer,int[]> map=new HashMap<>();
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])){
//更新出现的次数已经最后一次出现的位置
map.get(nums[i])[0]++;
map.get(nums[i])[2]=i;
}else {
map.put(nums[i],new int[]{1,i,i});
}
}
//依次获取每一个value 比较它们的次数以及对应的子数组的长度 得到答案
for (Map.Entry<Integer,int[]> entry:map.entrySet()){
int[] arr= entry.getValue();
if (maxCount<arr[0]){
maxCount=arr[0];//令maxCount=当前频数
minLen=arr[2]-arr[1]+1;//更改当前最短子数组长度
} else if (maxCount==arr[0]) {
minLen=Math.min(minLen,arr[2]-arr[1]+1);
}
}
return minLen;
}
}
(6)最长和谐子序列(594)
和谐数组是指一个数组里元素的最大值和最小值之间的差别 正好是 1 。
现在,给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你在所有可能的子序列中找到最长的和谐子序列的长度。
数组的子序列是一个由数组派生出来的序列,它可以通过删除一些元素或不删除元素、且不改变其余元素的顺序而得到。
输入:nums = [1,3,2,2,5,2,3,7]
输出:5
解释:最长的和谐子序列是 [3,2,2,2,3]
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4]
输出:2
输入:nums = [1,1,1,1]
输出:0
//排序
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3,4};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.findLHS(arr));
}
public int findLHS(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
if (n<2){
return 0;
}
int maxLen=0;//最长和谐子序列的长度
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
int j=i;
int preMin=nums[i];//当前和谐子序列最小值
//当当前子序列满足和谐子序列时
while (j<(n-1)&&(preMin+1)>=nums[j+1]){
j++;
}
//当当前最小值不等于最大值时 才成立
if (preMin!=nums[j]){
maxLen=Math.max(maxLen,j-i+1);
}
}
return maxLen;
}
}
//哈希表
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3,4};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.findLHS(arr));
}
public int findLHS(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
if (n<2){
return 0;
}
int maxLen=0;//最长和谐子序列的长度
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
//遍历数组 得到每个元素出现的次数
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])){
map.put(nums[i],map.get(nums[i])+1);
}else {
map.put(nums[i],1);
}
}
//遍历map 对每一个key值 如果找到key+1也在map里 那么它们对应的和谐子序列长度就是它们的value值相加
for (int key:map.keySet()){
if (map.containsKey(key+1)){
maxLen=Math.max(maxLen,map.get(key)+map.get(key+1));
}
}
return maxLen;
}
}
(7)寻找重复数(287)
给定一个包含 n + 1 个整数的数组 nums ,其数字都在 [1, n] 范围内(包括 1 和 n),可知至少存在一个重复的整数。
假设 nums 只有 一个重复的整数 ,返回 这个重复的数 。
你设计的解决方案必须 不修改 数组 nums 且只用常量级 O(1) 的额外空间。
输入:nums = [1,3,4,2,2]
输出:2
输入:nums = [3,1,3,4,2]
输出:3
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={3,1,3,4,2};
Solution solution=new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.findDuplicate(arr));
}
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int n= nums.length;
int repeatNum=0;//重复的整数
int left=1;
int right=n-1;
while (left<=right){
int mid=(left+right)>>1;
int count=0;//计数 来判断重复的数出现在哪
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
if (nums[i]<=mid){
count++;
}
}
if (count<=mid){
left=mid+1;
}else {
right=mid-1;
repeatNum=mid;
}
}
return repeatNum;
}
}
(8)优势洗牌(870)
给定两个大小相等的数组 nums1 和 nums2,nums1 相对于 nums2 的优势可以用满足 nums1[i] > nums2[i] 的索引 i 的数目来描述。
返回 nums1 的任意排列,使其相对于 nums2 的优势最大化。
输入:nums1 = [2,7,11,15], nums2 = [1,10,4,11]
输出:[2,11,7,15]
输入:nums1 = [12,24,8,32], nums2 = [13,25,32,11]
输出:[24,32,8,12]
public int[] advantageCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n= nums1.length;
int[] arr=new int[n];
Integer[] a=new Integer[n];
Integer[] b=new Integer[n];
int left=0;//数组当前左边界
int right=n-1;//数组当前有边界
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
a[i]=i;
b[i]=i;
}
//a b 分别来存储 nums1 nums2 排序后的下标值
Arrays.sort(a,(i,j)->nums1[i]-nums1[j]);
Arrays.sort(b,(i,j)->nums2[i]-nums2[j]);
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
//当nums1的当前最小值大于nums2的当前最小值时
if (nums1[a[i]]>nums2[b[left]]){
arr[b[left]]=nums1[a[i]];
left++;
}else {
arr[b[right]]=nums1[a[i]];
right--;
}
}
return arr;
}
