【算法】二叉树
❤️ Author: 老九
☕️ 个人博客:老九的CSDN博客
🙏 个人名言:不可控之事 乐观面对
😍 系列专栏:
文章目录
- 二叉树
- 数组转化为二叉树
- 二叉树转化为二叉链表
- 二叉树的遍历
- 排序二叉树BST(二叉搜索树)
二叉树
- 当一颗二叉树有n个结点时,就会有n-1个线条
- 完全二叉树:除最后一层的右不满以外,其他层都是满的
- 如果一个完全二叉树的结点从上到下,从左到右从0开始编号,一个结点和两个子结点的编号为,n,2n+1,2n+2,一个结点父结点是:Math.floor((m-1)/2)
{
val : 3,
left : {
val : 1,
left : null,
right : null,
},
right : {
val : 5,
left : null,
right : null
}
}
数组转化为二叉树
<script>
//将存储于array中的根节 点在rootPos位置的二叉树转换为二叉链表形式
function arrayToTree(array, rootPos = 0) {
if (array[rootPos] === null) {
return null
}
var root = {
var: array[rootPos],
left: null,
right: null,
}
root.left = arrayToTree(array, rootPos * 2 + 1)
root.right = arrayToTree(array, rootPos * 2 + 2)
return root
}
</script>
- 但是上面的做法会有null,比较占用空间
<script>
function condensedArrayToTree(ary) {
if (ary.length == 0) {
return null
}
var root = {
val: ary[0],
left: null,
right: null,
}
var nodes = [root]
for (var i = 1; i < ary.length; i++) {
var currNode = nodes.shift()
if (ary[i] != null) {
var node = {
val: ary[i],
left: null,
right: null
}
currNode.left = node
nodes.push(node)
}
i++
if (ary[i] != null) {
var node = {
val: ary[i],
left: null,
right: null
}
currNode.right = node
nodes.push(node)
}
}
return root
}
condensedArrayToTree([1,null,2,3,null,null,4,null,5])
</script>
二叉树转化为二叉链表
<script>
function treeToArray(root, pos = 0, result = []) {
if (root == null) {
return
}
result[pos] = root.val
treeToArray(root.left, pos * 2 + 1, result)
treeToArray(root.right, pos * 2 + 2, result)
return result
}
</script>
- 加强版树转数组
<script>
function treeToCondensedArray(root){
var ary = []
if(!root){
return ary
}
var nodes = [root]
while(nodes.length){
var node = nodes.shift()
if(node){
ary.push(node.val)
nodes.push(node.left)
nodes.push(node.right)
}else{
ary.push(node)
}
}
return ary
}
</script>
二叉树的遍历
- 按层遍历:从上到下,从左到右遍历每一层的结点
- 先序遍历,先遍历根节点,再遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树,对子树的遍历依然遵循此规则
- 还有中序遍历,后序遍历
- 先序遍历画轮廓,10628439578
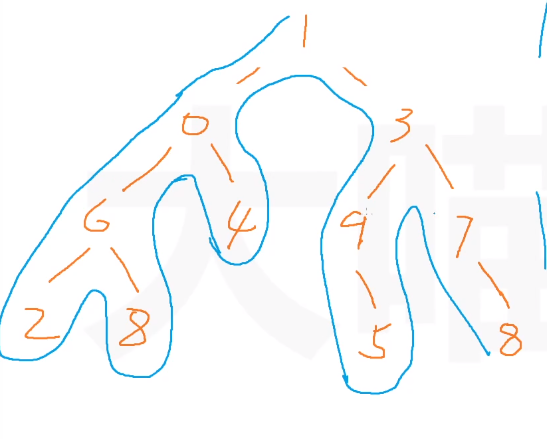
- 中序遍历也是画轮廓,先把叶子节点补上,然后数第二次碰到的结点,26804195378
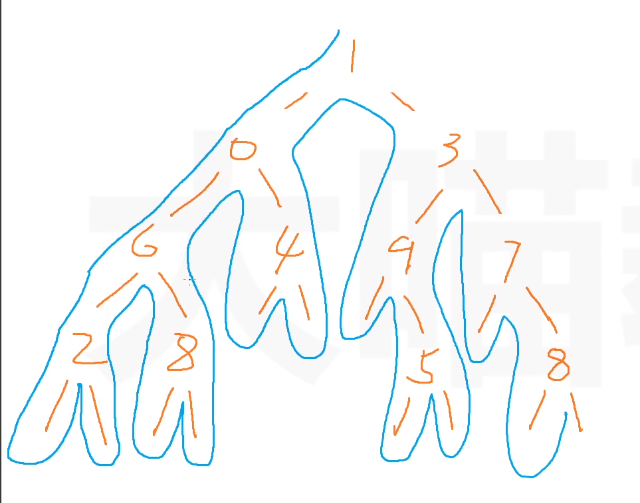
- 后序遍历是第三次碰到每个结点的时候计数,画法和中序遍历画法一样,28640598731
<script>
function preOrderTraverse(root) {
if (root) {
console.log(root.val)
preOrderTraverse(root.left)
preOrderTraverse(root.right)
}
}
function inOrderTraverse(root){
if(root){
inOrderTraverse(root.left)
console.log(root.val)
inOrderTraverse(root.right)
}
}
function postOrderTraverse(root){
if(root){
postOrderTraverse(root.left)
postOrderTraverse(root.right)
console.log(root.val)
}
}
condensedArrayToTree([1,0,3,6,4,9,7,2,8,,,,5,,8])
//高级版本
function preOrderTraverseH(root, action) {
if (root) {
action(root.val)
preOrderTraverse(root.left, action)
preOrderTraverse(root.right, action)
}
}
</script>
排序二叉树BST(二叉搜索树)
- 一颗二叉树中的每个结点左子树中的结点都比它根节点小,每个结点的右子树中的结点比它根节点大或等于
- 排序二叉树的中序遍历结果是有序的
- 时间复杂度最差是n的平方,平均情况是n*logn
- 空间复杂度是构建出来的二叉树占用的空间,为n
<script>
//通过val构建一个结点,并将结点插入到排序二叉树bst中的正确位置上,返回处理完成后的树的根节点
function insertIntoBST(bst, val) {
let node = {
val: val,
left: null,
right: null
}
if (!bst) {
return node
}
if (val < bst.val) {
bst.left = insertIntoBST(bst.left, val)
} else {
bst.right = insertIntoBST(bst.right, val)
}
return bst
}
function inOrderTraverse(root, action) {
if (root) {
inOrderTraverse(root.left, action)
action(root.val)
inOrderTraverse(root.right, action)
}
}
//利用二叉树来排序
//构建一颗空的排序二叉树,将数组ary中的元素都插入这颗二叉树
//完成后,中序遍历二叉树即可得到有序结果
function bstSort(ary) {
// var tree = null
// for (var i = 0; i < ary.length; i++) {
// tree = insertIntoBST(tree, ary[i])
// }
var tree = ary.reduce((tree,it) => {
return insertIntoBST(tree,it)
},null)
i = 0
inOrderTraverse(tree, val => {
ary[i] = val
i++
})
return ary
}
</script>
————————————————————————
♥♥♥码字不易,大家的支持就是我坚持下去的动力♥♥♥
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「亚太地区百大最帅面孔第101名」的原创文章
