Ajax基础
Ajax 是 Asynchronous JavaScript and XML(异步 JavaScript 和 XML)的简写
Ajax 中的异步:可以异步地向服务器发送请求,在等待响应的过程中,不会阻塞当前页面,浏览器可以做自己的事情。直到成功获取响应后,浏览器才开始处理响应数据
XML(可扩展标记语言)是前后端数据通信时传输数据的一种格式,而现在比较常用的是JSON
Ajax 其实就是浏览器与服务器之间的一种异步通信方式
使用 Ajax 可以在不重新加载整个页面的情况下,对页面的某部分进行更新
- 慕课网注册检测
- 慕课网搜索提示
搭建Ajax开发环境
Ajax 需要服务器环境,非服务器环境下,很多浏览器无法正常使用 Ajax,个人使用phpstudy
Ajax的基本用法
Ajax 想要实现浏览器与服务器之间的异步通信,需要依靠 XMLHttpRequest,它是一个构造函数
不论是 XMLHttpRequest,还是 Ajax,都没有和具体的某种数据格式绑定
Ajax的使用步骤
- 1创建xhr对象
- 2监听事件,处理响应
- 3准备发送请求
- 4发送请求
// 2.Ajax 的使用步骤
// 2.1.创建 xhr 对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2.2.监听事件,处理响应
// 当获取到响应后,会触发 xhr 对象的 readystatechange 事件,可以在该事件中对响应进行处理
// xhr.addEventListener('readystatechange', () => {}, false);
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState !== 4) return;
// // HTTP CODE
// // 获取到响应后,响应的内容会自动填充 xhr 对象的属性
// // xhr.status:HTTP 200 404
// // xhr.statusText:HTTP 状态说明 OK Not Found
if ((xhr.status >= 200) & (xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// console.log('正常使用响应数据');
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
};
// readystatechange 事件也可以配合 addEventListener 使用,不过要注意,IE6~8 不支持 addEventListener
// 为了兼容性,readystatechange 中不使用 this,而是直接使用 xhr
// 由于兼容性的原因,最好放在 open 之前
// 2.3.准备发送请求
// xhr.open(
// 'HTTP 方法 GET、POST、PUT、DELETE',
// '地址 URL https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js ./index.html ./index.xml ./index.txt',
// true
// );
// 调用 open 并不会真正发送请求,而只是做好发送请求前的准备工作
// 2.4.发送请求
// 调用 send() 正式发送请求
// send() 的参数是通过请求体携带的数据 如果是get请求 参数为null(为了兼容性)也可以不写(不建议)
// xhr.send(null);readystatechange 事件监听 readyState 这个状态的变化,它的值从 0 ~ 4,一共 5 个状态
- 0:未初始化。尚未调用 open()
- 1:启动。已经调用 open(),但尚未调用 send()
- 2:发送。已经调用 send(),但尚未接收到响应
- 3:接收。已经接收到部分响应数据
- 4:完成。已经接收到全部响应数据,而且已经可以在浏览器中使用了
// 3.使用 Ajax 完成前后端通信
const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState !== 4) return;
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
console.log(typeof xhr.responseText);
}
};
xhr.open('GET', url, true);
xhr.send(null);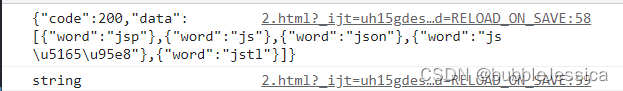
GET请求
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--<form action="https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js" method="get">
<input type="text" name="username" />
<input type="password" name="password" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>-->
<script>
// 1.携带数据
// GET 请求不能通过请求体携带数据,但可以通过请求头携带
// const url =
// 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js&username=alex&age=18';
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
// if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
// if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// console.log(xhr.responseText);
// }
// };
// xhr.open('GET', url, true);
// xhr.send(null);
// 不会报错,但不会发送数据
// xhr.send('sex=male');
// 2.数据编码
// 如果携带的数据是非英文字母的话,比如说汉字,就需要编码之后再发送给后端,不然会造成乱码问题
// 可以使用 encodeURIComponent() 编码
const url = `https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=${encodeURIComponent(
'前端'
)}`;
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState !== 4) return;
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
};
xhr.open('GET', url, true);
xhr.send(null);
</script>
</body>
</html>注意事项:ajax的get请求与form表单get请求相似,只不过form表单get请求action属性后面不能加参数加了也没用(看下面截图就明白了相当于没加)
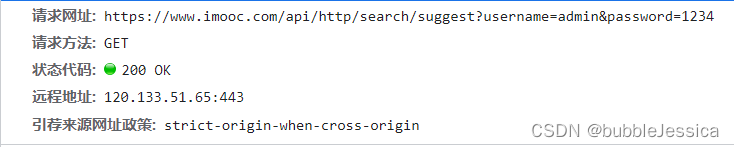
POST请求
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>POST 请求</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--<form
action="https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js"
method="post"
>
<input type="text" name="username" />
<input type="password" name="password" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>-->
<script>
// 1.携带数据
// POST 请求主要通过请求体携带数据,同时也可以通过请求头携带
const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
};
xhr.open('POST', url, true);
// 如果想发送数据,直接写在 send() 的参数位置,一般是字符串
xhr.send('username=alex&age=18');
// 不能直接传递对象,需要先将对象转换成字符串的形式
// xhr.send({
// username: 'alex',
// age: 18
// });
// [object Object]
// 2.数据编码
// xhr.send(`username=${encodeURIComponent('张三')}&age=18`);
</script>
</body>
</html>

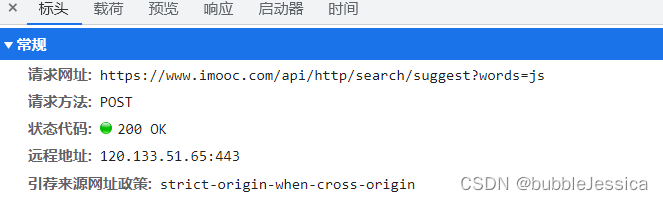
注意事项:ajax的post请求与form表单post请求相似,form表单post请求action属性后面可以加参数(看下面截图就明白了)


JSON(JAVASCRIPT OBJECT NOTATION)
JSON(js对象表示法)是Ajax发送和接收数据的一种格式
JSON有3种形式,每种形式的写法都和JS中的数据类型很像,可以很轻松的和JS中的数据类型互相转换 JS->JSON->Java/PHP
- 简单值形式 对应着JS中的基本数据类型(数字、字符串、布尔值、null)
- JSON中没有undefined值 JSON中字符串必须使用双引号 JSON中不能注释
- 对象形式 JSON 的对象形式就对应着 JS 中的对象
- JSON 中对象的属性名必须用双引号,属性值如果是字符串也必须用双引号 JSON 中只要涉及到字符串,就必须使用双引号 不支持 undefined
- 数组形式 JSON 的数组形式就对应着 JS 中的数组
- 数组中的字符串必须用双引号 JSON 中只要涉及到字符串,就必须使用双引号 不支持 undefined
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
console.log(typeof xhr.responseText);
}
};
// xhr.open('GET', './plain.json', true);
// xhr.open('GET', './obj.json', true);
xhr.open('GET', './arr.json', true);
xhr.send(null);JSON.parse():将json格式的字符串转化为js中对应的数据类型
JSON.stringify():将js中对应的数据类型转化为json格式的字符串
使用JSON.parse()和JSON.stringify()封装localStorage
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>JSON 的常用方法</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module">
// 1.JSON.parse()
// JSON.parse() 可以将 JSON 格式的字符串解析成 JS 中的对应值
// 一定要是合法的 JSON 字符串,否则会报错
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
// if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
//
// if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// console.log(xhr.responseText);
// console.log(typeof xhr.responseText);
//
// console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText));
// console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText).data);
// }
// };
// // xhr.open('GET', './plain.json', true);
// // xhr.open('GET', './obj.json', true);
// xhr.open('GET', './arr.json', true);
// xhr.open(
// 'GET',
// 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js',
// true
// );
// xhr.send(null);
// 2.JSON.stringify()
// JSON.stringify() 可以将 JS 的基本数据类型、对象或者数组转换成 JSON 格式的字符串
// console.log(
// JSON.stringify({
// username: 'alex',
// age: 18
// })
// );
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//
// xhr.open(
// 'POST',
// 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js',
// true
// );
// xhr.send(
// JSON.stringify({
// username: 'alex',
// age: 18
// })
// );
// 3.使用 JSON.parse() 和 JSON.stringify() 封装 localStorage
import { get, set, remove, clear } from './storage.js';
set('username', 'alex');
console.log(get('username'));
set('zs', {
name: '张三',
age: 18
});
console.log(get('zs'));
remove('username');
clear();
</script>
</body>
</html>
const storage = window.localStorage;
// 设置
const set = (key, value) => {
// {
// username: 'alex'
// }
storage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(value));
};
// 获取
const get = key => {
// 'alex'
// {
// "username": "alex"
// }
return JSON.parse(storage.getItem(key));
};
// 删除
const remove = key => {
storage.removeItem(key);
};
// 清空
const clear = () => {
storage.clear();
};
export { set, get, remove, clear };

跨域
不同域:只要协议/域名/端口号任何一个不一样,就是不同域
阻止跨域请求,其实是浏览器本身的一种安全策略--同源策略
其他客户端或服务器都不存在跨域被阻止的问题
跨域解决方案(了解即可)
- CORS跨域资源共享(优先使用)
- JSONP
const url='https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js'
const xhr=new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange=()=>{
if (xhr.readyState!==4) return;
if ((xhr.status>=200&&xhr.status<300)||xhr.status===304){
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
}
xhr.open('GET',url,true);
xhr.send(null);
// Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
// 表明允许所有的域名来跨域请求它,* 是通配符,没有任何限制
// 只允许指定域名的跨域请求
// Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://127.0.0.1:5500
// 2.使用 CORS 跨域的过程
// ① 浏览器发送请求
// ② 后端在响应头中添加 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 头信息
// ③ 浏览器接收到响应
// ④ 如果是同域下的请求,浏览器不会额外做什么,这次前后端通信就圆满完成了
// ⑤ 如果是跨域请求,浏览器会从响应头中查找是否允许跨域访问
// ⑥ 如果允许跨域,通信圆满完成
// ⑦ 如果没找到或不包含想要跨域的域名,就丢弃响应结果
// 3.CORS 的兼容性
// IE10 及以上版本的浏览器可以正常使用 CORS
// https://caniuse.com/
// JSONP<script>
// 1.JSONP 的原理
// script 标签跨域不会被浏览器阻止
// JSONP 主要就是利用 script 标签,加载跨域文件
// 2.使用 JSONP 实现跨域
// 服务器端准备好 JSONP 接口
// https://www.imooc.com/api/http/jsonp?callback=handleResponse
// 手动加载 JSONP 接口或动态加载 JSONP 接口
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.src =
'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/jsonp?callback=handleResponse';
document.body.appendChild(script);
// 声明函数
const handleResponse = data => {
console.log(data);
};
// 优先使用 CORS,如果浏览器不支持 CORS 的话,再使用 JSONP
</script>
<!-- <script src="https://www.imooc.com/api/http/jsonp?callback=handleResponse"></script> -->
<!-- 相当于 -->
<!-- <script>
handleResponse({
code: 200,
data: [
{
word: 'jsp'
},
{
word: 'js'
},
{
word: 'json'
},
{
word: 'js 入门'
},
{
word: 'jstl'
}
]
});
</script>XHR的属性
- responseType和response属性
- timeout属性(设置请求的超时时间ms)
- withCredentials属性
xhr.responseType='json' 浏览器会帮我们自动调用JSON.parse(xhr.response)给它转换成这种类型,也就是说服务器返回给我们的是JSON格式的字符串,不可能直接把js对象返回过来
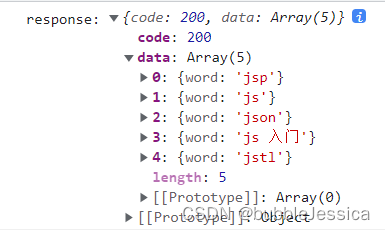
// 1.responseType 和 response 属性 IE6~9 不支持,IE10 开始支持
const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// // 文本形式的响应内容
// // responseText 只能在没有设置 responseType 或者 responseType = '' 或 'text' 的时候才能使用
// console.log('responseText:', xhr.responseText);
// // 可以用来替代 responseText
console.log('response:', xhr.response);
// console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText));
}
};
xhr.open('GET', url, true);
// // xhr.responseType = '';
// // xhr.responseType = 'text';
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.send(null);
xhr.timeout=10 出错变红了,请求被取消了,因为规定的时间内超时,没有完成
![]()
// 2.timeout 属性
// 设置请求的超时时间(单位 ms)
const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.response);
}
};
xhr.open('GET', url, true);
xhr.timeout=10;
// xhr.timeout = 10000;
xhr.send(null);
// IE6~7 不支持,IE8 开始支持使用 Ajax 发送请求,默认情况下,同域时,会携带 Cookie;跨域时,不会携带Cookie,要携带的话得设置xhr.withCredentials = true; 但是最终能否成功跨域携带 Cookie,还要看服务器同不同意
XHR的方法
- abort() 终止当前请求
- setRequestHeader()
当同时书写xhr.open('POST',url,true)post请求和xhr.send('username=alex&age=18')携带参数,才有必要加上xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
请求头中的Content-Type字段用来告诉服务器,浏览器发送的数据是什么格式的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>XHR 的方法</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--<form
action="https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js"
method="post"
>
<input type="text" name="username" />
<input type="password" name="password" />
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form>-->
<script>
// 1.abort()
// 终止当前请求
// 一般配合 abort 事件一起使用
// const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
//
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//
// xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
// if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
//
// if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// console.log(xhr.response);
// }
// };
//
// xhr.open('GET', url, true);
//
// xhr.send(null);
//
// xhr.abort();
// 2.setRequestHeader()
// 可以设置请求头信息
// xhr.setRequestHeader(头部字段的名称, 头部字段的值);
// const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/json/search/suggest?words=js';
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange = () => {
if (xhr.readyState != 4) return;
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.response);
}
};
xhr.open('POST', url, true);
//
// // 请求头中的 Content-Type 字段用来告诉服务器,浏览器发送的数据是什么格式的
// xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
// // xhr.send(null);
// xhr.send('username=alex&age=18');
xhr.send(
JSON.stringify({
username: 'alex'
})
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
XHR的事件
- load事件(响应数据可用时触发)
- error事件(请求发生错误时触发)
- abort事件(终止当前请求触发)
- timeout事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>XHR 的事件</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 1.load 事件
// 响应数据可用时触发
// const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// // xhr.onload = () => {
// // if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// // console.log(xhr.response);
// // }
// // };
// xhr.addEventListener(
// 'load',
// () => {
// if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// console.log(xhr.response);
// }
// },
// false
// );
// xhr.open('GET', url, true);
// xhr.send(null);
// IE6~8 不支持 load 事件
// 2.error 事件
// 请求发生错误时触发
// const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
// const url = 'https://www.iimooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// xhr.addEventListener(
// 'load',
// () => {
// if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// console.log(xhr.response);
// }
// },
// false
// );
// xhr.addEventListener(
// 'error',
// () => {
// console.log('error');
// },
// false
// );
// xhr.open('GET', url, true);
// xhr.send(null);
// IE10 开始支持
// 3.abort 事件
// 调用 abort() 终止请求时触发
// const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// xhr.addEventListener(
// 'load',
// () => {
// if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
// console.log(xhr.response);
// }
// },
// false
// );
// xhr.addEventListener(
// 'abort',
// () => {
// console.log('abort');
// },
// false
// );
// xhr.open('GET', url, true);
// xhr.send(null);
// xhr.abort();
// IE10 开始支持
// 4.timeout 事件
// 请求超时后触发
const url = 'https://www.imooc.com/api/http/search/suggest?words=js';
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.addEventListener(
'load',
() => {
if ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status === 304) {
console.log(xhr.response);
}
},
false
);
xhr.addEventListener(
'timeout',
() => {
console.log('timeout');
},
false
);
xhr.open('GET', url, true);
xhr.timeout = 10;
xhr.send(null);
// IE8 开始支持
</script>
</body>
</html>
