第18章_JDBC
一、JDBC概述
JDBC概述
什么是JDBC
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity, Java数据库连接) ,是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成
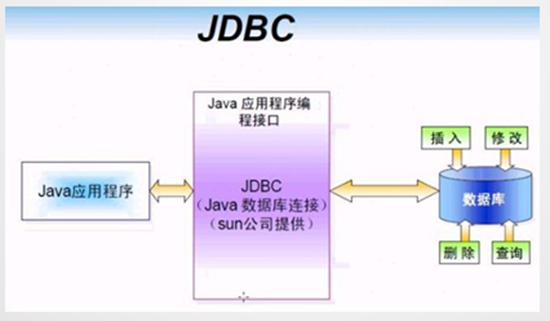
有了JDBC,程序员只需用JDBC API写一个程序,就可访问所有数据库。
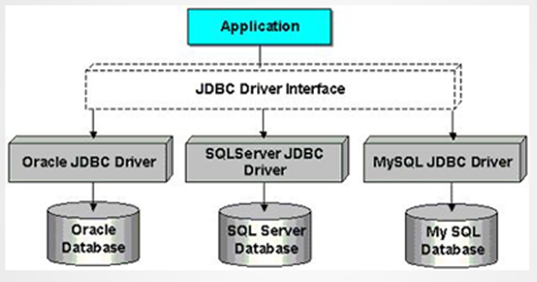
Sun公司、数据库厂商、程序员三方关系
SUN公司是规范制定者,制定了规范JDBC(连接数据库规范)
DriverManager类 作用:管理各种不同的JDBC驱动
Connection接口
Statement接口和PreparedStatement接口
ResultSet接口
数据库厂商微软、甲骨文等分别提供实现JDBC接口的驱动jar包
程序员学习JDBC规范来应用这些jar包里的类。
二、JDBC初识
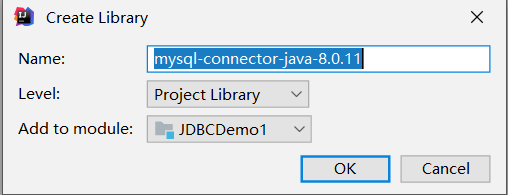
1创建项目和模块.将jar文件放入项目的lib目录中

2给当前项目添加依赖(告诉当前项目/模块可以依赖jar文件中的代码)
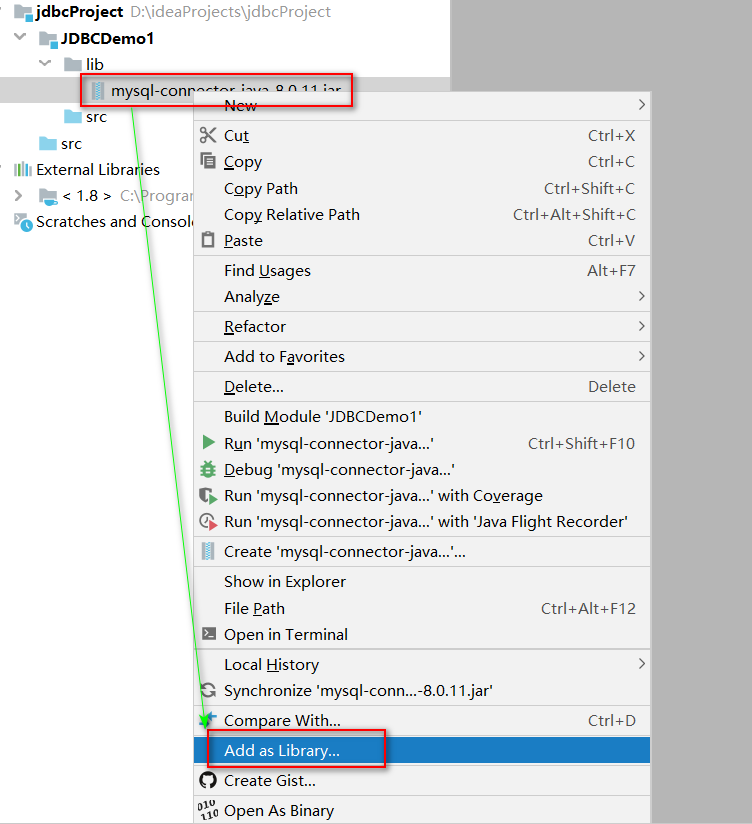
点击OK
向部门表中添加一条数据
package com.msb.test1;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Driver;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*
* 向Dept表增加一条数据
*
* */
//1加载驱动 Driver
Driver driver =new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver();
//2注册驱动 DriverManager
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
//3获得链接 Connection
/*
* user:用户名
* password:密码
* url:统一资源定位符 定位我们要连接的数据库的
* 1协议 jdbc:mysql
* 2IP 127.0.0.1/localhost
* 3端口号 3306
* 4数据库名字 mydb
* 5参数
* 协议://ip:端口/资源路径?参数名=参数值&参数名=参数值&....
* jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb
* */
String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
String user="root";
String password="root";
Connection connection =DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password );
//4获得语句对象 Statment
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5执行SQL语句,返回结果
/*
* insert delete update 操作都是调用statement.executeUpdate
* executeUpdate返回一个int值,代表数据库多少行数据发生了变化
* */
String sql="insert into dept values(50,'教学部','北京');";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响数据行数为:"+rows);
//6释放资源
/*
* 注意顺序
* 后获得的先关闭,先获得的后关闭
* */
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}总结
MySQL8中数据库连接的四个参数有两个发生了变化
String driver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
或者String url = ".......serverTimezone=GMT%2B8";
错误1:Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc2.Driver
原因:没有添加jar包或者com.mysql.jdbc2.Driver路径错误
错误2:Exception in thread "main" java.sql.SQLException:
No suitable driver found for jbdc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/stumgr
原因:url错误
错误3:Exception in thread "main" java.sql.SQLException:
Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
原因:用户名或者密码错误
错误4:Exception in thread "main" com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions
.jdbc4.MySQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException:Duplicate entry '90' for key 'PRIMARY'
原因:主键冲突
错误5:Public Key Retrieval is not allowed
如果用户使用 sha256_password 认证,密码在传输过程中必须使用 TLS 协议保护,但是如果 RSA 公钥不可用,可以使用服务器提供的公钥;可以在连接中通过 ServerRSAPublicKeyFile 指定服务器的 RSA 公钥,或者AllowPublicKeyRetrieval=True参数以允许客户端从服务器获取公钥;但是需要注意的是 AllowPublicKeyRetrieval=True可能会导致恶意的代理通过中间人攻击(MITM)获取到明文密码,所以默认是关闭的,必须显式开启,能不加就不加
在jdbc连接添加上参数allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true即可,注意参数间用&
驱动的加载
加载数据库驱动时,我们可以通过自己创建一个实例的方式,然后去注册驱动
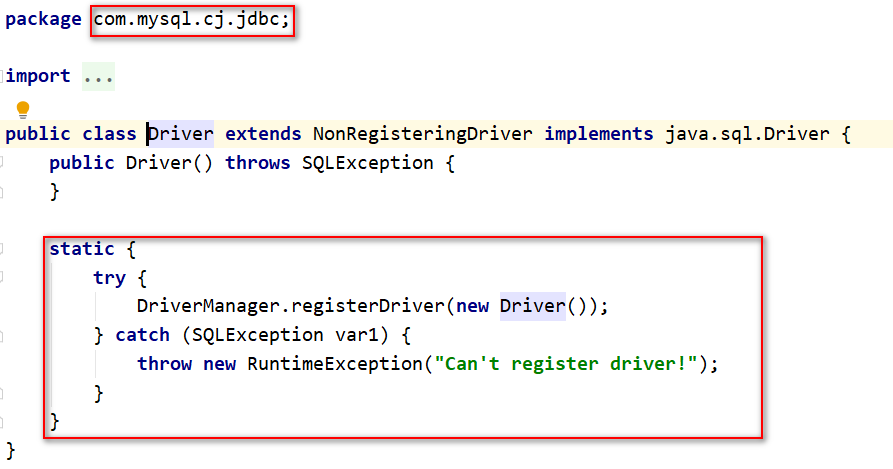
在查看Driver的源代码时我们发现,该类内部有一个静态代码块,在代码块中就是在实例化一个驱动并在驱动中心注册.静态代码块会在类进入内存时执行,也就是说,我们只要让该类字节码进入内存,就会自动完成注册,不需要我们手动去new
所以我们在代码中直接使用反射,通过Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"),加载该类进入内存即可
我们继续查看jar包发现,jar包中已经默认配置了驱动类的加载
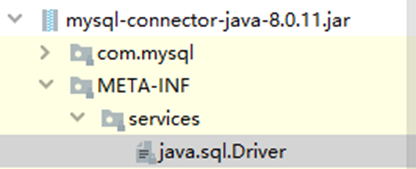
jar--META-INF--services--java.sql.Driver--com.mysql.jdbc.Driver,在加载jar包时,会自动读取该内容并加载驱动,所以我们不去编写Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"),程序也是可以自动完成加载驱动的
结合异常处理代码
package com.msb.test1;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestJDBC3 {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
try{
//Driver类中有一个静态代码块内容是DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver())会帮助注册
Class.forName(driver);
connection =DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql="insert into dept values(DEFAULT ,'助教部门','北京');";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响数据行数为:"+rows);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != statement){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}三、JDBC完成CURD
删除和修改部门信息
package com.msb.test1;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestJDBC4 {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//testDelete();
testUpdate();
}
public static void testUpdate(){
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection =DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql="update dept set dname='总部',loc='北京' where deptno= 30 ";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响数据行数为:"+rows);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != statement){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void testDelete(){
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection =DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql="delete from dept where deptno =40";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响数据行数为:"+rows);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != statement){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
需求:查询全部 员工信息
package com.msb.test1;
import java.sql.*;
public class TestJDBC5 {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
testQuery();
}
public static void testQuery(){
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql="select * from emp";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(resultSet.next()){
int empno = resultSet.getInt("empno");
String ename = resultSet.getString("ename");
String job = resultSet.getString("job");
int mgr = resultSet.getInt("mgr");
Date hiredate = resultSet.getDate("hiredate");
double sal= resultSet.getDouble("sal");
double comm= resultSet.getDouble("comm");
int deptno= resultSet.getInt("deptno");
System.out.println(""+empno+" "+ename+" "+job+" "+mgr+" "+hiredate+" "+sal+" "+comm+" "+deptno);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != statement){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
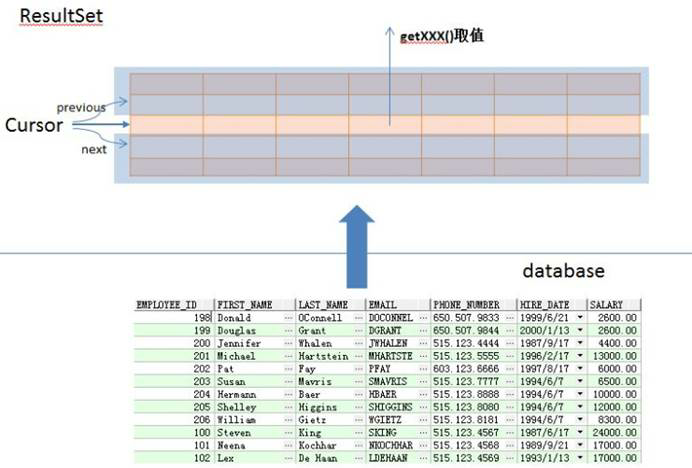
ResultSet里的数据一行一行排列,每行有多个字段,且有一个记录指针,指针所指的数据行叫做当前数据行,我们只能来操作当前的数据行。我们如果想要取得某一条记录,就要使用ResultSet的next()方法 ,如果我们想要得到ResultSet里的所有记录,就应该使用while循环。
ResultSet对象自动维护指向当前数据行的游标。每调用一次next()方法,游标向下移动一行。
初始状态下记录指针指向第一条记录的前面,通过next()方法指向第一条记录。循环完毕后指向最后一条记录的后面。
方法名 | 说 明 |
boolean next() | 将光标从当前位置向下移动一行 |
boolean previous() | 游标从当前位置向上移动一行 |
void close() | 关闭ResultSet 对象 |
int getInt(int colIndex) | 以int形式获取结果集当前行指定列号值 |
int getInt(String colLabel) | 以int形式获取结果集当前行指定列名值 |
float getFloat(int colIndex) | 以float形式获取结果集当前行指定列号值 |
Float getFloat(String colLabel) | 以float形式获取结果集当前行指定列名值 |
String getString(int colIndex) | 以String 形式获取结果集当前行指定列号值 |
StringgetString(String colLabel) | 以String形式获取结果集当前行指定列名值 |
四、SQL注入攻击
Sql注入
SQL注入攻击指的是通过构建特殊的输入作为参数传入Web应用程序,而这些输入大都是SQL语法里的一些组合,通过执行SQL语句进而执行攻击者所要的操作,其主要原因是程序没有细致地过滤用户输入的数据,致使非法数据侵入系统。
以模拟登录为例:在前台输入用户名和密码,后台判断信息是否正确,并给出前台反馈信息,前台输出反馈信息。
具体实现步骤为
创建数据库表
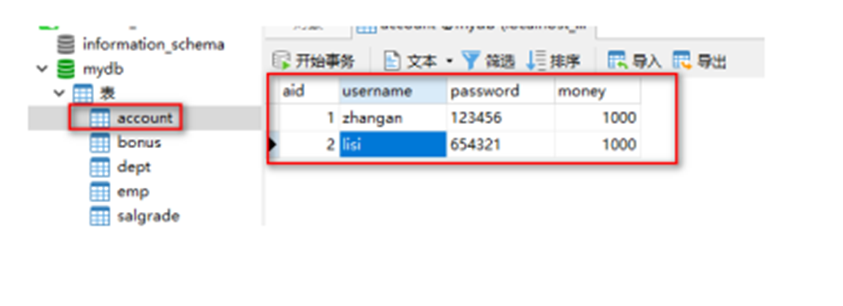
创建实体类
public class Account implements Serializable {
private int aid;
private String username;
private String password;
private int money;测试代码
package com.msb.test2;
import com.msb.entity.Account;
import com.msb.entity.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestInjection {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username=sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String pwd =sc.next();
Account account = getAccount(username, pwd);
System.out.println(null!= account?"登录成功":"登录失败");
sc.close();
}
public static Account getAccount(String username,String pwd){
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
Account account =null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql="select * from account where username ='"+username+"' and password ='"+pwd+"'";
System.out.println(sql);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(resultSet.next()){
int aid = resultSet.getInt("aid");
String usernamea = resultSet.getString("username");
String pwda = resultSet.getString("password");
double money = resultSet.getDouble("money");
account=new Account(aid,usernamea,pwda,money);
System.out.println(account);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != statement){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return account;
}
}测试结果为:
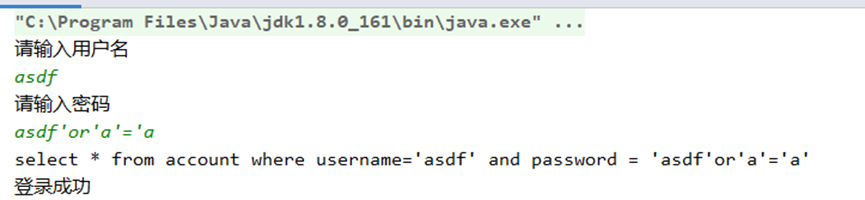
当输入了精心设计的用户名密码后,即使是错误的,也能登录成功。让登录功能形同虚设。这是为什么呢,这就是SQL注入风险,原因在于SQL语句是字符串拼接的。SQL语句中拼接的内容破坏了SQL语句原有的判断逻辑
如何解决呢?使用PreparedStatement预编译语句对象就可以解决掉。
五、预编译语句对象
使用预编译语句对象防止注入攻击
package com.msb.test2;
import com.msb.entity.Account;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestInjection2 {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username=sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String pwd =sc.next();
Account account = getAccount(username, pwd);
System.out.println(null!= account?"登录成功":"登录失败");
sc.close();
}
public static Account getAccount(String username,String pwd){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
Account account =null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
/*
* 1使用PreparedStatement语句对象防止注入攻击
* 2PreparedStatement 可以使用 ? 作为参数的占位符
* 3使用?作为占位符,即使是字符串和日期类型,也不使用单独再添加 ''
* 4connection.createStatement();获得的是普通语句对象 Statement
* 5connection.prepareStatement(sql);可以获得一个预编译语句对象PreparedStatement
* 6如果SQL语句中有?作为参数占位符号,那么要在执行CURD之前先设置参数
* 7通过set***(问号的编号,数据) 方法设置参数
* */
String sql="select * from account where username = ? and password = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setString(1,username );
preparedStatement.setString(2,pwd );
//执行CURD
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
while(resultSet.next()){
int aid = resultSet.getInt("aid");
String usernamea = resultSet.getString("username");
String pwda = resultSet.getString("password");
double money = resultSet.getDouble("money");
account=new Account(aid,usernamea,pwda,money);
System.out.println(account);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return account;
}
}
prepareStatment对象在set***方法上,会对单引号进行转译处理,也就是说,?中的数据的单引号 ‘ 会被转义成 \’,这样就单引号就不会破坏sql语句的结构,
SELECT * FROM users WHERE userName = ? AND password = ?
preparedStatement.setString(1,"xiaoming");
preparedStatement.setString(2,'anything' OR 'x'='x');
会被转义为
SELECT * FROM users WHERE userName = 'xiaoming' AND password = 'anything\' OR\'x\'=\'x\''
而不是
SELECT * FROM users WHERE userName = 'xiaoming' AND password = 'anything' OR 'x'='x'说白了就是把值当中的所有单引号给转义了!这就达到了防止sql注入的目的,说白了mysql驱动的PreparedStatement实现类的setString();方法内部做了单引号的转义,而Statement不能防止sql注入,就是因为它没有把单引号做转义,而是简单粗暴的直接拼接字符串,所以达不到防止sql注入的目的。
预编译
当客户端发送一条sql语句给DBMS时,MySQL的执行流程如下图
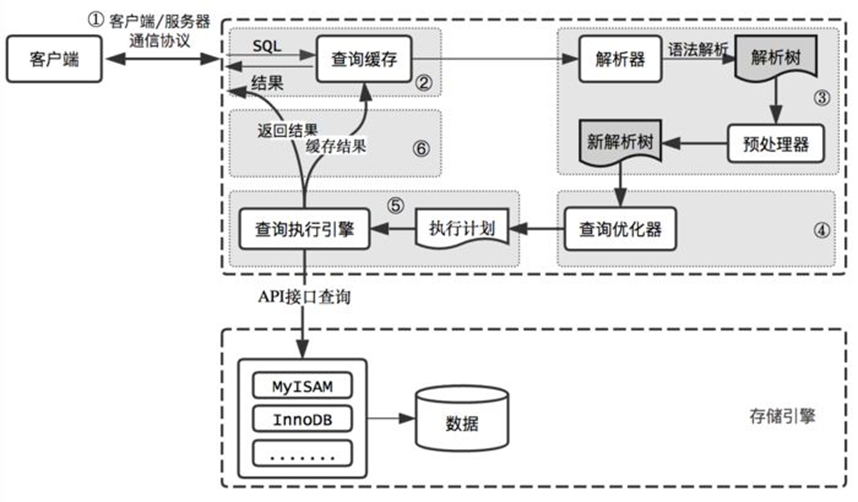
sql命令的执行流程如下
1. 客户端向服务器端发送SQL命令
2. 服务器端连接模块连接并验证
3. 缓存模块解析SQL为Hash并与缓存中Hash表对应。如果有结果直接返回结果,如果没有对应继续向下执行
4. 解析器解析SQL为解析树,如果出现错误,报SQL解析错误。如果正确,向下传递
5. 预处理器对解析树继续处理,处理成新的解析树。
6. 优化器根据开销自动选择最优执行计划,生成执行计划
7. 执行器执行执行计划,访问存储引擎接口
8. 存储引擎访问物理文件并返回结果
9. 如果开启缓存,缓存管理器把结果放入到查询缓存中。
10. 返回结果给客户端
当客户发送一条SQL语句给DBMS后,DBMS总是需要校验SQL语句的语法格式是否正确,然后把SQL语句编译成可执行的函数,最后才是执行SQL语句。其中校验语法,和编译所花的时间可能比执行SQL语句花的时间还要多。
预编译语句PreparedStatement 是java.sql中的一个接口,它是Statement的子接口。通过Statement对象执行SQL语句时,需要将SQL语句发送给DBMS,由DBMS首先进行编译后再执行。预编译语句和Statement不同,在创建PreparedStatement 对象时就指定了SQL语句,该语句立即发送给DBMS进行编译。当该编译语句被执行时,DBMS直接运行编译后的SQL语句,而不需要像其他SQL语句那样首先将其编译。预编译的SQL语句处理性能稍微高于普通的传递变量的办法。
例如:我们需要执行多次insert语句,但只是每次插入的值不同,MySQL服务器也是需要每次都去校验SQL语句的语法格式,以及编译,这就浪费了太多的时间。如果使用预编译功能,那么只对SQL语句进行一次语法校验和编译,所以效率要高。
预编译如何开启?
我们可以通过设置URL中的参数来控制预编译是否开启
useServerPrepStmts是否开启预编译
cachePrepStmts 是否启用预编译缓存
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?*****&useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true";值得注意的是,我们的Connector/J 5.0.5及之后useServerPrepStmts默认false,就是默认没有开启预编译,之前默认为true, cachePrepStmts 一直默认为false,需要我们手动设置才可以启用预编译,在开启预编译的同时要同时开启预编译缓存才能带来些许的性能提升
Statement和PreparedStatment的关系和区别
关系:public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement
区别
PreparedStatment安全性高,可以避免SQL注入
PreparedStatment简单不繁琐,不用进行字符串拼接
PreparedStatment性能高,用在执行多个相同数据库DML操作时,可以减少sql语句的编译次数
六、PrepareStatement完成CURD
package com.msb.test3;
import com.msb.entity.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TestPreparedSstatement {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//testAdd();
//testUpdate();
//testDelete();
testQuery();
}
public static void testAdd(){
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="insert into emp values(DEFAULT ,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setString(1,"Mark");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"MANAGER" );
preparedStatement.setInt(3,7839);
preparedStatement.setDate(4,new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
preparedStatement.setDouble(5,3000.12);
preparedStatement.setDouble(6,0.0);
preparedStatement.setDouble(7,30);
//执行CURD
int rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
System.out.println(rows);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void testUpdate(){
// 根据工号修改员工表中的数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="update emp set ename =? ,job=? where empno =?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setString(1,"Jhon");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"ANALYST" );
preparedStatement.setInt(3,7935);
//执行CURD
int rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
System.out.println(rows);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void testDelete(){
// 根据工号删除员工表中的数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="delete from emp where empno =?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setInt(1,7935);
//执行CURD
int rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
System.out.println(rows);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void testQuery(){
// 查询名字中包含字母A的员工信息
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
List<Emp> list =null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
/*
* 1使用PreparedStatement语句对象防止注入攻击
* 2PreparedStatement 可以使用 ? 作为参数的占位符
* 3使用?作为占位符,即使是字符串和日期类型,也不使用单独再添加 ''
* 4connection.createStatement();获得的是普通语句对象 Statement
* 5connection.prepareStatement(sql);可以获得一个预编译语句对象PreparedStatement
* 6如果SQL语句中有?作为参数占位符号,那么要在执行CURD之前先设置参数
* 7通过set***(问号的编号,数据) 方法设置参数
* */
String sql="select * from emp where ename like ? ";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setString(1,"%A%");
//执行CURD
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
list=new ArrayList<Emp>() ;
while(resultSet.next()){
int empno = resultSet.getInt("empno");
String ename = resultSet.getString("ename");
String job = resultSet.getString("job");
int mgr = resultSet.getInt("mgr");
Date hiredate = resultSet.getDate("hiredate");
double sal= resultSet.getDouble("sal");
double comm= resultSet.getDouble("comm");
int deptno= resultSet.getInt("deptno");
Emp emp =new Emp(empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno);
list.add(emp);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 遍历集合
for (Emp emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
}
七、批处理
PreparedStatement批处理
什么是批处理?
当我们有多条sql语句需要发送到数据库执行的时候,有两种发送方式,一种是执行一条发送一条sql语句给数据库,另一个种是发送一个sql集合给数据库,也就是发送一个批sql到数据库。普通的执行过程是:每处理一条数据,就访问一次数据库;而批处理是:累积到一定数量,再一次性提交到数据库,减少了与数据库的交互次数,所以效率会大大提高,很显然两者的数据库执行效率是不同的,我们发送批处理sql的时候数据库执行效率要高
所以增删改可以进行批处理,查不用进行批处理
statement语句对象实现批处理有如下问题
缺点:采用硬编码效率低,安全性较差。
原理:硬编码,每次执行时相似SQL都会进行编译
PreparedStatement+批处理
优点:语句只编译一次,减少编译次数。提高了安全性(阻止了SQL注入)
原理:相似SQL只编译一次,减少编译次数
注意: 需要设置批处理开启&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
package com.msb.test4;
import java.sql.*;
public class TestBatch {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true&&rewriteBatchedStatements=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
testAddBatch();
}
// 定义一个方法,向部门表增加1000条数据
public static void testAddBatch(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="insert into dept values (DEFAULT ,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
for (int i = 1; i <= 10663; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, "name");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "loc");
preparedStatement.addBatch();// 将修改放入一个批次中
if(i%1000==0){
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();// 清除批处理中的数据
}
}
/*
* 整数数组中的元素代表执行的结果代号
* SUCCESS_NO_INFO -2
* EXECUTE_FAILED -3
* */
/*int[] ints = */
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}八、事务及回滚点
JDBC中使用事务
事务回顾:
事务概念:在逻辑上一组不可分割的操作,由多个sql语句组成,多个sql语句要么全都执行成功,要么都不执行. 原子性 一致性 隔离性 持久性
JDBC控制事物主要就是在学习如何让多个数据库操作成为一个整体,实现要么全都执行成功,要么全都不执行
在JDBC中,事务操作是自动提交。一条对数据库的DML(insert、update、delete)代表一项事务操作,操作成功后,系统将自动调用commit()提交,否则自动调用rollback()回滚,在JDBC中,事务操作方法都位于接口java.sql.Connection中,可以通过调用setAutoCommit(false)来禁止自动提交。之后就可以把多个数据库操作的表达式作为一个事务,在操作完成后调用commit()来进行整体提交,倘若其中一个表达式操作失败,都不会执行到commit(),并且将产生响应的异常;此时就可以在异常捕获时调用rollback()进行回滚,回复至数据初始状态.事务开始的边界则不是那么明显了,它会开始于组成当前事务的所有statement中的第一个被执行的时候。事务结束的边界是commit或者rollback方法的调用
使用事务保证转账安全性
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestTransaction {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true&&rewriteBatchedStatements=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
testTransaction();
}
// 定义一个方法,向部门表增加1000条数据
public static void testTransaction(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
/*
* JDBC 默认是自动提交事务
* 每条DML都是默认提交事务的,多个preparedStatement.executeUpdate();都会提交一次事务
* 如果想手动控制事务,那么就不能让事务自动提交
* 通过Connection对象控制connection.setAutoCommit(false);
* 如果不设置 默认值为true,自动提交,设置为false之后就是手动提交了
* 无论是否发生回滚,事务最终会一定要提交的 提交我们建议放在finally之中进行提交
* 如果是转账的过程中出现异常了,那么我们就要执行回滚,回滚操作应该方法catch语句块中
*
* */
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
// 设置事务手动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql="update account set money =money- ? where aid = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
// 转出
preparedStatement.setDouble(1, 100);
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 1);
//一个sql提交一次
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
// 产生异常
//int i =1/0;
// 转入
preparedStatement.setDouble(1, -100);
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 2);
//一个sql提交一次
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}catch (Exception e){
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.rollback();// 回滚事务
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 提交事务
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
设置回滚点
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class TestTransaction2 {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true&&rewriteBatchedStatements=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public static void main(String[] args) {
testAddBatch();
}
// 定义一个方法,向部门表增加1000条数据
public static void testAddBatch(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
LinkedList<Savepoint> savepoints =new LinkedList<Savepoint>();
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql="insert into dept values (DEFAULT ,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
for (int i = 1; i <= 10663; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, "name");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "loc");
preparedStatement.addBatch();// 将修改放入一个批次中
if(i%1000==0){
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();// 清除批处理中的数据
// 设置回滚点
Savepoint savepoint = connection.setSavepoint();
savepoints.addLast(savepoint);
}
// 数据在 100001条插入的时候出现异常
if(i ==10001){
int x =1/0;
}
}
/*
* 整数数组中的元素代表执行的结果代号
* SUCCESS_NO_INFO -2
* EXECUTE_FAILED -3
* */
/*int[] ints = */
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}catch (Exception e){
if(null != connection){
try {
//Savepoint sp = savepoints.getLast();
Savepoint sp = savepoints.get(4);
if(null != sp){
// 选择回滚点
connection.rollback(sp);// 回滚
}
} catch (SQLException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.commit();// 提交
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}九、JDBCAPI总结
JDBC API总结
Connection接口
作用:代表数据库连接
方法摘要 | |
void | close() 立即释放此 Connection 对象的数据库和 JDBC 资源,而不是等待它们被自动释放。 |
void | commmit 使所有上一次提交/回滚后进行的更改成为持久更改,并释放此 Connection 对象当前持有的所有数据库锁。 |
Statement | creatStatement() 创建一个 Statement 对象来将 SQL 语句发送到数据库。 |
CallableStatement | prepareCall(String sql) 创建一个 CallableStatement 对象来调用数据库存储过程。 |
PreparedStatement | prepareStatement(String sql) 创建一个 PreparedStatement 对象来将参数化的 SQL 语句发送到数据库。 |
PreparedStatement | prepareStatement(String sql,int autoGeneratedKeys) 创建一个默认 PreparedStatement 对象,该对象能获取自动生成的键。 |
void | rollback() 取消在当前事务中进行的所有更改,并释放此 Connection 对象当前持有的所有数据库锁。 |
void | setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) 将此连接的自动提交模式设置为给定状态。 |
DriverManager类
作用:管理一组 JDBC 驱动程序的基本服务
应用程序不再需要使用 Class.forName() 显式地加载 JDBC 驱动程序。在调用 getConnection 方法时,DriverManager 会试着从初始化时加载的那些驱动程序以及使用与当前 applet 或应用程序相同的类加载器显式加载的那些驱动程序中查找合适的驱动程序。
方法摘要 | |
static Connection | getConnection(String url) 试图建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接。 |
static Connection | getConnection (String url, Properties info) 试图建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接。 |
static Connection | getConnection (String url, String user, String password) 试图建立到给定数据库 URL 的连接。 |
Statement接口
作用:用于将 SQL 语句发送到数据库中,或理解为执行sql语句
有三种 Statement对象:
Statement:用于执行不带参数的简单SQL语句;
PreparedStatement(从 Statement 继承):用于执行带或不带参数的预编译SQL语句;
CallableStatement(从PreparedStatement 继承):用于执行数据库存储过程的调用。
方法摘要 | |
ResultSet | executeQuery(String sql) 执行SQL查询并获取到ResultSet对象 |
int | executeUpdate(String sql) 可以执行插入、删除、更新等操作,返回值是执行该操作所影响的行数 |
PreparedStatement接口
关系:public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement
区别
PreparedStatment安全性高,可以避免SQL注入
PreparedStatment简单不繁琐,不用进行字符串拼接
PreparedStatment性能高,用在执行多个相同数据库DML操作时
ResultSet接口
ResultSet对象是executeQuery()方法的返回值,它被称为结果集,它代表符合SQL语句条件的所有行,并且它通过一套getXXX方法(这些get方法可以访问当前行中的不同列)提供了对这些行中数据的访问。
ResultSet里的数据一行一行排列,每行有多个字段,且有一个记录指针,指针所指的数据行叫做当前数据行,我们只能来操作当前的数据行。我们如果想要取得某一条记录,就要使用ResultSet的next()方法 ,如果我们想要得到ResultSet里的所有记录,就应该使用while循环。
ResultSet对象自动维护指向当前数据行的游标。每调用一次next()方法,游标向下移动一行。
初始状态下记录指针指向第一条记录的前面,通过next()方法指向第一条记录。循环完毕后指向最后一条记录的后面。
方法摘要 | |
boolean | next() 将光标从当前位置向下移动一行 |
boolean | previous() 游标从当前位置向上移动一行 |
void | close() 关闭ResultSet 对象 |
int | getInt(int colIndex) 以int形式获取结果集当前行指定列号值 |
int | getInt(String colLabel) 以int形式获取结果集当前行指定列名值 |
float | getFloat(int colIndex) 以float形式获取结果集当前行指定列号值 |
Float | getFloat(String colLabel) 以float形式获取结果集当前行指定列名值 |
String | getString(int colIndex) 以String 形式获取结果集当前行指定列号值 |
String | getString(String colLabel) 以String形式获取结果集当前行指定列名值 |
十、DAO模式
DAO(Data Access Object)是一个数据访问接口,数据访问:顾名思义就是与数据库打交道。夹在业务逻辑与数据库资源中间。
在核心J2EE模式中是这样介绍DAO模式的:为了建立一个健壮的J2EE应用,应该将所有对数据源的访问操作抽象封装在一个公共API中。用程序设计的语言来说,就是建立一个接口,接口中定义了此应用程序中将会用到的所有事务方法。在这个应用程序中,当需要和数据源进行交互的时候则使用这个接口,并且编写一个单独的类来实现这个接口在逻辑上对应这个特定的数据存储.
简单来说,就是定义一个接口,规定一些增删改查的方法,然后交给实现类去实现, 它介于数据库和业务逻辑代码之间,这样当我们需要操作数据库是,根据接口定义的API去操作数据库就可以了,每个方法都是一个原子性的操作,例如:增加、修改、删除等
Dao模式要求项目必须具备这样几个结构
1实体类:和数据库表格一一对应的类,单独放入一个包中,包名往往是 pojo/entity/bean,要操作的每个表格都应该有对应的实体类
emp > class Emp
dept > class Dept
account > class Account
2DAO 层:定义了对数据要执行那些操作的接口和实现类,包名往往是 dao/mapper,要操作的每个表格都应该有对应的接口和实现类
emp > interface EmpDao >EmpDaoImpl
dept > interface DeptDao> DeptDaoImpl
3Mybatis/Spring JDBCTemplate 中,对DAO层代码进行了封装,代码编写方式会有其他变化
项目的搭建
1.创建项目
2.添加jar包
3.创建包
4.创建实体类Emp
5.创建后台的接口EmpDao和实现类EmpDaoImpl
导入各个层级的接口和页面之后的项目
项目结构截图如下
实体类代码
package pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
public class Emp implements Serializable {
private Integer empno;
private String ename;
private String job;
private Integer mgr;
private Date hiredate;
private Double sal;
private Double comm;
private Integer deptno;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"empno=" + empno +
", ename='" + ename + '\'' +
", job='" + job + '\'' +
", mgr=" + mgr +
", hiredate=" + hiredate +
", sal=" + sal +
", comm=" + comm +
", deptno=" + deptno +
'}';
}
public Emp(Integer empno, String ename, String job, Integer mgr, Date hiredate, Double sal, Double comm, Integer deptno) {
this.empno = empno;
this.ename = ename;
this.job = job;
this.mgr = mgr;
this.hiredate = hiredate;
this.sal = sal;
this.comm = comm;
this.deptno = deptno;
}
}package pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Dept implements Serializable {
private Integer deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
public Dept(Integer deptno, String dname, String loc) {
this.deptno = deptno;
this.dname = dname;
this.loc = loc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dept{" +
"deptno=" + deptno +
", dname='" + dname + '\'' +
", loc='" + loc + '\'' +
'}';
}
}DAO接口代码
package com.msb.dao;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
public interface EmpDao {
/**
* 向数据库Emp表中增加一条数据的方法
* @param emp 要增加的数据封装成的Emp类的对象
* @return 增加成功返回大于0 的整数,增加失败返回0
*/
int addEmp(Emp emp);
/**
* 根据员工编号删除员工信息的方法
* @param empno 要删除的员工编号
* @return 删除成功返回大于0的整数,失败返回0
*/
int deleteByEmpno(int empno);
}DAO实现类代码
package com.msb.dao.impl;
import com.msb.dao.EmpDao;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
public class EmpDaoImpl implements EmpDao {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
@Override
public int addEmp(Emp emp) {
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="insert into emp values(DEFAULT ,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,emp.getEname());
preparedStatement.setObject(2,emp.getJob() );
preparedStatement.setObject(3,emp.getMgr());
preparedStatement.setObject(4,emp.getHiredate());
preparedStatement.setObject(5,emp.getSal());
preparedStatement.setObject(6,emp.getComm());
preparedStatement.setObject(7,emp.getDeptno());
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return rows;
}
@Override
public int deleteByEmpno(int empno) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="delete from emp where empno =?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,empno);
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return rows;
}
}十一、员工管理系统开发
DAO接口
package com.msb.dao;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.util.List;
public interface EmpDao {
/**
* 向数据库Emp表中增加一条数据的方法
* @param emp 要增加的数据封装成的Emp类的对象
* @return 增加成功返回大于0 的整数,增加失败返回0
*/
int addEmp(Emp emp);
/**
* 根据员工编号删除员工信息的方法
* @param empno 要删除的员工编号
* @return 删除成功返回大于0的整数,失败返回0
*/
int deleteByEmpno(int empno);
/**
* 查看数据库表格中所有的员工信息
* @return 所有员工信息封装的一个List<Emp>集合
*/
List<Emp> findAll();
/**
* 根据员工编号修改员工其他所有字段的方法
* @param emp 员工编号和其他7个字段封装的一个Emp类对象
* @return 修改成功返回大于0的整数,失败返回0
*/
int updateEmp(Emp emp);
}
package com.msb.dao;
import com.msb.pojo.Dept;
import java.util.List;
public interface DeptDao {
/**
* 查询全部门的方法
* @return Dept对象封装的List集合
*/
List<Dept> findAll();
int addDept(Dept dept);
}DAO实现类
package com.msb.dao.impl;
import com.msb.dao.EmpDao;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class EmpDaoImpl implements EmpDao {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
@Override
public int addEmp(Emp emp) {
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="insert into emp values(DEFAULT ,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,emp.getEname());
preparedStatement.setObject(2,emp.getJob() );
preparedStatement.setObject(3,emp.getMgr());
preparedStatement.setObject(4,emp.getHiredate());
preparedStatement.setObject(5,emp.getSal());
preparedStatement.setObject(6,emp.getComm());
preparedStatement.setObject(7,emp.getDeptno());
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return rows;
}
@Override
public int deleteByEmpno(int empno) {
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="delete from emp where empno =?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,empno);
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return rows;
}
@Override
public List<Emp> findAll() {
// 查询名字中包含字母A的员工信息
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
List<Emp> list =null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="select * from emp";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//执行CURD
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
list=new ArrayList<Emp>() ;
while(resultSet.next()){
int empno = resultSet.getInt("empno");
String ename = resultSet.getString("ename");
String job = resultSet.getString("job");
int mgr = resultSet.getInt("mgr");
Date hiredate = resultSet.getDate("hiredate");
double sal= resultSet.getDouble("sal");
double comm= resultSet.getDouble("comm");
int deptno= resultSet.getInt("deptno");
Emp emp =new Emp(empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno);
list.add(emp);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
@Override
public int updateEmp(Emp emp) {
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="update emp set ename =? ,job=?, mgr =?,hiredate =?,sal=?,comm=?,deptno=? where empno =?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,emp.getEname());
preparedStatement.setObject(2,emp.getJob() );
preparedStatement.setObject(3,emp.getMgr());
preparedStatement.setObject(4,emp.getHiredate());
preparedStatement.setObject(5,emp.getSal());
preparedStatement.setObject(6,emp.getComm());
preparedStatement.setObject(7,emp.getDeptno());
preparedStatement.setObject(8,emp.getEmpno());
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return rows;
}
}
package com.msb.dao.impl;
import com.msb.dao.DeptDao;
import com.msb.pojo.Dept;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class DeptDaoImpl implements DeptDao {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
@Override
public List<Dept> findAll() {
// 查询名字中包含字母A的员工信息
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
List<Dept> list =null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="select * from dept";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//执行CURD
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
list=new ArrayList<Dept>() ;
while(resultSet.next()){
int deptno = resultSet.getInt("deptno");
String dname = resultSet.getString("dname");
String loc = resultSet.getString("loc");
Dept dept =new Dept(deptno,dname,loc);
list.add(dept);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
@Override
public int addDept(Dept dept) {
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
String sql="insert into dept values(?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
preparedStatement.setObject(1,dept.getDeptno());
preparedStatement.setObject(2,dept.getDname());
preparedStatement.setObject(3,dept.getLoc() );
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return rows;
}
}
EmpManageSystem类
package com.msb.view;
import com.msb.dao.DeptDao;
import com.msb.dao.EmpDao;
import com.msb.dao.impl.DeptDaoImpl;
import com.msb.dao.impl.EmpDaoImpl;
import com.msb.pojo.Dept;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class EmpManageSystem {
private static Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
private static EmpDao empDao =new EmpDaoImpl();
private static DeptDao deptDao=new DeptDaoImpl();
private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");;
public static void main(String[] args) {
while(true){
showMenu();
System.out.println("请录入选项");
int option =sc.nextInt();
switch (option){
case 1:
case1();
break;
case 2:
case2();
break;
case 3:
case3();
break;
case 4:
case4();
break;
case 5:
case5();
break;
case 6:
case6();
break;
case 7: break;
default:
System.out.println("请正确输入选项");
}
}
}
private static void case1(){
List<Emp> emps = empDao.findAll();
emps.forEach(System.out::println);
}
private static void case2(){
List<Dept> depts = deptDao.findAll();
depts.forEach(System.out::println);
}
private static void case3(){
System.out.println("请输入要删除的员工编号");
int empno=sc.nextInt();
empDao.deleteByEmpno(empno);
}
private static void case4(){
System.out.println("请输入员工编号");
int empno =sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入员工姓名");
String ename =sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入员工职位");
String job =sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入员工上级");
int mgr =sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入员工入职日期,格式为yyyy-MM-dd");
Date hiredate =null;
try {
hiredate = simpleDateFormat.parse(sc.next());
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请输入员工工资");
double sal =sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入员工补助");
double comm=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入员工部门号");
int deptno =sc.nextInt();
Emp emp=new Emp(empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm,deptno);
empDao.updateEmp(emp);
}
private static void case5(){
System.out.println("请输入员工姓名");
String ename =sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入员工职位");
String job =sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入员工上级");
int mgr =sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入员工入职日期,格式为yyyy-MM-dd");
Date hiredate =null;
try {
hiredate = simpleDateFormat.parse(sc.next());
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("请输入员工工资");
double sal =sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入员工补助");
double comm=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入员工部门号");
int deptno =sc.nextInt();
Emp emp=new Emp(null, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm,deptno);
empDao.addEmp(emp);
}
private static void case6(){
System.out.println("请录入部门号");
int deptno =sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入部门名称");
String dname =sc.next();
System.out.println("请录入部门位置");
String loc =sc.next();
Dept dept =new Dept(deptno,dname,loc);
deptDao.addDept(dept);
}
public static void showMenu(){
System.out.println("************************************");
System.out.println("* 1 查看所有员工信息");
System.out.println("* 2 查看所有部门信息");
System.out.println("* 3 根据工号删除员工信息");
System.out.println("* 4 根据工号修改员工信息");
System.out.println("* 5 增加员工信息");
System.out.println("* 6 增加部门信息");
System.out.println("* 7 退出");
System.out.println("************************************");
}
}
十二、BaseDao抽取
BaseDAO代码
package com.msb.dao;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public abstract class BaseDao {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
public int baseUpdate(String sql,Object ... args){
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数
for (int i = 0; i <args.length ; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return rows;
}
public List baseQuery(Class clazz,String sql,Object ... args) {
// 查询名字中包含字母A的员工信息
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
List list =null;
try{
Class.forName(driver);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
for (int i = 0; i <args.length ; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
//执行CURD
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
list=new ArrayList() ;
// 根据字节码获取所有 的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);// 设置属性可以 访问
}
while(resultSet.next()){
// 通过反射创建对象
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();//默认在通过反射调用对象的空参构造方法
for (Field field : fields) {// 临时用Field设置属性
String fieldName = field.getName();// empno ename job .... ...
Object data = resultSet.getObject(fieldName);
field.set(obj,data);
}
list.add(obj);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != connection){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
到实现类代码
package com.msb.dao.impl;
import com.msb.dao.BaseDao;
import com.msb.dao.EmpDao;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class EmpDaoImpl extends BaseDao implements EmpDao {
@Override
public int addEmp(Emp emp) {
String sql="insert into emp values(DEFAULT ,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
return baseUpdate(sql, emp.getEname(),emp.getJob(),emp.getMgr(),emp.getHiredate(),emp.getSal(),emp.getComm(),emp.getDeptno());
}
@Override
public int deleteByEmpno(int empno) {
String sql="delete from emp where empno =?";
return baseUpdate(sql, empno);
}
@Override
public List<Emp> findAll() {
String sql ="select * from emp";
return baseQuery(Emp.class, sql );
}
@Override
public int updateEmp(Emp emp) {
String sql="update emp set ename =? ,job=?, mgr =?,hiredate =?,sal=?,comm=?,deptno=? where empno =?";
return baseUpdate(sql, emp.getEname(),emp.getJob(),emp.getMgr(),emp.getHiredate(),emp.getSal(),emp.getComm(),emp.getDeptno(),emp.getEmpno());
}
}
package com.msb.dao.impl;
import com.msb.dao.BaseDao;
import com.msb.dao.DeptDao;
import com.msb.pojo.Dept;
import com.msb.pojo.Emp;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class DeptDaoImpl extends BaseDao implements DeptDao {
@Override
public List<Dept> findAll() {
String sql="select * from dept";
return baseQuery(Dept.class, sql);
}
@Override
public int addDept(Dept dept) {
String sql="insert into dept values(?,?,?)";
return baseUpdate(sql, dept.getDeptno(),dept.getDname(),dept.getLoc());
}
}十三、连接池的使用
建立数据库连接的两种方式:
传统连接方式:
首先调用Class.forName()方法加载数据库驱动,然后调用DriverManager.getConnection()方法建立连接.
连接池方式:
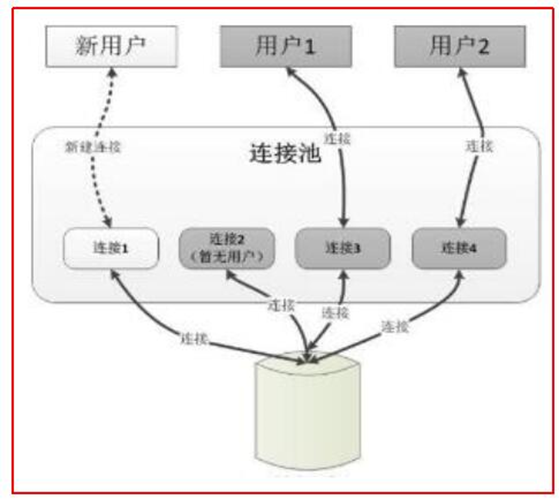
连接池解决方案是在应用程序启动时就预先建立多个数据库连接对象,然后将连接对象保存到连接池中。当客户请求到来时,从池中取出一个连接对象为客户服务。当请求完成时,客户程序调用close()方法,将连接对象放回池中.对于多于连接池中连接数的请求,排队等待。应用程序还可根据连接池中连接的使用率,动态增加或减少池中的连接数。
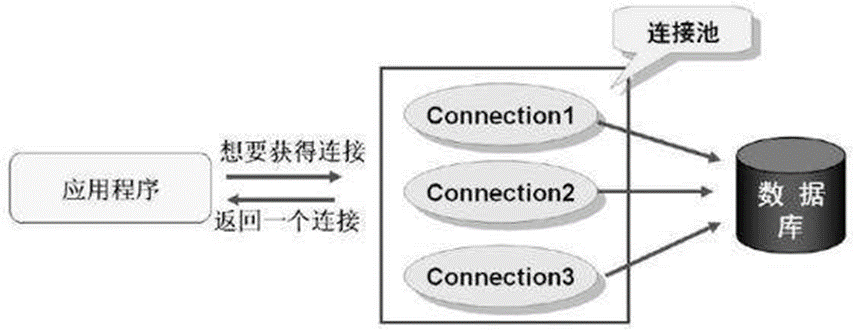
传统方式存在问题
Connection对象在每次执行DML和DQL的过程中都要创建一次,DML和DQL执行完毕后,connection对象都会被销毁. connection对象是可以反复使用的,没有必要每次都创建新的.该对象的创建和销毁都是比较消耗系统资源的,如何实现connection对象的反复使用呢?使用连接池技术实现.
连接池的优势
1预先准备一些链接对象,放入连接池中,当多个线程并发执行时,可以避免短时间内一次性大量创建链接对象,减少计算机单位时间内的运算压力,提高程序的响应速度
2实现链接对象的反复使用,可以大大减少链接对象的创建次数,减少资源的消耗
具体实现如下
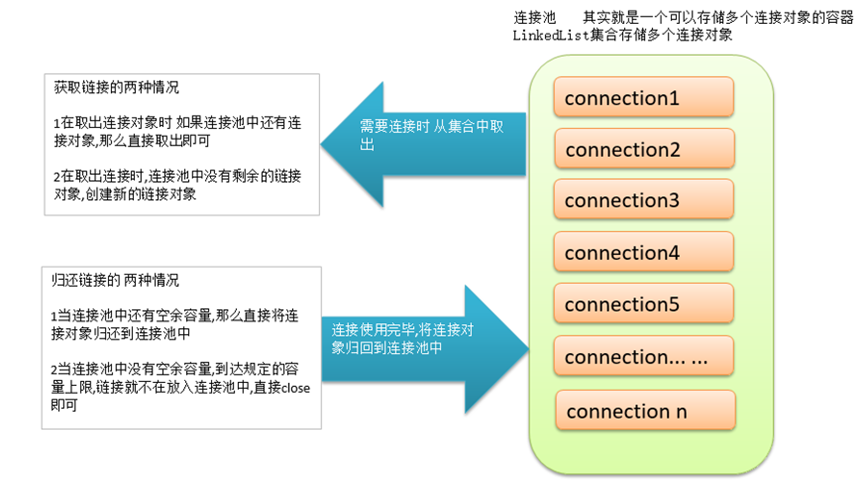
1定义连接池
package com.msb.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MyConnectionPool {
private static String driver ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private static String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="root";
private static int initSize=1;
private static int maxSize=1;
private static LinkedList<Connection> pool;
static{
// 加载驱动
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 初始化pool
pool=new LinkedList<Connection>();
// 创建5个链接对象
for (int i = 0; i <initSize ; i++) {
Connection connection = initConnection();
if(null != connection){
pool.add(connection);
System.out.println("初始化连接"+connection.hashCode()+"放入连接池");
}
}
}
// 私有的初始化一个链接对象的方法
private static Connection initConnection(){
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 共有的向外界提供链接对象的
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection =null;
if(pool.size()>0){
connection= pool.removeFirst();// 移除集合中的第一个元素
System.out.println("连接池中还有连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}else{
connection = initConnection();
System.out.println("连接池空,创建新连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}
return connection;
}
// 共有的向连接池归还连接对象的方法
public static void returnConnection(Connection connection){
if(null != connection){
try {
if(!connection.isClosed()){
if(pool.size()<maxSize){
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(true);// 调整事务状态
System.out.println("设置连接:"+connection.hashCode()+"自动提交为true");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
pool.addLast(connection);
System.out.println("连接池未满,归还连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}else{
try {
connection.close();
System.out.println("连接池满了,关闭连接:"+connection.hashCode());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}else{
System.out.println("连接:"+connection.hashCode()+"已经关闭,无需归还");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
System.out.println("传入的连接为null,不可归还");
}
}
}2修改BaseDao
package com.msb.dao;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public abstract class BaseDao {
public int baseUpdate(String sql,Object ... args){
// 向 Emp表中增加一条数据
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
int rows=0;
try{
connection = MyConnectionPool.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数
for (int i = 0; i <args.length ; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
//执行CURD
rows =preparedStatement.executeUpdate();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
MyConnectionPool.returnConnection(connection);
}
return rows;
}
public List baseQuery(Class clazz,String sql,Object ... args) {
// 查询名字中包含字母A的员工信息
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
List list =null;
try{
connection = MyConnectionPool.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//这里已经传入SQL语句
//设置参数
for (int i = 0; i <args.length ; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
//执行CURD
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();// 这里不需要再传入SQL语句
list=new ArrayList() ;
// 根据字节码获取所有 的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);// 设置属性可以 访问
}
while(resultSet.next()){
// 通过反射创建对象
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();//默认在通过反射调用对象的空参构造方法
for (Field field : fields) {// 临时用Field设置属性
String fieldName = field.getName();// empno ename job .... ...
Object data = resultSet.getObject(fieldName);
field.set(obj,data);
}
list.add(obj);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != resultSet){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != preparedStatement){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
MyConnectionPool.returnConnection(connection);
}
return list;
}
}
配置文件优化参数存储
准备jdbc.properties配置文件,放在src下
## key=value
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
user=root
password=root
initSize=1
maxSize=1
准备PropertiesUtil工具类
package com.msb.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesUtil {
private Properties properties;
public PropertiesUtil(String path){
properties=new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream(path);
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String getProperties(String key){
return properties.getProperty(key);
}
}连接池中代码修改
package com.msb.dao;
import com.msb.util.PropertiesUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MyConnectionPool {
private static String driver;
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static int initSize;
private static int maxSize;
private static LinkedList<Connection> pool;
static{
// 初始化参数
PropertiesUtil propertiesUtil=new PropertiesUtil("/jdbc.properties");
driver=propertiesUtil.getProperties("driver");
url=propertiesUtil.getProperties("url");
user=propertiesUtil.getProperties("user");
password=propertiesUtil.getProperties("password");
initSize=Integer.parseInt(propertiesUtil.getProperties("initSize"));
maxSize=Integer.parseInt(propertiesUtil.getProperties("maxSize"));
// 加载驱动
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 初始化pool
pool=new LinkedList<Connection>();
// 创建5个链接对象
for (int i = 0; i <initSize ; i++) {
Connection connection = initConnection();
if(null != connection){
pool.add(connection);
System.out.println("初始化连接"+connection.hashCode()+"放入连接池");
}
}
}
// 私有的初始化一个链接对象的方法
private static Connection initConnection(){
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 共有的向外界提供链接对象的
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection =null;
if(pool.size()>0){
connection= pool.removeFirst();// 移除集合中的第一个元素
System.out.println("连接池中还有连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}else{
connection = initConnection();
System.out.println("连接池空,创建新连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}
return connection;
}
// 共有的向连接池归还连接对象的方法
public static void returnConnection(Connection connection){
if(null != connection){
try {
if(!connection.isClosed()){
if(pool.size()<maxSize){
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(true);// 调整事务状态
System.out.println("设置连接:"+connection.hashCode()+"自动提交为true");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
pool.addLast(connection);
System.out.println("连接池未满,归还连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}else{
try {
connection.close();
System.out.println("连接池满了,关闭连接:"+connection.hashCode());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}else{
System.out.println("连接:"+connection.hashCode()+"已经关闭,无需归还");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
System.out.println("传入的连接为null,不可归还");
}
}
}十四、log4j日志框架
log4j日志处理
1) 什么是日志log
异常信息 登录成功失败的信息 其他重要操作的信息
日志可以记录程序的运行状态,运行信息,用户的一些常用操作.日志可以帮助我们分析程序的运行状态,帮我们分析用户的操作习惯,进而对程序进行改进
2) 如何记录日志
方式1:System.out.println(.....) e.printStackTrace();
缺点:不是保存到文件,不能长久存储
方式2:IO流 将System.out.println(.....) e.printStackTrace();写入文件
缺点:操作繁琐,IO流操作容易阻塞线程,日志是有等级,日志的格式不能很好的定制,要想实行编程复杂
方式3:使用现成的日志框架,比如log4j
优点:1长久保存 2有等级3格式可以很好的定制 4代码编写简单
3) log4j日志的级别
FATAL: 指出现非常严重的错误事件,这些错误可能导致应用程序异常中止
ERROR: 指虽有错误,但仍允许应用程序继续运行
WARN: 指运行环境潜藏着危害
INFO: 指报告信息,这些信息在粗粒度级别上突出显示应用程序的进程
DEBUG: 指细粒度信息事件,对于应用程序的调试是最有用的
4) 使用log4j记录日志
1.加入jar包 log4j-1.2.8.jar
2.加入属性文件 src 下 log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=error,logfile
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.err
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.SimpleLayout
log4j.appender.logfile=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.logfile.File=d:/msb.log
log4j.appender.logfile.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.logfile.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %l %F %p %m%n通过属性文件理解log4j的主要API
Appender 日志目的地 :ConsoleAppender FileAppender
Layout 日志格式化器 :SimpleLayout PatternLayout
3.代码中记录日志
//创建一个日志记录器
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(DBUtil.class.getName());
//在合适的地方添加日志
logger.info("正确的读取了属性文件:"+prop);
logger.debug("正确的关闭了结果集");
logger.error("DML操作错误:"+e);5) 理解日志格式化字符的含义
%p:输出日志信息的优先级,即DEBUG,INFO,WARN,ERROR,FATAL。
%d:输出日志时间点的日期或时间,默认格式为ISO8601,也可以在其后指定格式,如:%d{yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss,SSS}。
%r:输出自应用程序启动到输出该log信息耗费的毫秒数。
%t:输出产生该日志事件的线程名。
%l:输出日志事件的发生位置,相当于%c.%M(%F:%L)的组合,包括类全名、方法、文件名以及在代码中的行数。例如
test.TestLog4j.main(TestLog4j.java:10)。
%c:输出日志信息所属的类目,通常就是所在类的全名。
%M:输出产生日志信息的方法名。
%F:输出日志消息产生时所在的文件名称。
%L::输出代码中的行号。
%m::输出代码中指定的具体日志信息。
%n:输出一个回车换行符,Windows平台为"rn",Unix平台为"n"。
%x:输出和当前线程相关联的NDC(嵌套诊断环境),尤其用到像java servlets这样的多客户多线程的应用中。
%%:输出一个"%"字符。
6) 使用log4j记录日志 连接池中通过log4j记录日志
package com.msb.dao;
import com.msb.util.PropertiesUtil;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MyConnectionPool {
private static String driver;
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static int initSize;
private static int maxSize;
private static Logger logger;
private static LinkedList<Connection> pool;
static{
logger=Logger.getLogger(MyConnectionPool.class);
// 初始化参数
PropertiesUtil propertiesUtil=new PropertiesUtil("/jdbc.properties");
driver=propertiesUtil.getProperties("driver");
url=propertiesUtil.getProperties("url");
user=propertiesUtil.getProperties("user");
password=propertiesUtil.getProperties("password");
initSize=Integer.parseInt(propertiesUtil.getProperties("initSize"));
maxSize=Integer.parseInt(propertiesUtil.getProperties("maxSize"));
// 加载驱动
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
logger.fatal("找不到数据库驱动类"+driver,e);
}
// 初始化pool
pool=new LinkedList<Connection>();
// 创建5个链接对象
for (int i = 0; i <initSize ; i++) {
Connection connection = initConnection();
if(null != connection){
pool.add(connection);
logger.info("初始化连接"+connection.hashCode()+"放入连接池");
}
}
}
// 私有的初始化一个链接对象的方法
private static Connection initConnection(){
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
logger.fatal("初始化连接异常",e);
}
return null;
}
// 共有的向外界提供链接对象的
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection connection =null;
if(pool.size()>0){
connection= pool.removeFirst();// 移除集合中的第一个元素
logger.info("连接池中还有连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}else{
connection = initConnection();
logger.info("连接池空,创建新连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}
return connection;
}
// 共有的向连接池归还连接对象的方法
public static void returnConnection(Connection connection){
if(null != connection){
try {
if(!connection.isClosed()){
if(pool.size()<maxSize){
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(true);// 调整事务状态
logger.debug("设置连接:"+connection.hashCode()+"自动提交为true");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
pool.addLast(connection);
logger.info("连接池未满,归还连接:"+connection.hashCode());
}else{
try {
connection.close();
logger.info("连接池满了,关闭连接:"+connection.hashCode());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}else{
logger.info("连接:"+connection.hashCode()+"已经关闭,无需归还");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
logger.warn("传入的连接为null,不可归还");
}
}
}十五、三大范式
什么是范式
必须保证数据库设计的合理性,对数据库设计总结的一些经验性的规范,称之为范式
1.数据库设计关系整个系统的架构,关系到后续开发效率和运行效率
2.数据库的设计主要包含了设计表结构和表之间的联系
如何是合理数据库
1.结构合理
2.冗余较小
3.尽量避免插入删除修改异常
如何才能保证数据库设计水平
1.遵循一定的规则
2.在关系型数据库中这种规则就称为范式
什么是范式(NF= NormalForm)
1.范式是符合某一种设计要求的总结。
2.要想设计一个结构合理的关系型数据库,必须满足一定的范式。
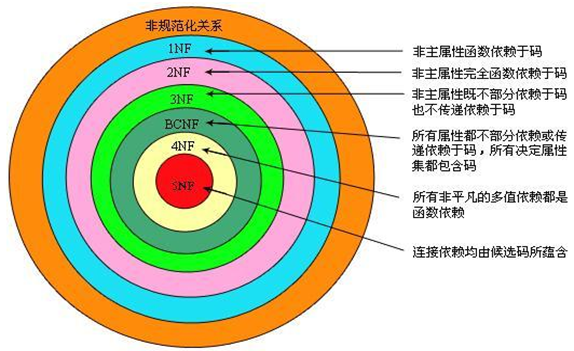
范式分类
第一范式:列原子性
第二范式:数据和联合主键完全相关性
第三范式:数据和主键直接相关性
1.Boyce Codd范式=BCNF
2.由Boyce和Codd提出的,
3.比3NF又进了一步
4.通常认为是修正的第三范式.
第四范式
第五范式
各个范式是依次嵌套包含的
范式越高,设计质量越高,在现实设计中也越难实现
一般数据库设计,只要达到第三范式,即可避免异常的出现
第一范式
要求
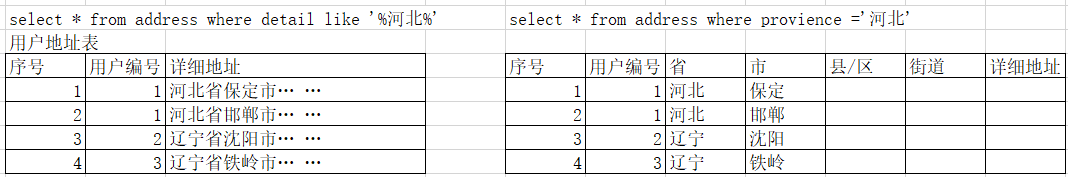
最基本的范式
数据库表每一列都是不可分割基本数据项,同一列中不能有多个值
简单说就是要确保每列保持原子性
第一范式的合理遵循需要根据系统的实际需求来定
第二范式
要求
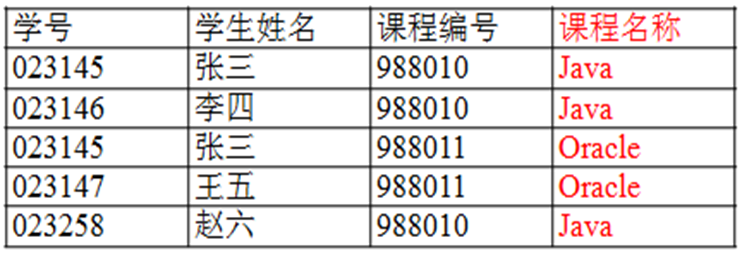
第二范式需要确保数据库表中的每一列都和主键相关,而不能只与主键的某一部分相关(言)。即在一个数据库表中只能保存一种数据,不可以把多种数据保存在同一张数据库表中。
第三范式
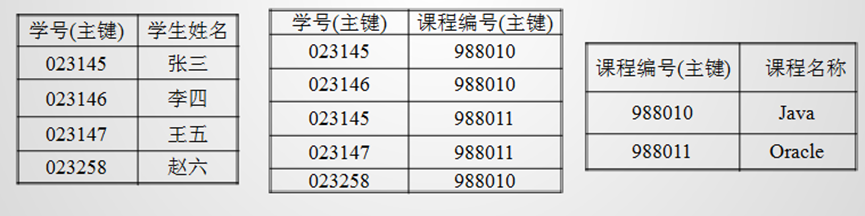
要求
确保数据表中的每一列数据都和主键直接相关,而不能间接相关
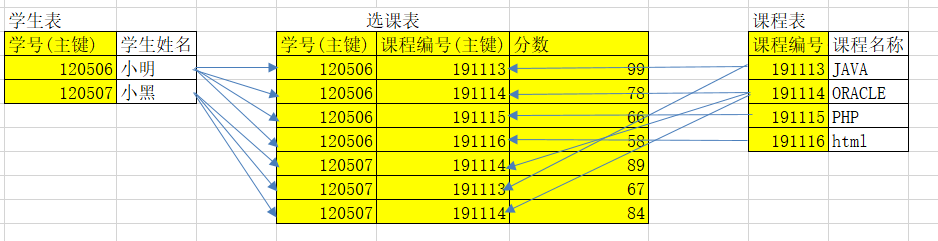
属性不依赖于其他非主属性。
学生班级表
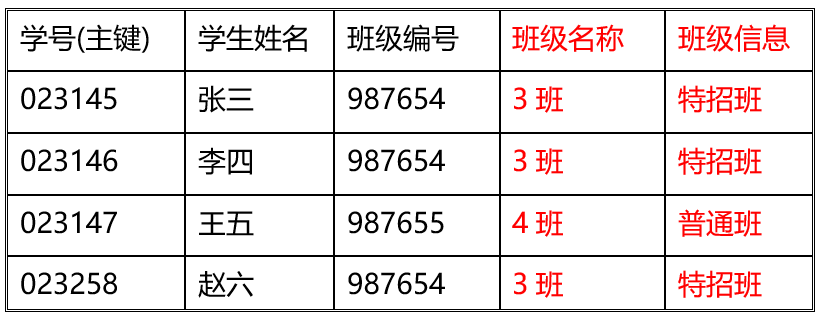
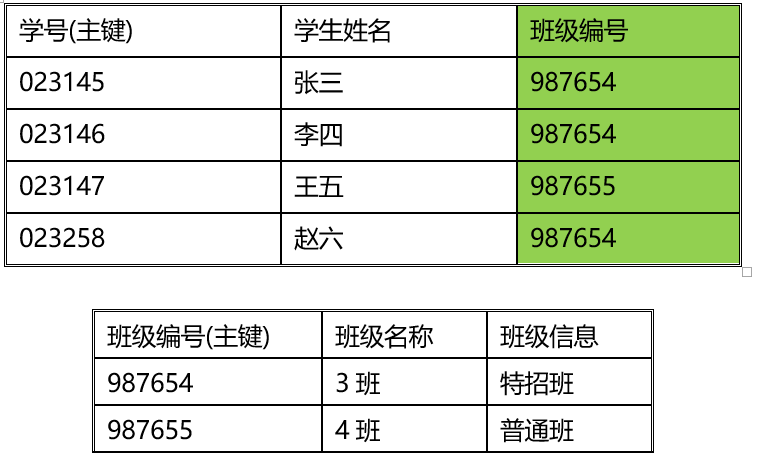
范式的总结
• 优点
• 结构合理
• 冗余较小
• 尽量避免插入删除修改异常
• 缺点
• 性能降低
• 多表查询比单表查询速度慢
• 数据库的设计应该根据当前情况和需求做出灵活的处理。
• 在实际设计中,要整体遵循范式理论。
• 如果在某些特定的情况下还死死遵循范式也是不可取的,因为可能降低数据库的效率,此时可以适当增加冗余而提高性能。
• 示例:
• 比如经常购物车条目的中除了条目编号,商品编号,商品数量外,可以增加经常使用的商品名称,商品价格等
图书表
订单表中增加冗余列图书名称、价格,以空间换时间。
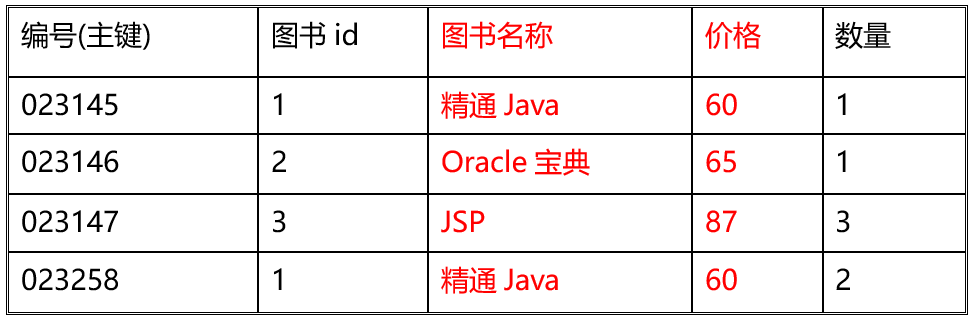
• 范式是指导数据设计的规范化理论,可以保证数据库设计质量
• 第一范式:字段不能再分
• 第二范式:不存在局部依赖
• 第三范式:不含传递依赖(间接依赖)
• 使用范式可以减少冗余,但是会降低性能
• 特定表的的设计可以违反第三范式,增加冗余提高性能
十六、数据之间的三大关系
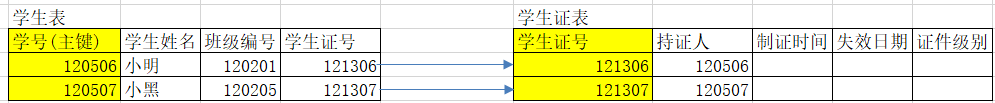
一对一 A表中的一条数据对应B表中的一条数据
一对多 A表中的一条数据对应B表中的多条数据
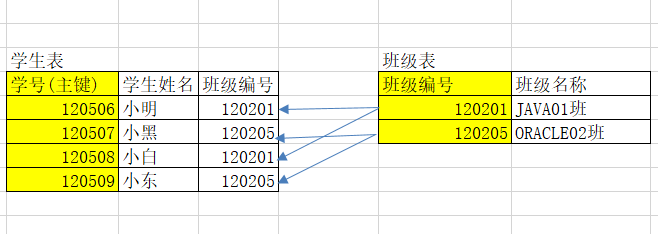
多对多 A表中对应B表中多条数据,同样B表中对应A表中多条数据
多对多需要通过中间表体现关系
中间表讲多对多的关系转变成两个一对多