MySQL高级语句(二)
一、VIEW(视图)
1、 概念
可以被当作是虚拟表或存储查询
视图跟表格的不同是,表格中有实际储存资料,而视图是建立在表格之上的一个架构,它本身并不实际储存资料。
临时表在用户退出或同数据库的连接断开后就自动消失了,而视图不会消失。
视图不含有数据,只存储它的定义,它的用途一般可以简化复杂的查询。比如你要对几个表进行连接查询,而且还要进行统计排序等操作,写SQL语句会很麻烦的,用视图将几个表联结起来,然后对这个视图进行查询操作,就和对一个表查询一样,很方便。
2、 创建、查看和删除视图
CREATE VIEW "视图表名" AS "SELECT 语句"; #创建视图表
SELECT * FROM `V_NAME_VALUE`; #查看视图表
DROP VIEW V_NAME_VALUE; #删除视图表
实例操作:
create view v_test1_2 as select A.name,A.xueke from test2 A where name in (select B.name from test1 B where age > 20);
select *from v_test1_2;
drop view v_test1_2;

二、联集
将两个SQL语句的结果合并起来,两个SQL语句所产生的字段需要是同样的
1、UNION
生成结果值将没有重复,且按照字段的顺序进行排序
语法:[SELECT 语句 1] UNION [SELECT 语句 2];
实例操作:
select name from test1 union select name from test2;

2、UNION ALL
将生成结果的值都列出来,无论有无重复
语法:[SELECT 语句 1] UNION ALL [SELECT 语句 2];
实例操作:
select name from test1 union all select name from test2;

三、交集值
取两个SQL语句结果的交集
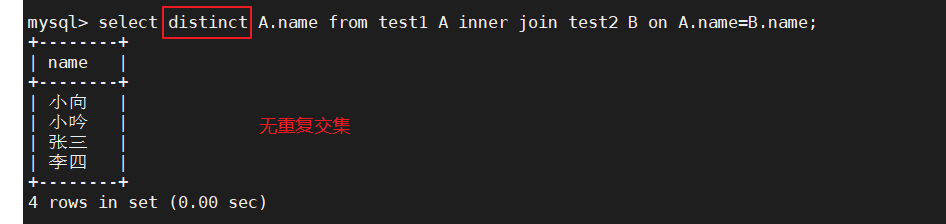
1、取交集值的方法1(2种简单方法,内连接+on/using,去重则加上distinct)
select A.name from test1 A inner join test2 B on A.name=B.name;
select A.name from test1 A inner join test2 B using(name);
select distinct A.name from test1 A inner join test2 B on A.name=B.name;


2、取交集方法2(1种,union all结合group by)
两表其中的一个表没有指定的行,而另一个表这个行有重复不可用,要求两个表确实有交集的时候用
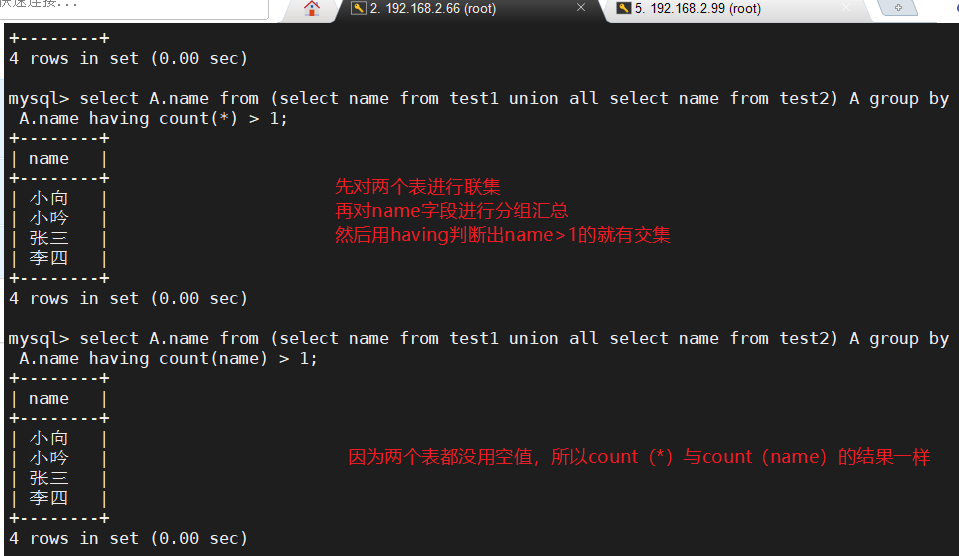
select A.name from (select name from test1 union all select name from test2) A group by A.name having count(*) > 1;
select A.name from (select name from test1 union all select name from test2) A group by A.name having count(name) > 1;
select name from test1 union all select name from test7; #拆分上面的SQL语句
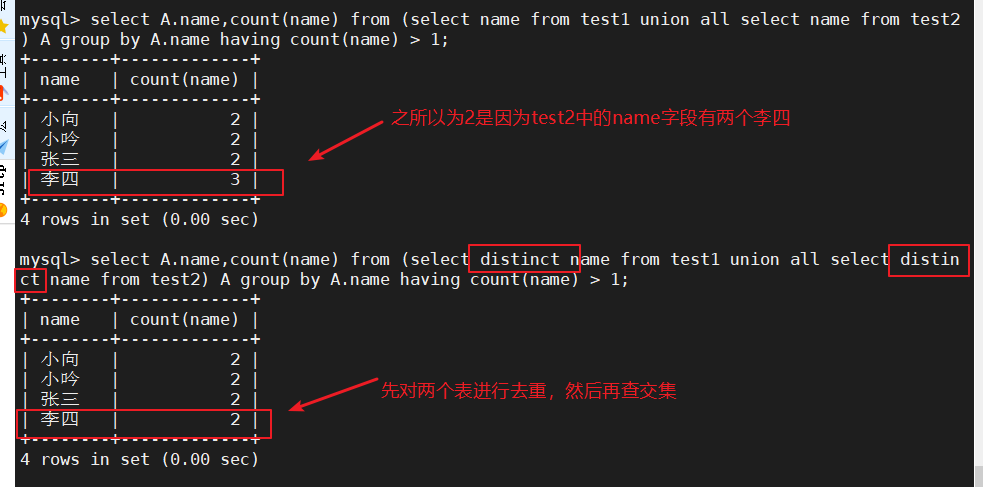
select A.name,count(name) from (select name from test1 union all select name from test2) A group by A.name having count(name) > 1; #显示count值,便于理解
select A.name,count(name) from (select distinct name from test1 union all select distinct name from test2) A group by A.name having count(name) > 1; #去重显示,在联集两个表之前先把表去重,以防一个表中本身就有重复值
3、取交集(去重)——4种方法
取两个SQL语句结果的交集,且没有重复
方法一:
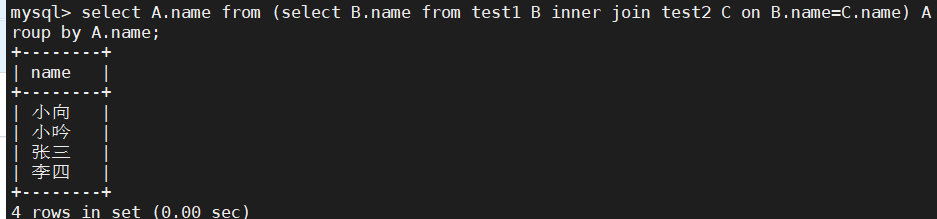
mysql> select A.name from (select B.name from test1 B inner join test2 C on B.name=C.name) A group by A.name;
方法二:
select distinct A.name from test1 A inner join test2 B using(name);
方法三:
select distinct name from test1 where name in (select name from test2);
方法四:
select distinct A.name from test1 A left join test2 B using(name) where B.name is NOT NULL;
方法一:内连接取交集结合group by去重
方法二:内连接取交集结合distinct去重

方法三:where+in遍历取交集并结合distinct去重

方法四:使用左连接(也可用右连接)+where 判断NOT NULL 取交集并结合distinct去重

四、无交集值
显示第一个SQL语句的结果,且与第二个SQL语句没有交集的结果,且没有重复
方法一:
select A.name from (select distinct name from test1 union all select distinct name from test2) A group by A.name having count(name)=1;
方法二:
select distinct name from test2 where name not in (select distinct name from test1);
select distinct name from test1 where name not in (select distinct name from test2);
方法三:
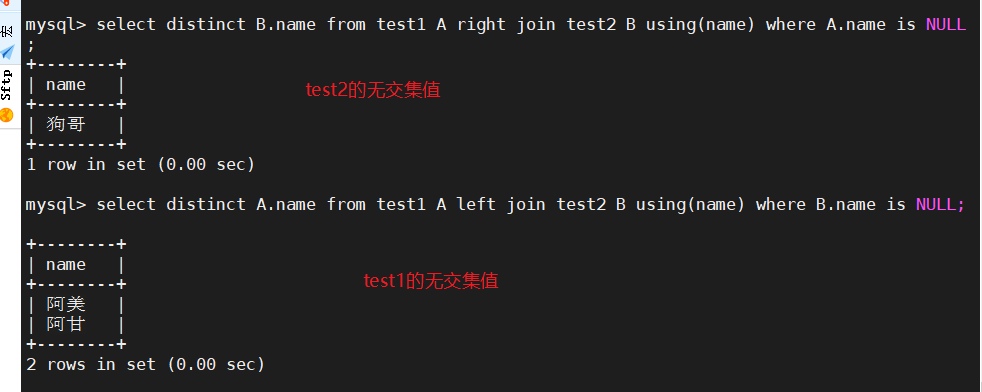
select distinct A.name from test1 A left join test2 B using(name) where B.name is NULL;
select distinct B.name from test1 A right join test2 B using(name) where A.name is NULL;
方法一:union all结合group by进行分组汇总并使用count=1取无交集值

方法二:where+not in遍历取无交集值并结合distinct去重

方法三:使用左连接(或者右连接)+where 判断NULL 取无交集并结合distinct去重
五、CASE的用法
是SQL用来作为IF-THEN-ELSE之类逻辑的关键字
1、语法格式:
SELECT CASE (字段名)
WHEN "条件1" THEN "结果1"
WHEN "条件2" THEN "结果2"
……
ELSE "结果N"
END
FROM "表名"
条件可以是一个数值或是公式。ELSE子句不是必须的
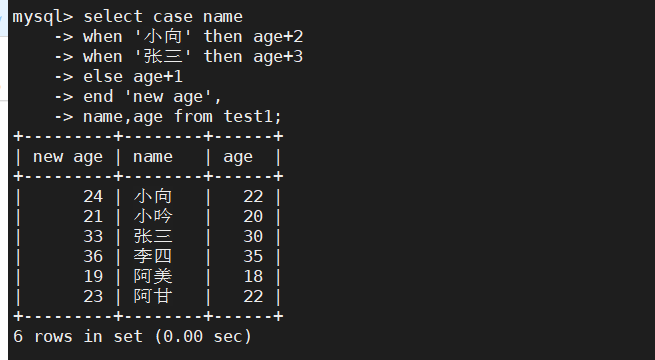
2、实例操作
六、空值(NULL)和无值(“”)的区别
区别:
无值的长度为0,不占用空间;而空值null 的长度是null,是占用空间的;
IS NULL或者IS NOT NULL,是用来判断字段是不是NULL或者不是NULL,是不能查出是不是无值的;
无值的判断使用=’‘或者<>’'来处理。<>代表不等于;
在通过count()指定字段统计有多少行数时,如果遇到NULL值会自动忽略掉,遇到空值会自动加入记录中进行计算。
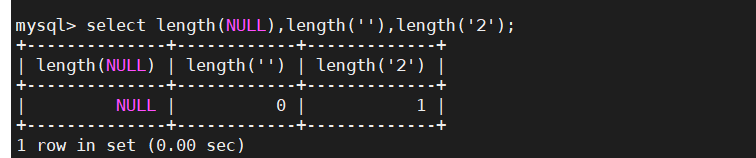
1、判断空值和无值的字符长度
select length(NULL),length(''),length('1');
2、使用count统计行数(体现null与空值的区别)
count(*) 表示包括所有列的行数,不会忽略null值;空值正常统计
count(列名) 表示只包括这一列,统计时会忽略null值的行;空值正常统计
