Node.js——开发博客项目之接口(处理请求、搭建开发环境、开发路由)
个人简介
👀个人主页: 前端杂货铺
🙋♂️学习方向: 主攻前端方向,也会涉及到服务端
📃个人状态: 在校大学生一枚,已拿 offer(秋招)
🥇推荐学习:🍍前端面试宝典 🍉Vue2 🍋Vue3 🍓Vue2&Vue3项目实战 🥝Node.js
Node.js系列文章目录
| 内容 | 参考链接 |
|---|---|
| Node.js(一) | 初识 Node.js |
文章目录
- Node.js系列文章目录
- 一、http 请求概述
- 二、处理请求
- 1、处理 get 请求
- 2、处理 post 请求
- 三、搭建开发环境
- 1、搭建环境
- 2、安装 nodemon
- 四、开发路由
- 1、初始化路由
- 2、使用 Promise 读取文件
一、http 请求概述
- DNS 解析,建立 TCP 连接,发送 http 请求
- server 接收 http 请求,处理,并返回
- 客户端接收到返回数据,处理数据(如渲染页面,执行 JS)
二、处理请求
1、处理 get 请求
- get 请求,即客户端要向 server 端获取数据,如查询博客列表
- 通过 querystring 来传递数据,如 a.html?a=100&b=200
- 浏览器直接访问,就发送 get 请求
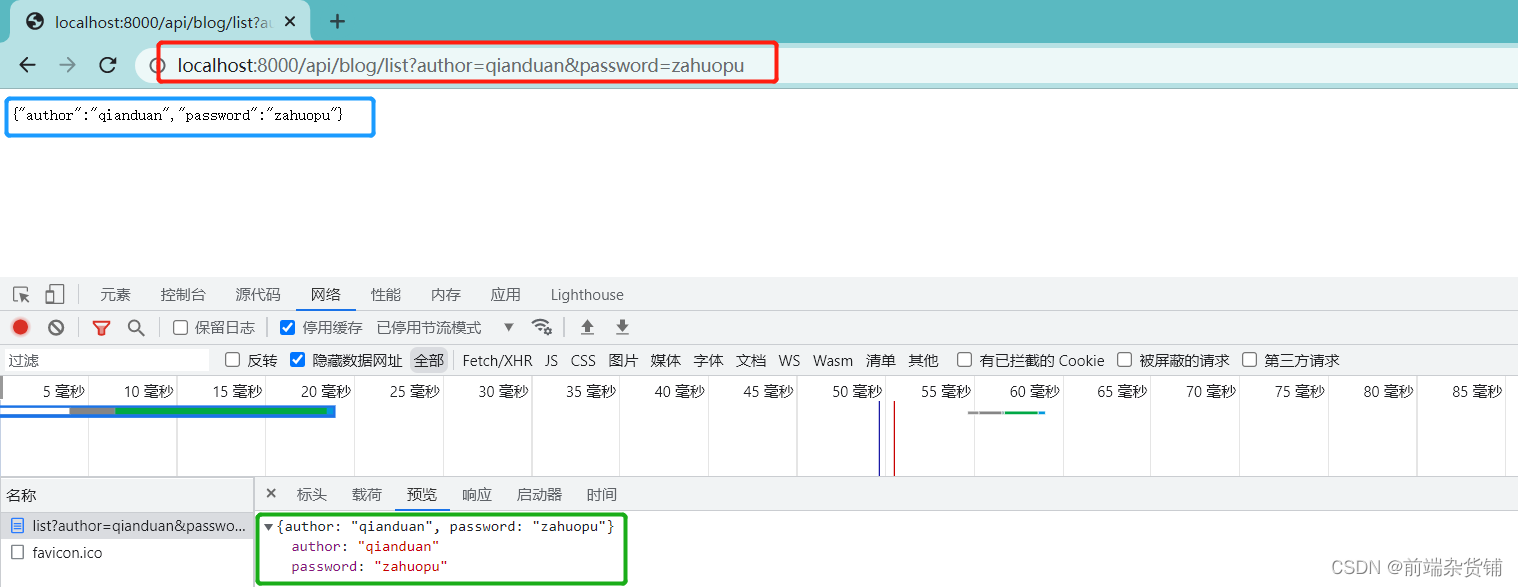
示例:GET 请求
// 获取 node.js 提供的原生 http 模块
const http = require('http')
const querystring = require('querystring')
// 创建服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log('method: ', req.method) // GET
const url = req.url // 获取请求的完整 url
console.log('url: ', url)
req.query = querystring.parse(url.split('?')[1]) // 解析 querystring
console.log('query: ', req.query)
res.end(JSON.stringify(req.query)) // 将 querystring 返回
})
// 监听端口
server.listen(8000)
console.log('OK')
2、处理 post 请求
- post 请求,即客户端要像服务端传递数据,如新建博客
- 通过 post data 传递数据
- 浏览器无法直接模拟,需要手写 js,或者使用 postman
示例:POST 请求
const http = require('http')
// 创建服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// POST 请求
if (req.method === 'POST') {
// req 数据格式
console.log('req content-type', req.headers['content-type'])
// 接收数据
let postData = ''
// 每次来数据都会触发 data 事件
req.on('data', chunk => {
postData += chunk.toString()
})
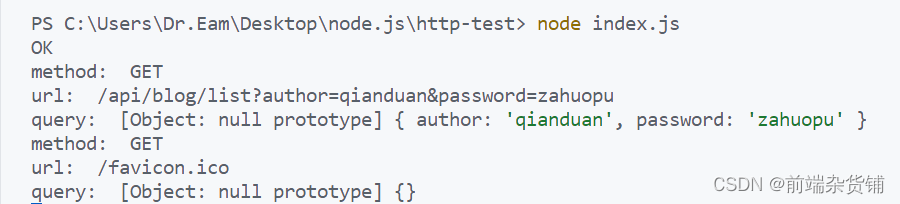
req.on('end', () => {
console.log('postData: ', postData)
res.end('hello world')
})
}
})
// 监听端口
server.listen(8000)
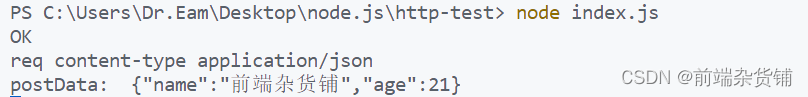
console.log('OK')
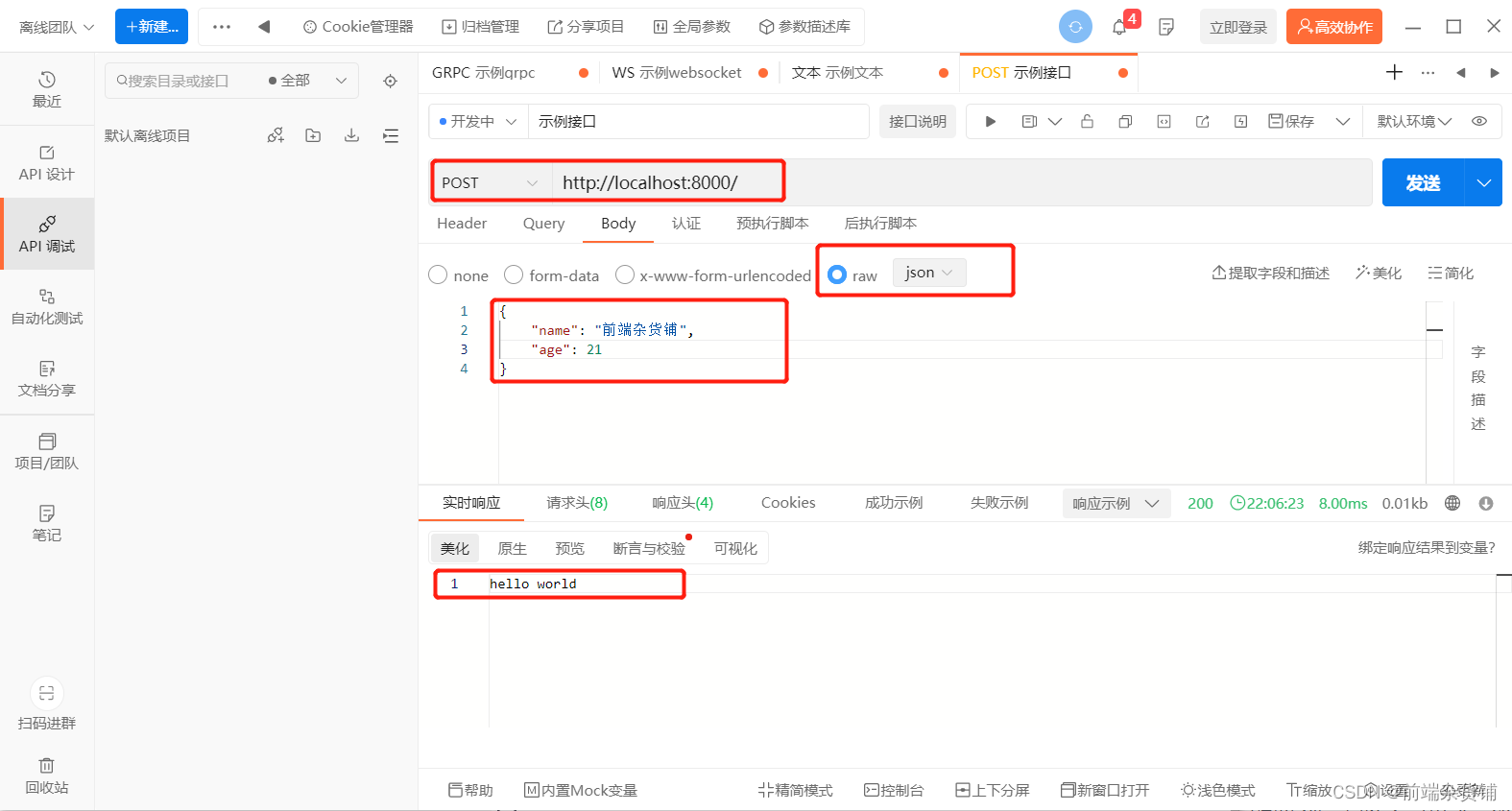
测试:使用 postman 或者 ApiPost
三、搭建开发环境
- 从 0 开始搭建,不使用任何框架
- 使用 nodemon 监测文件变化,自动重启 node
- 使用 cross-env 设置环境变量,兼容 windows mac 和 linux
1、搭建环境
文件格式如下:
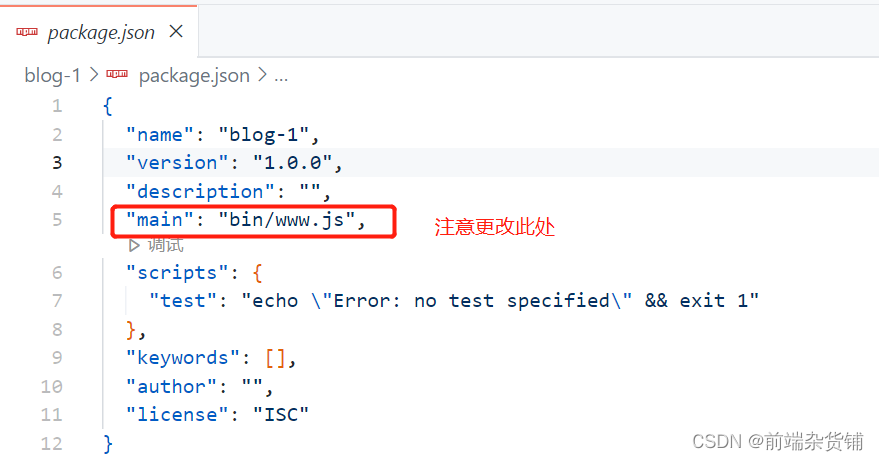
更改 main 的值:
app.js 文件
const serverHandle = (req, res) => {
// 设置返回格式 JSON
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'application/json')
// 返回的数据
const resData = {
name: '杂货铺',
site: 'CSDN'
}
// 服务器端要返回给客户端的数据
res.end(
JSON.stringify(resData)
)
}
// 模块化 把 serverHandle 暴露出去
module.exports = serverHandle
www.js 文件
const http = require('http')
// 端口
const PORT = 8000
// 引入 app.js
const serverHandle = require('../app')
// 创建服务
const server = http.createServer(serverHandle)
// 监听端口
server.listen(PORT)
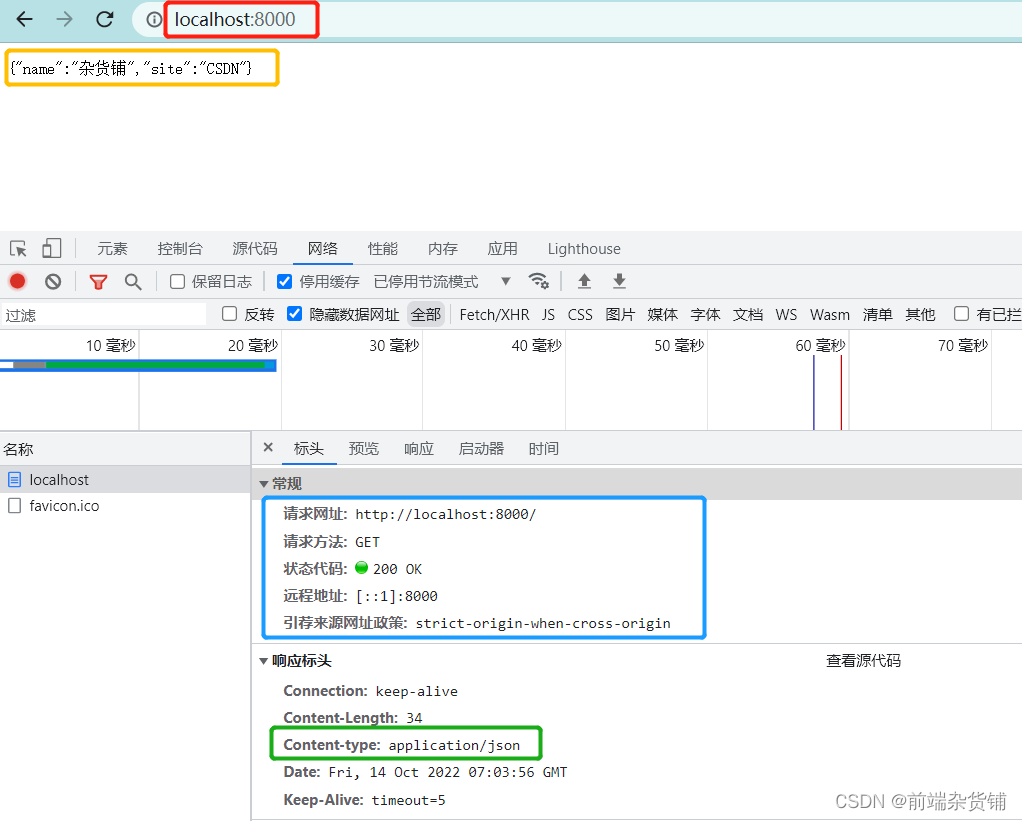
在当前文件夹路径下终端键入 node bin/www.js 启动服务,打开 8000 端口
2、安装 nodemon
nodemon 作用:可以监控文件变化,自动重启,无需手动
安装 nodemon,终端键入如下命令:
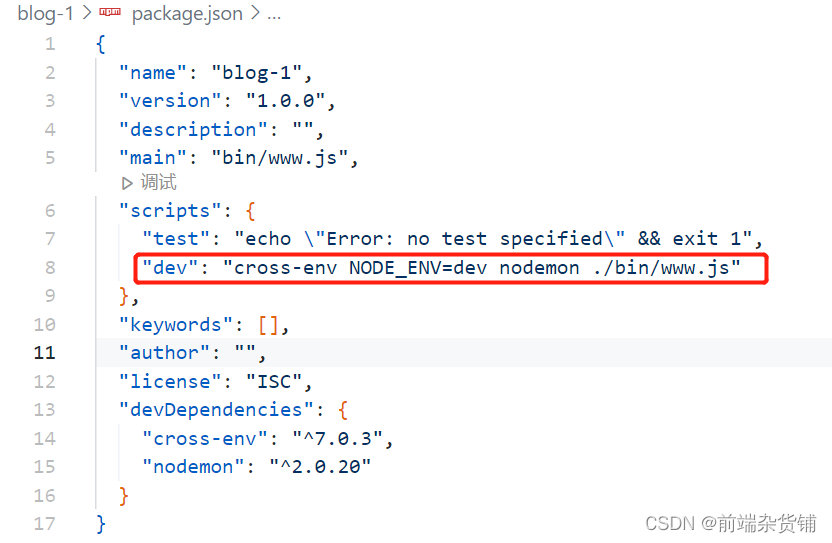
npm install nodemon cross-env --save-dev
在 package.json 中 添加 如下内容(测试环境,兼容多种操作系统):
四、开发路由
1、初始化路由
- 初始化路由:根据技术方案的设计,做出路由
- 返回假数据:将路由和数据处理分离,以符合设计规则
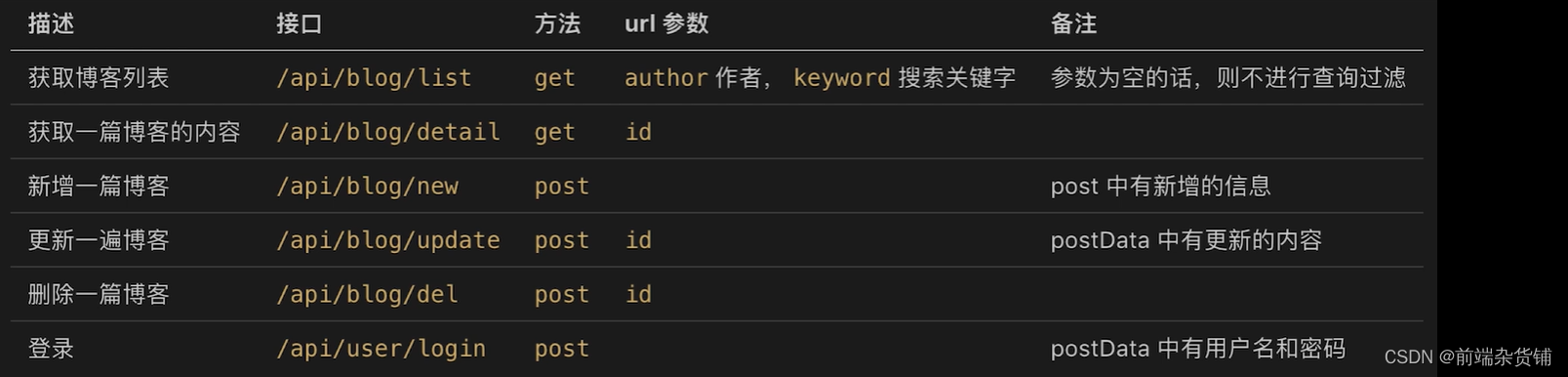
示例:开发接口,并测试使用
文件格式如下:
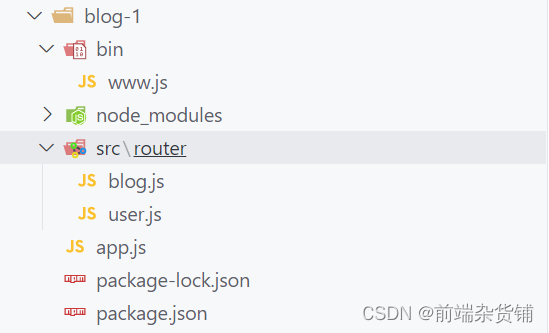
www.js 文件
- 创建服务,监听端口
- 最终
nodemon ./bin/www.js运行就是在此文件位置
const http = require('http')
// 端口
const PORT = 8000
// 引入 app.js
const serverHandle = require('../app')
// 创建服务
const server = http.createServer(serverHandle)
// 监听端口
server.listen(PORT)
app.js 文件
- 整合的文件
- 处理 blog 和 user 的相关接口
const handleBlogRouter = require('./src/router/blog')
const handleUserRouter = require('./src/router/user')
const serverHandle = (req, res) => {
// 设置返回格式 JSON
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'application/json')
// 获取 path
const url = req.url
req.path = url.split('?')[1] // 获取 ? 的后半部分
// 处理 blog 路由
const blogData = handleBlogRouter(req, res)
if (blogData) {
res.end(
JSON.stringify(blogData)
)
return
}
// 处理 user 路由
const userData = handleUserRouter(req, res)
if (userData) {
res.end(
JSON.stringify(userData)
)
return
}
// 未命中路由,返回 404
res.writeHead(404, {"Content-type": "text/plain"})
res.write("404 Not Found\n")
res.end()
}
// 模块化 把 serverHandle 暴露出去
module.exports = serverHandle
blog.js 文件
- 博客相关接口
- 最后暴露出去
const handleBlogRouter = (req, res) => {
const method = req.method // GET POST
// 获取博客列表
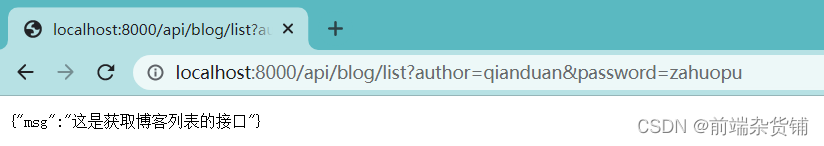
if (method === 'GET' && req.path === '/api/blog/list') {
return {
msg: '这是获取博客列表的接口'
}
}
// 获取博客详情
if (method === 'GET' && req.path === '/api/blog/detail') {
return {
msg: '这是获取博客详情的接口'
}
}
// 新建一篇博客
if (method === 'POST' && req.path === '/api/blog/new') {
return {
msg: '这是新建博客的接口'
}
}
// 更新一篇博客
if (method === 'POST' && req.path === '/api/blog/update') {
return {
msg: '这是更新博客的接口'
}
}
// 删除一篇博客
if (method === 'POST' && req.path === '/api/blog/delete') {
return {
msg: '这是删除博客的接口'
}
}
}
module.exports = handleBlogRouter
user.js 文件
- 登录相关接口
- 最后暴露出去
const handleUserRouter = (req, res) => {
const method = req.method
// 登录
if (method === 'POST' && req.path === '/api/user/login') {
return {
msg: '这是登录接口'
}
}
}
module.exports = handleUserRouter
测试如下:
获取博客列表:
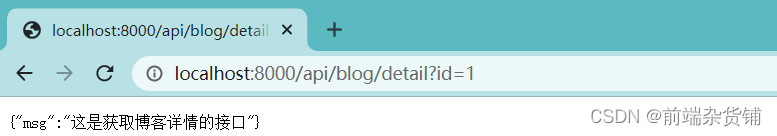
获取博客详情:
资源未找到 404:

2、使用 Promise 读取文件
示例:使用 Promise 读取三个 json 文件
a.json 文件
{
"next": "b.json",
"msg": "this is a"
}
b.json 文件
{
"next": "c.json",
"msg": "this is b"
}
c.json 文件
{
"next": null,
"msg": "this is c"
}
index.js 文件
- 封装获取文件内容的函数
- 依次读取文件内容
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
// 用 promise 获取文件内容
function getFileContent(fileName) {
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 获取文件全名, __dirname 表示当前文件所在的目录
const fullFileName = path.resolve(__dirname, 'files', fileName)
// 读取文件
fs.readFile(fullFileName, (err, data) => {
// 失败
if (err) {
reject(err)
return
}
// 成功
resolve(
JSON.parse(data.toString())
)
})
})
// 返回 promise 实例
return promise
}
// then 的链式调用
getFileContent('a.json').then(aData => {
console.log('a data', aData)
return getFileContent(aData.next)
}).then(bData => {
console.log('b data', bData)
return getFileContent(bData.next)
}).then(cData => {
console.log('c data', cData)
})
终端键入 nodemon index.js 测试结果如下: