Spring之AOP简单讲解
目录
一:基本概念
二:案例:模拟AOP的基础代码
三:AOP相关概念
四:AOP入门案例思路分析
五:AOP工作流程
六:AOP核心概念
七:AOP切入点表达式
八:xml方式AOP快速入门
九:案例:测量业务层接口万次执行效率
JoinPoint对象
十:案例:百度网盘密码数据兼容处理
语法形式不同:
可配置的切面数量不同:
使用场景不同:
xml方式AOP原理剖析
注解方式AOP基本使用
注解方式AOP原理剖析
十一:AOP总结
一:基本概念
AOP, Aspect Oriented Programming, 面向切面编程,一种编程范式,指导开发者如何组织程序结构, 是对面向对象编程OOP的升华。OOP(Object Oriented Programming)是纵向对一个事物的抽象, 一个对象包括静态的属性信息, 包括动态的方法信息等。而AOP是横向的对不同事物的抽象, 属性与属性、方法与方法、对象与对象都可以组成一个切面,而用这种思维去设计编程的方式叫做面向切面编程
作用:在不惊动原始设计的基础上为其进行功能增强
Spring理念:无入侵式/无侵入式
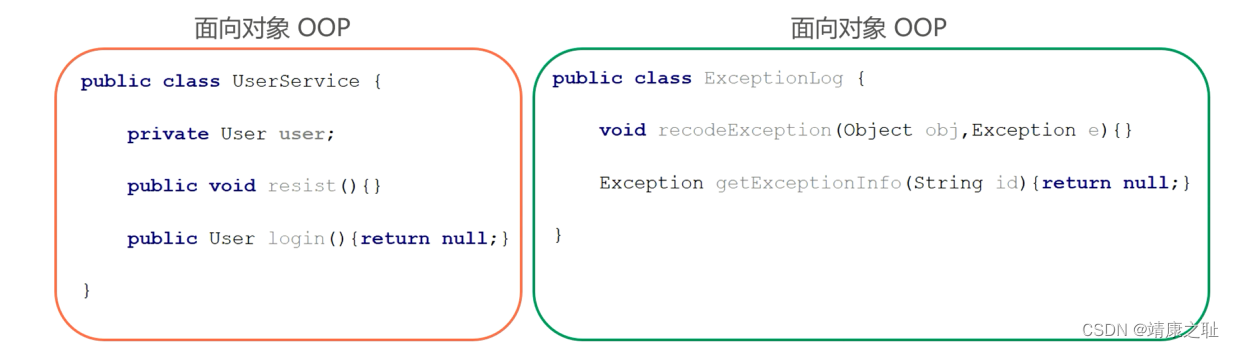
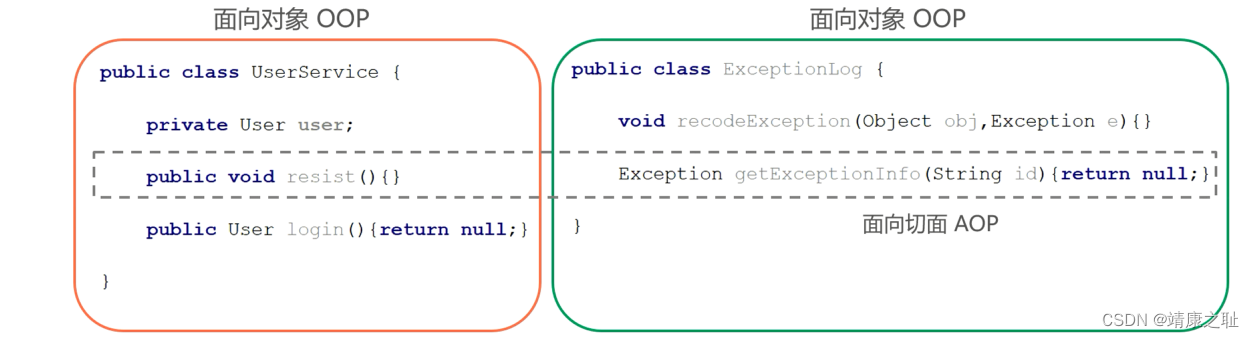

二:案例:模拟AOP的基础代码
其实在之前学习BeanPostProcessor时, 在BeanPostProcessor的after方法中使用动态代理对Bean进行了增强, 实际存储到单例池singleObjects中的不是当前目标对象本身, 而是当前目标对象的代理对象Proxy, 这样在调用目标对象方法时, 实际调用的是代理对象Proxy的同名方法, 起到了目标方法前后都进行增强的功能,对该方式进行一下优化,将增强的方法提取出去到一个增强类中,且只对com.tangyuan.service.impl包下的任何类的任何方法进行增强
//自定义增强类
public class My Advice{
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("beforeAdvice...") ;
}
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("afterAdvice...") ;
}
}1.创建service类
public interface UserService {
void show1();
void show2();
} 2.实现service的实现类
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void show1() {
System.out.println(show1.....);
}
@Override
public void show2() {
System.out.println(show2.....);
}
}ps:以上目标对象,目标类已经准备完成
3.创建增强类,内部提供增强方法
public class MyAdvice{
//前置增强方法
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println(前置的增强.....);
}
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println(后置的增强.....);
}
}
目的:在执行show1()方法的同时,也要将before和after的方法执行
4.将UserServiceImpl类和MyAdvic类配置到xml文件Spring容器中
<bean id="userService" class="com.tangyuan.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.tangyuan.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>5.BeanProxy对象创建
public class MockAopBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor,ApplicationContextAware{
//成员变量
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//目的:对UserServiceImpl中的show1和show2方法进行增强,增强方法存在于MyAdvice类中
//问题:1.筛选Service,impl包下的所有的类的所有方法都可以进行增强----解决方案if-else
//2.MyAdvice怎么获取到?解决方案:从Spring容器中获得MyAdvice
if(bean.getClass().getPackage().getName().equals("com.tangyuan.service.impl")){
//生成当前bean的Proxy对象
Object beanProxy=Proxy.newProxyInstance(
bean.getClass().getClassLoader(),
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(),
(Object proxy,Method method,Object[] args) -> {
MyAdvice myAdvice=applicationContext.getBean(MyAdvice.class);
//执行增强对象的before方法
myAdvice.beforeAdvice();
//执行目标对象的目标方法
Object result = method.invoke(bean, args);
//执行增强对象的after法
myAdvice.afterAdvice();
return result;
}
);
return beanProxy;
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext=applicationContext;
}
}
6.将 MockAopBeanPostProcessor类配置到xml文件Spring容器中
7.测试
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.show1();三:AOP相关概念
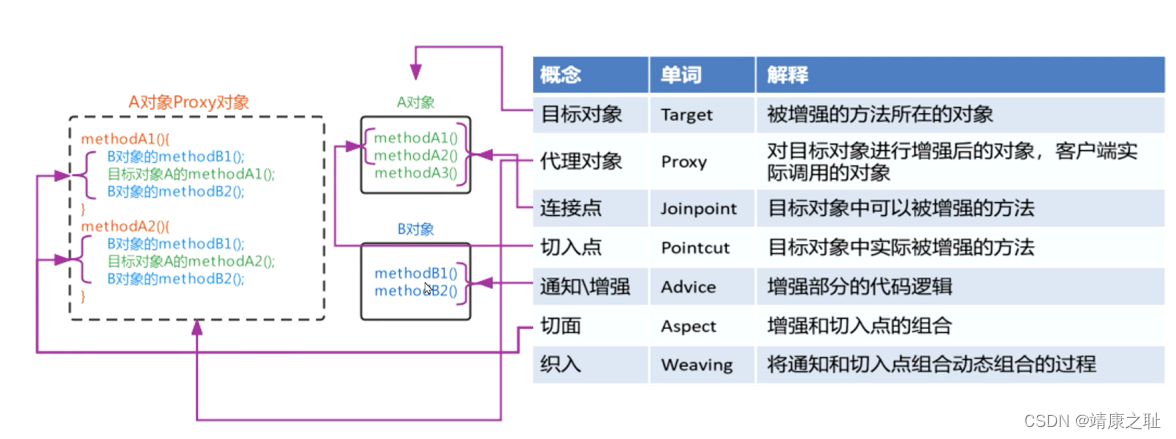
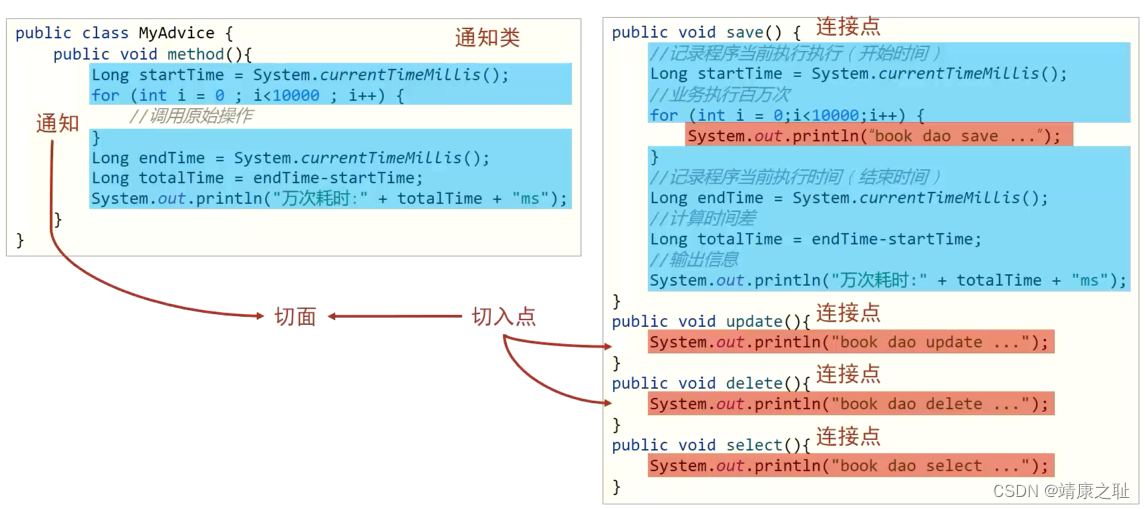

切入点范围小,连接点范围大,切入点一定在连接点中
四:AOP入门案例思路分析
目的:在接口执行前输出当前系统时间
开发模式:xml or 注解
思路分析:
1.导入坐标(pom.xml)
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>spring-context坐标依赖spring-aop坐标:

2.制作连接点方法(原始操作,Dao接口与实现类)
public interface BookDao {
public void save();
public void update();
}import com.tangyuan.dao.BookDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("book dao save ...");
}
public void update(){
System.out.println("book dao update ...");
}3.制作共性功能(通知类与通知)
创建一个类,用来存储共性功能
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//通知类必须配置成Spring管理的bean
@Component
//设置当前类为切面类类
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
//4.定义切入点
//设置切入点,要求配置在方法上方
@Pointcut("execution(void com.tangyuan.dao.BookDao.update())")
private void pt(){}
//5.绑定切入点与通知关系(切面)
//设置在切入点pt()的前面运行当前操作(前置通知)
@Before("pt()")
public void method(){
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}4.定义切入点
切入点定义依托一个不具有实际意义的方法进行,即无参数,无返回值,方法体无实际逻辑
5.绑定切入点与通知关系(切面),并指定通知添加到原始接点的具体执行位置
6.定义通知类受Spring容器管理,并定义当前类为切面类
7.在配置类中进行相关属性的配置,开启Spring对AOP注解驱动支持
五:AOP工作流程
1.Spring容器启动
2.读取所有切面配置中的切入点
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice{
@Pointcut("execution(void com.tangyuan.dao.BookDao.save())")
private void ptx() {}
@Pointcut("execution(void com.tangyuan.dao.BookDao.update())")
private void pt() {}
@Before("pt() ")
public void method() {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMiLLis() ) ;
}
}
3.初始化bean,判定bean对应的类中的方法是否匹配到任意切入点
匹配失败,创建对象
匹配成功,创建原始对象(目标对象)的代理对象
4.获取bean执行方法
获取bean,调用方法并执行,完成操作
获取的bean是代理对象时,根据代理对象的运行模式运行原始方法与增强的内容,完成操作
六:AOP核心概念
目标对象(Target) :原始功能去掉共性功能对应的类产生的对象, 这种对象是无法直接完成最终工作的
代理(Proxy) :目标对象无法直接完成工作, 需要对其进行功能回填, 通过原始对象的代理对象实现
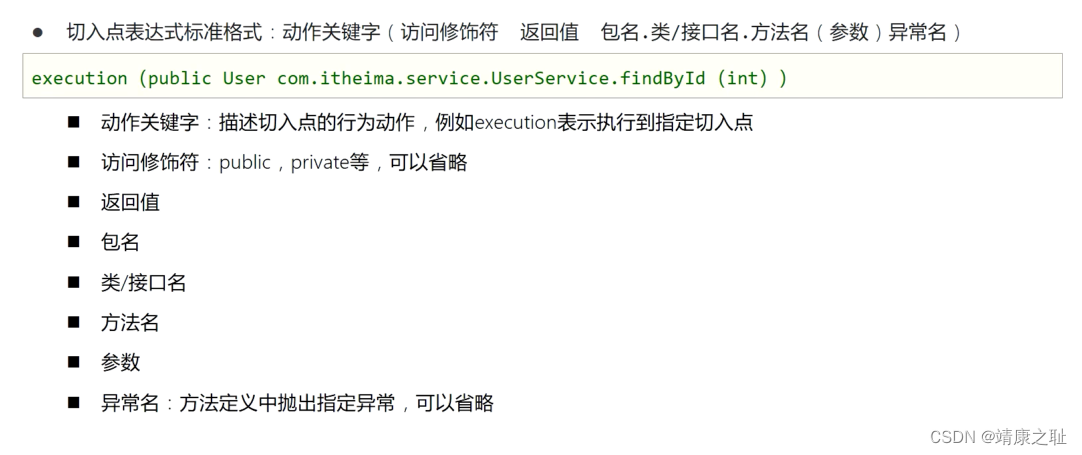
七:AOP切入点表达式
切入点:要进行增强的方法
切入点表达式:要进行增强的方法的描述方式



八:xml方式AOP快速入门
前面我们自己编写的AOP基础代码还是存在一些问题的, 主要如下:
-
被增强的包名在代码写死了
-
通知对象的方法在代码中写死了
if("com.tangyuan.service.impl".equals(packageName) ) {
//对Bean进行动态代理, 返回的是Proxy代理对象
Object proxy Bean=Proxy.new Proxy Instance(
bean.getClass() .getClassLoader() ,
bean.getClass() .get Interfaces() ,
(Object proxy,Method method, Object[] args)->{
myAdvice.beforeAdvice() ; //执行Advice的before方法
Object result=method.invoke(bean, args) ; //执行目标
myAdvice.afterAdvice() ; //执行Advice的after方法
return result;
});
//返回代理对象
return proxyBean;
}
return bean;
}通过配置文件的方式去解决上述问题
-
配置哪些包、哪些类、哪些方法需要被增强
-
配置目标方法要被哪些通知方法所增强,在目标方法执行之前还是之后执行增强
配置方式的设计、配置文件(注解) 的解析工作, Spring已经帮我们封装好了
xml方式配置AOP的步骤:
1、导入AOP相关坐标;
2、准备目标类、准备增强类, 并配置给Spring管理;
3、配置切点表达式(哪些方法被增强);
4、配置织入(切点被哪些通知方法增强,是前置增强还是后置增强)。
1.导入AOP相关坐标;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>2.目标和通知
<!--配置目标类-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.tangyuan.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--配置通知类-->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.tangyuan.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>3.配置aop的命名空间
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd4.配置切点表达式
<!--aop配置-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切点表达式,目的是要指定哪些方法被增强-->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(void com.tangyuan.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.show1() ) "/>
<!--配置织入,目的是要执行哪些切点与那些通知进行结合-->
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
xml配置AOP的方式还是比较简单的, 下面看一下AOP详细配置的细节:
-
切点表达式的配置方式
-
切点表达式的配置语法
-
通知的类型
-
AOP的配置的两种方式
ps:
1.切点表达式可以配置在外部,可以使用pointcut-ref来引用切点表达式的id
2.pointcut="execution(void com.tangyuan.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.show1() )"
3.切点表达式可以配置多个
切点表达式是配置要对哪些连接点(哪些类的哪些方法)进行通知的增强,语法如下:
execution([访问修饰符] 返回值类型包名.类名.方法名(参数) )其中,
-
访问修饰符可以省略不写;
-
返回值类型、某一级包名、类名、方法名可以使用*表示任意;
-
包名与类名之间使用单点.表示该包下的类,使用双点..表示该包及其子包下的类;
-
参数列表可以使用两个点..表示任意参数。
切点表达式举几个例子方便理解
//表示访问修饰符为public、无返回值、在com.tangyuan.aop包下的TargetImpl类的无参方法show
execution(public void com.tangyuan.aop.TargetImpl.show() )
//表述com.tangyuan.aop包下的Target Impl类的任意方法
execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.Target Impl.*(..) )
//表示com.tangyuan.aop包下的任意类的任意方法
execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.*.*(..) )
//表示com.tangyuan.aop包及其子包下的任意类的任意方法
execution(*com.tangyuan.aop..*.*(..) )
//表示任意包中的任意类的任意方法
execution(**..*.*(..) )AOP通知描述了抽取的共性功能,根据共性功能抽取的位置不同,最终运行代码时要将其加入到合理的位置

public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置的增强....") ;
}
public void after Returning Advice() {
System.out.println("后置的增强....") ;
}
<!--环绕通知方法-->
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint)throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕前的增强....") ;
Object res=proceedingJoinPoint.proceed() ; //执行目标方法
System.out.println("环绕后的增强....") ;
return res;
}
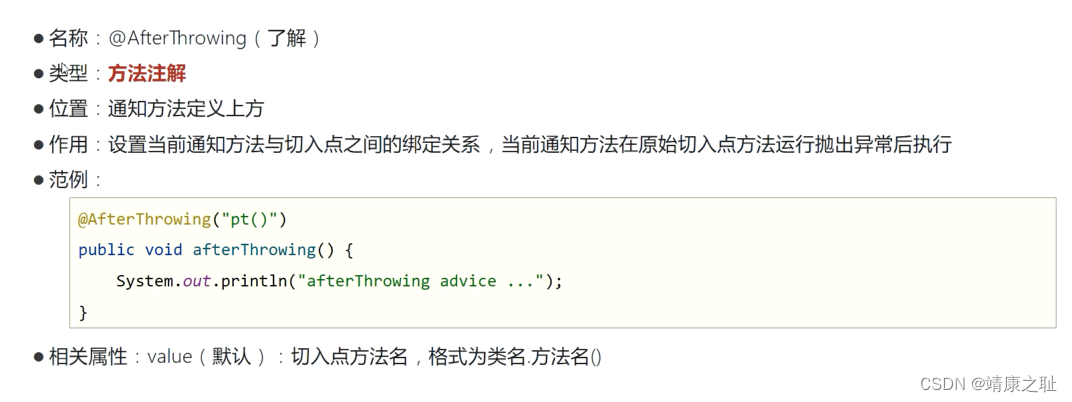
public void afterThrowingAdvice() {
System.out.println("异常抛出通知...报异常才执行") ;
}
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("最终的增强....") ;
}
<!--前置通知-->
<aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointout-ref="myPointcut2"/>
<!--后置通知-->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningAdvice" pointcut-ref-"myPointcut2”
<!--坏绕通知-->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="myPointcut2"/>
<!--异常抛出通知-->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut2"/>
<!--最终通知-->
<aop:after method="afterAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut2"/> 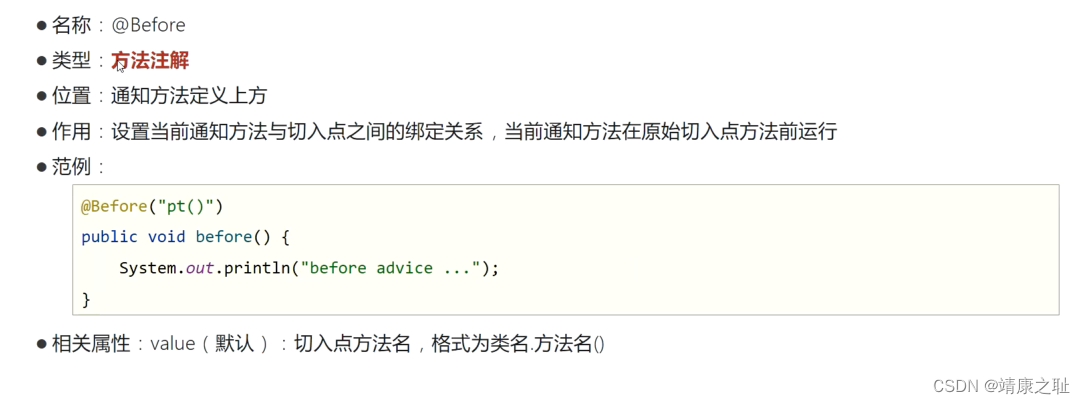




九:案例:测量业务层接口万次执行效率

1.dao接口
import com.tangyuan.domain.Account;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountDao {
@Insert("insert into tbl_account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money})")
void save(Account account);
@Delete("delete from tbl_account where id = #{id} ")
void delete(Integer id);
@Update("update tbl_account set name = #{name} , money = #{money} where id = #{id} ")
void update(Account account);
@Select("select * from tbl_account")
List<Account> findAll();
@Select("select * from tbl_account where id = #{id} ")
Account findById(Integer id);
}2.service接口及实现类
import com.tangyuan.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountService {
void save(Account account);
void delete(Integer id);
void update(Account account);
List<Account> findAll();
Account findById(Integer id);
}import com.tangyuan.dao.AccountDao;
import com.tangyuan.domain.Account;
import com.tangyuan.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.save(account);
}
public void update(Account account){
accountDao.update(account);
}
public void delete(Integer id) {
accountDao.delete(id);
}
public Account findById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.findById(id);
}
public List<Account> findAll() {
return accountDao.findAll();
}
}3.实体类
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Double money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}4.配置类
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String userName;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(userName);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
}import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.itheima.domain");
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
return ssfb;
}
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer(){
MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
msc.setBasePackage("com.itheima.dao");
return msc;
}
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration@ComponentScan("com.itheima")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class,MybatisConfig.class})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfig {}5.切面类
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class ProjectAdvice {
//匹配业务层的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.service.*Service.*(..))")
private void servicePt(){}
//设置环绕通知,在原始操作的运行前后记录执行时间
@Around("ProjectAdvice.servicePt()")
public void runSpeed(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//获取执行的签名对象
Signature signature = pjp.getSignature();
//通过签名获取执行类型(接口名)
String className = signature.getDeclaringTypeName();//com.tangyuan.service.AccountService
//通过签名获取执行操作名称(方法名)
String methodName = signature.getName();//findById
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pjp.proceed();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("万次执行:"+ className+"."+methodName+"---->" +(end-start) + "ms");
}
当前测试的接口效率仅仅是一个理论值,并不是一次完整的执行过程
通知方法在被调用时, Spring可以为其传递一些必要的参数
| 参数类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| JoinPoint | 连接点对象,任何通知都可使用,可以获得当前目标对象、目标方法参数等信息 |
| ProceedingJoinPoint | JoinPoint子类对象, 主要是在环绕通知中执行proceed() , 进而执行目标方法 |
| Throwable | 异常对象,使用在异常通知中,需要在配置文件中指出异常对象名称 |

JoinPoint对象
描述了连接点方法的运行状态,可以获取到原始方法的调用参数
public void 通知方法名称(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//获得目标方法的参数
System.out.println(joinPoint.getArgs() ) ;
//获得目标对象
System.out.println(joinPoint.getTarget() ) ;
//获得精确的切点表达式信息
System.out.println(joinPoint.getStaticPart() ) ;
}ProceedingJoinPoint对象是JoinPoint的子类
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{ System.out.println(joinPoint.getArgs() ) ; //获得目标方法的参数 System.out.println(joinPoint.getTarget() ) ; //获得目标对象 System.out.println(joinPoint.getStaticPart() ) ; //获得精确的切点表达 Objectresult=joinPoint.proceed() ; //执行目标方法 return result; //返回目标方法返回值}Throwable对象
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable th) {
//获得异常信息
System.out.println("异常对象是:"+th+"异常信息是:"+th.get Message() )
}<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="myPointcut" throwing="th"/>
十:案例:百度网盘密码数据兼容处理
1.dao接口及实现类
public interface ResourcesDao {
boolean readResources(String url, String password);
}@Repository
public class ResourcesDaoImpl implements ResourcesDao {
public boolean readResources(String url, String password) {
System.out.println(password.length());
//模拟校验
return password.equals("root");
}
}2.service接口及实现类
public interface ResourcesService {
public boolean openURL(String url ,String password);
}import com.tangyuan.dao.ResourcesDao;
import com.tangyaun.service.ResourcesService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ResourcesServiceImpl implements ResourcesService {
@Autowired
private ResourcesDao resourcesDao;
public boolean openURL(String url, String password) {
return resourcesDao.readResources(url,password);
}
}3.配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.tangyuan")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfig {
}4.切面类
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class DataAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(boolean com.tangyuan.service.*Service.*(*,*))")
private void servicePt(){}
@Around("DataAdvice.servicePt()")
public Object trimStr(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//获取参数
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
//遍历参数
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
//判断参数是不是字符串
if(args[i].getClass().equals(String.class)){
args[i] = args[i].toString().trim();
}
}
Object ret = pjp.proceed(args);
return ret;
}
}5.测试
import com.tangyuan.config.SpringConfig;
import com.tangyuan.service.ResourcesService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
ResourcesService resourcesService = ctx.getBean(ResourcesService.class);
boolean flag = resourcesService.openURL("http://pan.baidu.com/haha", "root ");
System.out.println(flag);
}
}AOP配置的两种语法形式
AOP的xml有两种配置方式, 如下:
-
使用<advisor>配置切面
-
使用<aspect>配置切面
Spring定义了一个Advice接口, 实现了该接口的类都可以作为通知类出现
public interface Advice{ }advisor需要的通知类需要实现Advice的子功能接口, 例如:MethodBeforeAdvice、AfterReturningAdvice等, 是通过实现的接口去确定具备哪些通知增强的, 见代码演示
<!--通知规范类-->
public class MyAdvice2 implements MethodBeforeAdvice, AfterReturningAdvice{
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("前置通知.."}
}
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable
System.out.println("后置通知...........") ;
}
}public class MyAdvice3 implements MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕前...........") ;
//执行目标方法
Object res=method Invocation.getMethod() .invoke(methodInvocation.getThis(),methodInvocation.getArguments() ) ;
System.out.println("环绕后...........") ;
return res;
}AOP配置的两种语法形式不同点
语法形式不同:
-
advisor是通过实现接口来确认通知的类型,如MyAdvice2
-
aspect是通过配置确认通知的类型, 更加灵活,如
-
<aop:aspect ref="myadvice"> <aop:after method="afterAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut2"/> /aop:aspect
可配置的切面数量不同:
-
一个advisor只能配置一个固定通知和一个切点表达式
-
一个aspect可以配置多个通知和多个切点表达式任意组合
使用场景不同:
-
允许随意搭配情况下可以使用aspect进行配置
-
如果通知类型单一、切面单一的情况下可以使用advisor进行配置
-
在通知类型已经固定, 不用人为指定通知类型时, 可以使用advisor进行配置, 例如后面要学习的Spring事务控制的配置
-
xml方式AOP原理剖析

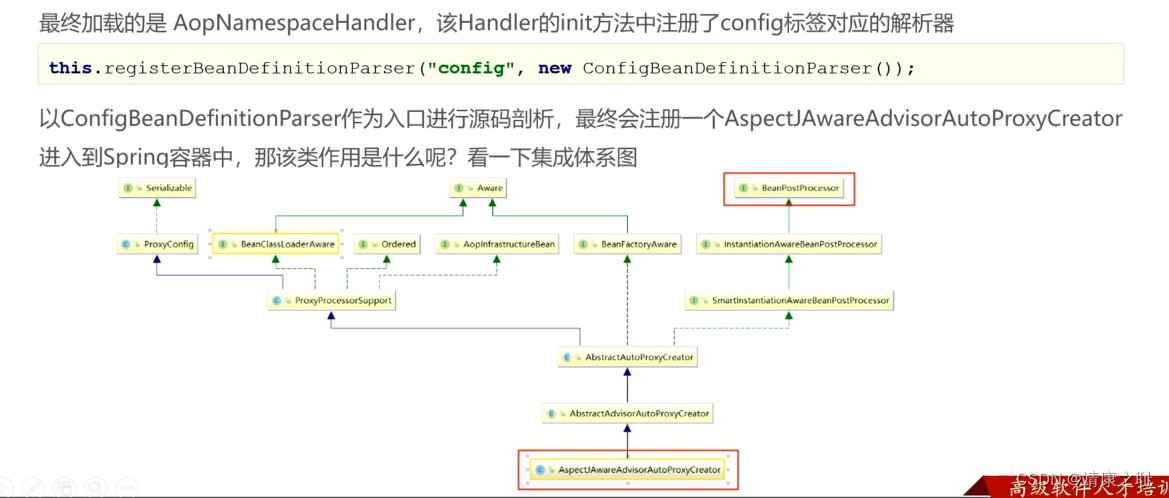




JDK的动态代理代码, 之前已经写过了, 下面看一下Cglib基于超类的动态代理
Target target=new Target() ; //目标对象
Advices advices三new Advices() ; //通知对象
Enhancer enhancer=new Enhancer() ; //增强器对象
enhancer.setSuperclass(Target.class) ; //增强器设置父类
//增强器设置回调
enhancer.set Callback( (MethodInterceptor) (o, method,objects,method Proxy)一>{
advices.before() ;
Object result=method.invoke(target, objects) ;
advices.afterReturning() ;
return result;
});
//创建代理对象
Target targetProxy=(Target) enhancer.create() ;
//测试
String result=targetProxy.show("haohao") ;-
注解方式AOP基本使用
Spring的AOP也提供了注解方式配置, 使用相应的注解替代之前的xml配置, xml配置AOP时, 我们主要配置了三 部分:目标类被Spring容器管理、通知类被Spring管理、通知与切点的织入(切面) , 如下
<!--配置目标-->
<bean id="target"class="com.tangyuan.aop.Target Impl"></bean>
<!--配置通知-->
<bean id="advices"class="com.tangyuan.aop.Advices"></bean>
<!--配置aop-->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:aspect ref="advices">
<aop:around method="around"pointcut="execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.*.*(..))"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>1.接口service类
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ }2.增强类
//增强类,内部提供增强方法
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice{
//<aop:beforemethod="beforeAdvice"pointcut="execution(*com.tangyuan.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
@Before("execution(*com.tangyuan.service.impl.*.*(..) ) ")
public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("当前目标对象是:"+joinPoint.getTarget() ) ;
System.out.println("表达式:"+joinPoint.getStaticPart() ) ;
System.out.println("前置的增强....") ;
}
}3.在xml文件中进行配置
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.tangyuan"/>
<!--使用注解配置AOP, 需要开启AOP自动代理-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>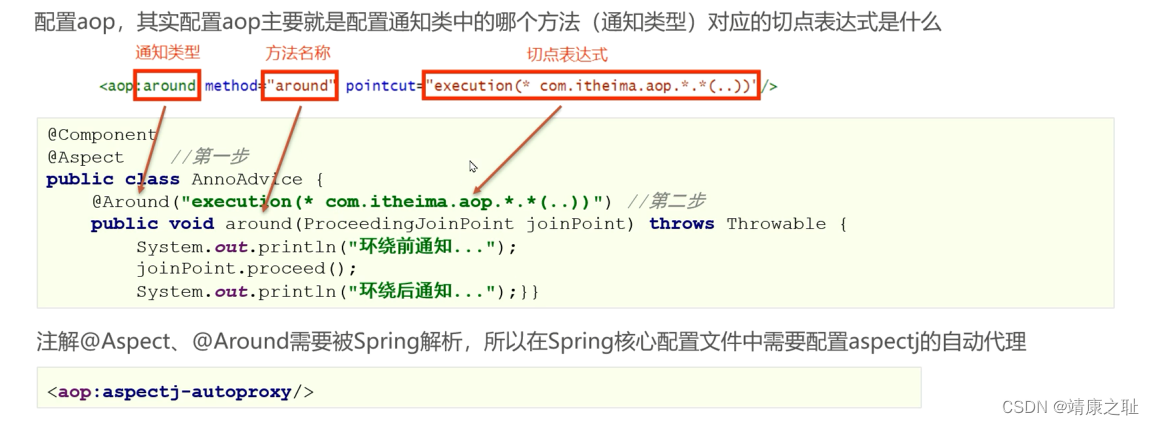
各种注解方式通知类型
//前置通知
@Before("execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.*.*(..) ) ")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {}
//后置通知
@AfterReturning("execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.*.*(..) ) ")
public void AfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint) {}
//环绕通知
@Around("execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.*.*(..) ) ")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing("execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.*.*(..) ) ")
public void AfterThrowing(Join Point join Point) {}
//最终通知
@After("execution(*com.tangyuan.aop.*.*(..) ) ")
public void After(JoinPoint joinPoint) {}
//切点表达式的抽取
@Pointcut("execution(*com.tangyuan.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void myPointcut() {}
使用:
@Around(“类名.myPointcut()”)@Confiquration
@ComponentScan("com.tangyuan")//<context:component-scan base-package="com.tangyuan"/>
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
public class Spring Config{ }
-
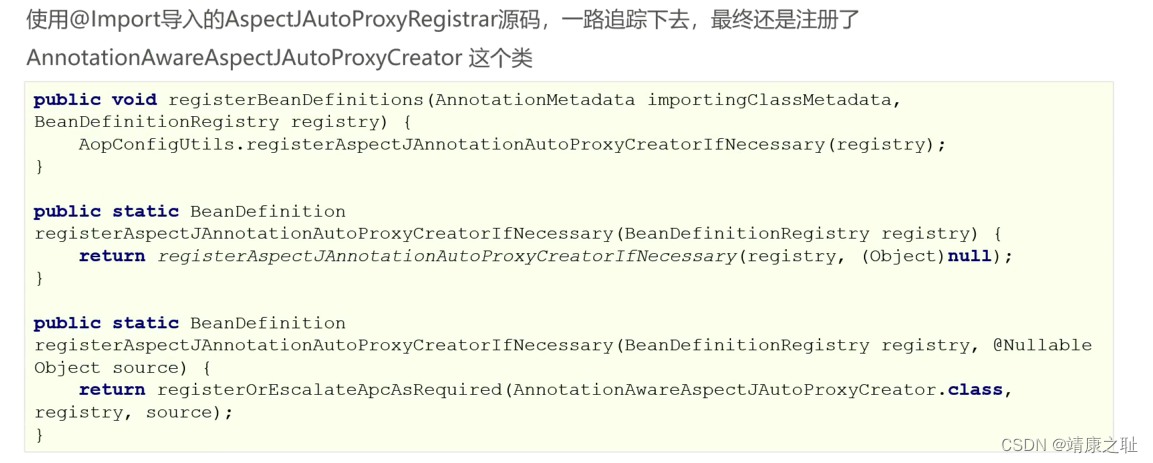
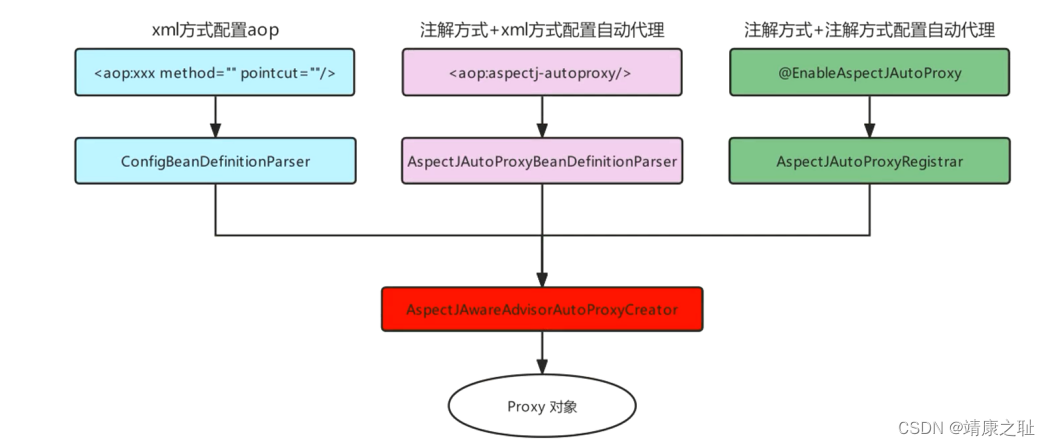
注解方式AOP原理剖析



十一:AOP总结




