prometheus的remotewrite解析
特性
目的是为了向远端的存储写入数据。
为了提高写入效率,Prometheus在将采集到的samples写入远程存储之前,会先缓存在内存队列中,然后打包发送给远端存储。而这个内存队列的配置参数,对于Prometheus写入远程存储的效率影响较大,
prometheus配置了remote write的目标地址后,它会从WAL读取数据,然后把采样数据写入各分片的内存队列,最后发起向远程目标地址的请求。

WAL是每两小时压缩一次,如果远程写入的目标地址挂了超过两个小时,就会导致这段时间没被发送的数据丢失。如果远程写入的目标地址无响应时间较短(两小时以内),prometheus是会重试的,这种情况不会造成数据丢失。
当一个分片的队列被塞满时,promtheus将阻塞继续从WAL读取数据到任意分片。
在操作过程中,prometheus根据以下条件来持续计算要是用的最佳的分片数:
- 摄入样本的速率(incoming sample rate)
- 还未发送的样本数量(number of outstanding samples not sent)
- 发送每个样本的时间(time taken to send each sample)
在官方给的高可用方案中作用如下:
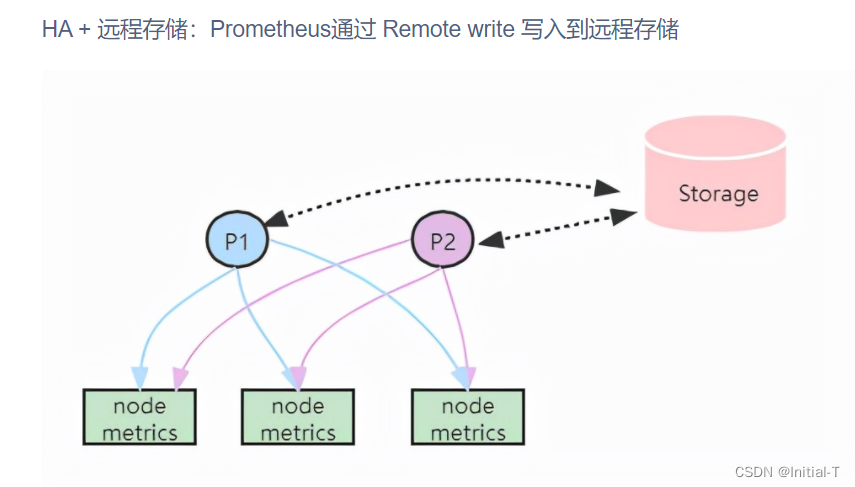
使用
1 配置
prometheus没有提供远程存储,但提供了远程存储的接口,远程存储只要实现这一接口,即可存储和读取prometheus的数据;
prom端的配置:
remote_write: - url: "https://1.2.3.4/api/monitor/v1/prom/write"2 remote-write数据协议
prometheus的samples,经过protobuf的序列化,然后再经过snappy压缩,最后通过HTTP发送给remoteStorage;
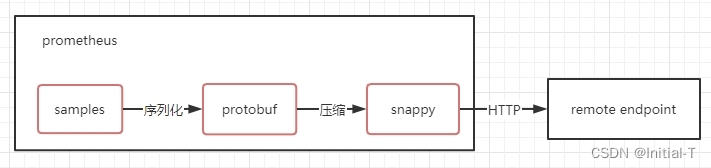
对应的源代码:

remoteStorage 实现remote-write协议接口
remoteStorage要实现remoteConfigs中定义的HTTP接口,这里主要参考influxdb的实现。
HTTP接口:
// 实现如下的API
Route{
"prometheus-write", // Prometheus remote write
"POST", "/api/v1/prom/write", false, true, h.servePromWrite,
},实现:与prometheus做的事情相反,先进行sappy的解压缩,然后再protobuf反序列化,得到真实的数据。

样例
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"github.com/prometheus/common/model"
"github.com/prometheus/prometheus/storage/remote"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/receive", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
req, err := remote.DecodeWriteRequest(r.Body)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
for _, ts := range req.Timeseries {
m := make(model.Metric, len(ts.Labels))
for _, l := range ts.Labels {
m[model.LabelName(l.Name)] = model.LabelValue(l.Value)
}
fmt.Println(m)
for _, s := range ts.Samples {
fmt.Printf("\tSample: %f %d\n", s.Value, s.Timestamp)
}
for _, e := range ts.Exemplars {
m := make(model.Metric, len(e.Labels))
for _, l := range e.Labels {
m[model.LabelName(l.Name)] = model.LabelValue(l.Value)
}
fmt.Printf("\tExemplar: %+v %f %d\n", m, e.Value, e.Timestamp)
}
}
})
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":1234", nil))
}官方文档:
Remote write tuning | Prometheus
Integrations | Prometheus
参考文档:
prometheus的remote write功能_felix_yujing的博客-CSDN博客_remote write
kubernetes - prometheus remote-write解析(一) -- 使用 - 个人文章 - SegmentFault 思否
Prometheus的remote_write的样例_双天至尊的博客-CSDN博客_prometheus remote_write
