05-SA8155 QNX SPI框架及代码分析
1. 描述
本文主要描述QNX SPI Drvier的相关内容,并以SA8155P处理器为例讲解SPI框架。
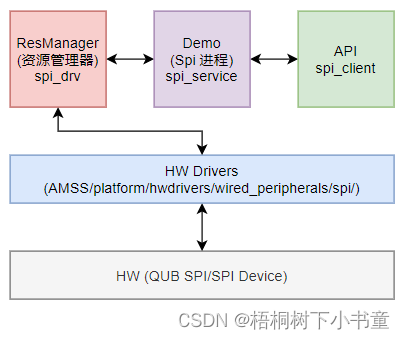
2. 目录结构
2.1 HW Drivers:
路径:apps/qnx_ap/AMSS/platform/hwdrivers/wired_peripherals/spi
├── aarch64
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── so-le
├── arm
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── so-le-v7
│ └── Makefile
├── common.mk
├── device
│ ├── inc
│ │ ├── SpiDalProps.h
│ │ ├── SpiDeviceError.h
│ │ ├── SpiDevice.h
│ │ ├── SpiDeviceInternal.h
│ │ ├── SpiDeviceOsSvc.h
│ │ ├── SpiDevicePlatSvc.h
│ │ ├── SpiDeviceTransfer.h
│ │ └── SpiDeviceTypes.h
│ ├── SpiDalProps.c
│ ├── SpiDevice.c
│ ├── SpiDeviceOsSvc.c
│ ├── SpiDevicePlatSvc.c
│ └── SpiDeviceTransfer.c
├── driver
│ ├── inc
│ │ └── SpiDriverTypes.h
│ └── SpiDriver.c
├── logs
│ ├── inc
│ │ └── SpiLog.h
│ └── SpiLog.c
├── Makefile
└── public
└── amss
└── core
2.2. SPI Resource(SPI资源管理器)
apps/qnx_ap/AMSS/platform/resources/spi_drv
├── aarch64
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── so-le
├── arm
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── so-le-v7
│ └── Makefile
├── common.mk
├── Makefile
├── protected
│ ├── spi_devctls.h
│ └── spi_lib.h
└── spi_drv.c
2.3. SPI Service(SPI服务进程)
/apps/qnx_ap/AMSS/platform/services/daemons/spi_service
├── aarch64
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── o-le
├── arm
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── o-le-v7
│ └── Makefile
├── common.mk
├── Makefile
└── src
└── spi_service.c
2.4. API
apps/qnx_ap/AMSS/platform/qal/clients/spi_client
app/qnx_ap/qnx_bins/prebuilt_QNX700/target/qnx7/usr/include/hw/spi-master.h
├── aarch64
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── so-le
├── arm
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── so-le-v7
│ └── Makefile
├── common.mk
├── Makefile
├── pinfo.mk
├── public
│ └── amss
│ └── spi_client.h
└── src
└── spi_client.c
3. API
3.1 API接口
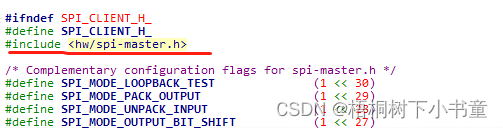
app/qnx_ap/qnx_bins/prebuilt_QNX700/target/qnx7/usr/include/hw/spi-master.h
* SPI API calls
*/
int spi_open(const char *path);
int spi_close(int fd);
int spi_setcfg(int fd, uint32_t device, spi_cfg_t *cfg);
int spi_getdevinfo(int fd, uint32_t device, spi_devinfo_t *devinfo);
int spi_getdrvinfo(int fd, spi_drvinfo_t *drvinfo);
int spi_read(int fd, uint32_t device, void *buf, int len);
int spi_write(int fd, uint32_t device, void *buf, int len);
int spi_xchange(int fd, uint32_t device, void *wbuf, void *rbuf, int len);
int spi_cmdread(int fd, uint32_t device, void *cbuf, int16_t clen, void *rbuf, int rlen);
int spi_dma_xchange(int fd, uint32_t device, void *wbuf, void *rbuf, int len);
int spi_dma_xfer(int fd, uint32_t device, void *paddr, int len);4. SPI资源管理器设计
在QNX下开发驱动程序,最主要的工作除了了解底层硬件具体工作流程外,就是建立一个能与操
作系统兼容且支持POSIX的Resource manger框架了。在任何一段程序的执行过程中一段都是从
main函数开始的,然而在操作系统中的main函数还传递了两个参数:int argc, char argv,这两个
参数是用来传递从shell命令行或者buildfile中传来对Resource manger具体参数的,使用options
(int argc, char argv);函数实现,所以这个函数在main函数中最开始的位置,可以开发的driver具有
不同可选的特性,提供使用的便利性。

4.1 Spi Service Demo进程
spi_service.c 基本没做什么,就是一个壳子,核心工作如下
- 调用spi_drv.c资源管理初始化spi驱动spi_drv_init()
- 启动服务spi_service(后台进程)
4.2 spi资源管理器核心spi_drv.c
入口函数:spi_drv_init
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: spi_drv_init
DESCRIPTION : This function init the SPI-RM
===========================================================================*/
int spi_drv_init(void)
{
int i = 0, idx = 0, rc = 0;
uint64_t chip_id = 0;
const void *fdt_paddr = 0;
pthread_t threadID;
DALSYSPropertyVar PropVar;
DALSYS_PROPERTY_HANDLE_DECLARE(hDALProps);
DALSYS_InitMod(NULL);
DALSYS_RegisterMod(&gDALModDriverInfoList);
fdt_paddr = fdt_get_root();
if (!fdt_paddr) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Failed to load device tree");
return -1;
}
rc = fdt_foreach_subnode_byname((void*) fdt_paddr , "/chip_info",
&get_chip_info, &chip_id);
if (rc) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Failed to find dt chip_info");
return -1;
}
/* Create RM's for each active SPI bus */
int ret = EOK;
int policy;
struct sched_param param;
pthread_attr_t attr;
if (waitfor_attach(QCORE_SERVICE, 5000))
{
SPI_SLOGE("Timed out waiting for %s to be ready", QCORE_SERVICE);
return -1;
}
//线程配置
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_getschedparam(pthread_self(), &policy, ¶m);
param.sched_priority = 100;
pthread_attr_setschedparam(&attr, ¶m);
//资源管理器创建
for (i = 0; i < MAX_NUM_SPI_DEVS; i++)
{
if(DALSYS_GetDALPropertyHandle(DeviceID[i], hDALProps)==DAL_SUCCESS)
{
if (DAL_SUCCESS != DALSYS_GetPropertyValue(hDALProps, "SPI_ENABLED", 0, &PropVar)
|| PropVar.Val.dwVal == 0)
{
continue;
}
devs[idx] = calloc(1, sizeof(spi_dev_t));
if (devs[idx] == NULL)
{
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return -1;
}
snprintf(devs[idx]->devname, MAX_DEVNAME_LENGTH, "/dev/spi%d", i+1);
devs[idx]->spi_idx = i;
devs[idx]->initialized = 0;
#ifdef SPI_LPM_TIMER
devs[idx]->timer_created = 0;
#endif
if (DAL_SUCCESS != DALSYS_GetPropertyValue(hDALProps, "CLOCK_SE_NAME", 0, &PropVar)
|| PropVar.Val.pszVal == 0)
{
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return -1;
}
if (!strncmp(PropVar.Val.pszVal, "scc", 3)) {
devs[idx]->is_ssc = true;
}
//具体实现核心代码
ret = pthread_create(&threadID, &attr, (void *)&spi_device_main_thread,
(void *)devs[idx]);
if (ret == EOK)
{
pthread_setname_np(threadID, devs[idx]->devname);
SPI_SLOGD("SPI_RM: Created RM thread for device-%d:name-%s", DeviceID[i], devs[idx]->devname);
idx++;
}
else
{
SPI_SLOGE("Couldn't create RM thread for device-%d:name-%s:ret-%d",
DeviceID[i], devs[idx]->devname, ret);
}
}
}
SPI_SLOGI("SPI_RM created %d threads.", idx);
if (ID_6155 == chip_id) {
if ((rc = spi_register_ssr())) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Failed to register for SSR ret=%x\n", ret);
return -1;
}
SPI_SLOGI("SPI_RM registered for SSR.");
}
return 0;
}资源管理器创建线程实现:
标准步骤:
- 建立一个上下文切换句柄dpp = dispatch_create();这个东东主要用在mainloop中产生一个block特性,可以让我们等待接受消息;
- iofunc初始化。这一步是将自己实现的函数与POSIX层函数进行接口,解析从read、write、devctl等函数传来的消息进行解析,以实现底层与应用层函数之间的交互,通过io_funcs.read = io_read,io_funcs.write = io_write,进行函数重载;
- 注册设备名,使设备在命名空间中产生相应的名称,这一点是整个过程的关键了,形如 pathID = resmgr_attach (dpp, &rattr, "/dev/Null",_FTYPE_ANY, 0, &connect_funcs,&io_funcs, &ioattr),这样不仅注册了一个设备名,还让系统知道了我们实习的IO函数对应关系;
- 为之前创建的上下文句柄分配空间,例如ctp = dispatch_context_alloc (dpp);为了第六步使用;
- 通过不断循环等待dispatch_block()来调用MsgReceive()使Resource manger处于receive block状态,以接收上层发送来的消息,通过dispatch_handler (ctp)去调用我们自己定义的IO函数
SA8155平台是如何做的呢?
看下代码,基本类似。
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: spi_device_main_thread
DESCRIPTION : main thread to create and handle device.
===========================================================================*/
int spi_device_main_thread(spi_dev_t *dev)
{
resmgr_connect_funcs_t connect_funcs;
resmgr_io_funcs_t io_funcs;
resmgr_attr_t rattr;
iofunc_funcs_t ocb_funcs = { _IOFUNC_NFUNCS, _ocb_calloc, _ocb_free };
iofunc_mount_t mount = { 0, 0, 0, 0, &ocb_funcs };
int pathID;
/*
* Without this InterruptLock() in dalinterrupt will cause SIGSEGV
* when calling from multiple threads
*/
ThreadCtl(_NTO_TCTL_IO, 0);
#ifdef SPI_LPM_TIMER
pthread_cond_init(&dev->clk_mutex, NULL);
#endif /* SPI_LPM_TIMER */
//创建一个通讯Channel,返回chid
dev->chid = ChannelCreate(_NTO_CHF_DISCONNECT | _NTO_CHF_UNBLOCK);
if (dev->chid == -1) {
SPI_SLOGE("ChannelCreate() failed, err=%d\n", errno);
goto exit;
}
//1. 建立一个上下文切换句柄dpp
/*
* allocate and initialize a dispatch structure for use by our
* main loop
*/
dev->dpp = dispatch_create_channel( dev->chid, 0 );
if (dev->dpp == NULL) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: couldn't dispatch_create. ");
goto exit;
}
/* register internal communication channel */
dev->int_coid = ConnectAttach(ND_LOCAL_NODE, 0 /* pid */, dev->chid, _NTO_SIDE_CHANNEL, 0);
if (-1 == dev->int_coid) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM internal ConnectAttach failed (%s)", strerror(errno));
goto exit;
}
/*
* set up the resource manager attributes structure, we'll
* use this as a way of passing information to resmgr_attach().
* For now, we just use defaults.
*/
memset(&rattr, 0, sizeof(rattr)); /* using the defaults for rattr */
rattr.nparts_max = 10;
rattr.msg_max_size = (64 *4* 1024); //Max HW allowed transaction 64k
//2. 调用iofunc_func_init初始化iofunc,connect_funcs
/*
* intialize the connect functions and I/O functions tables to
* their defaults by calling iofunc_func_init().
*
* connect_funcs, and io_funcs variables are already declared.
*
*/
iofunc_func_init(_RESMGR_CONNECT_NFUNCS, &connect_funcs, _RESMGR_IO_NFUNCS,
&io_funcs);
/* over-ride the connect_funcs handler for open with our io_open,
* and over-ride the io_funcs handlers for read and write with our
* io_read and io_write handlers
*/
connect_funcs.open = io_open;
io_funcs.devctl = io_devctl;
io_funcs.write = io_write;
io_funcs.close_ocb = io_close;
/* initialize our device description structure
*/
/* io_attr 其实可以想像成一个文件相关的参数,比如读写权限等等 */
iofunc_attr_init(&dev->hdr, S_IFCHR | 0666, NULL, NULL);
dev->hdr.mount = &mount; // so we can alloc an OCB per open
//3. resmgr_attach注册设备,注册一个资源设备名为dev->devname
/*
* call resmgr_attach to register our prefix with the
* process manager, and also to let it know about our connect
* and I/O functions.
*
* On error, returns -1 and errno is set.
*/
pathID = resmgr_attach(dev->dpp, &rattr, dev->devname, _FTYPE_ANY, 0,
&connect_funcs, &io_funcs, (IOFUNC_ATTR_T*)dev);
if (pathID == -1) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Couldn't attach pathname: %s", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
#ifdef SPI_LPM_TIMER
if ((dev->pulse_code = pulse_attach(dev->dpp, MSG_FLAG_ALLOC_PULSE, 0,
&spi_stop_timer, (void*)dev)) == -1) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: pulse_attach failed - %s", strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
#endif
//4. 为之前创建的上下文句柄分配空间
dev->ctp = dispatch_context_alloc(dev->dpp);
if (dev->ctp == NULL) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Could't alloc resmgr context - %s", strerror(errno));
dispatch_destroy(dev->dpp);
exit(1);
}
/* Notify bmetrics this device is ready */
int fd = open("/dev/bmetrics", O_WRONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Couldn't open /dev/bmetrics");
} else {
char buf[30];
snprintf(buf, 30, "bootmarker %s ready", dev->devname);
if (-1 == write(fd, buf, 30)) {
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Couldn't write /dev/bmetrics");
}
close(fd);
}
/* register LPM pulses */
if (EOK != spi_register_lpm_pulse(dev))
{
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Failed to register pulses for %s(%s)", dev->devname, strerror(errno));
}
/* register internal pulses */
if (EOK != spi_register_timeout_pulse(dev))
{
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Failed to register timeout pulse for %s(%s)", dev->devname, strerror(errno));
}
/* Initialize Spi device */
if (EOK != spi_hwd_init(dev))
{
SPI_SLOGE("SPI_RM: Failed to init spi hardware %s(%s)", dev->devname, strerror(errno));
dispatch_destroy(dev->dpp);
exit(1);
}
/**5. 通过不断循环等待dispatch_block()与dispatch_handler (ctp)执行IO
函数处理。
dispath_block() 相当于阻塞并等待,而 dispatch_handle() 则根据不同的挂接,调用不同的回调函
数进行处理。其实在_spi_register_interface里进行了dispatch_context_alloc的操作。通过不断循环
等待dispatch_block()来调用MsgReceive()使Resource manger处于receive block状态,以接收上层
发送来的消息,通过dispatch_handler (ctp)去调用我们自己定义的IO函数。
*/
/*Message handling*/
while (1)
{
if (dispatch_block(dev->ctp))
{
dispatch_handler(dev->ctp);
}
else if (errno != EFAULT)
{
break;
}
else
{
/* Do nothing */
}
}
exit:
return -1;
}4.3 API与资源管理器之间的关联
devctl:
extern int devctl(int fd, int dcmd, void *dev_data_ptr, size_t nbytes, int *dev_info_ptr);
extern int devctlv(int fd, int dcmd, int sparts, int rparts, const struct iovec *sv, const struct iovec *rv, int *dev_info_ptr);


open:

5. APP例子
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mmdefs.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "spi_driver.h"
#ifdef __QNX__
#include "spi_client.h"
#include "SpiDriver.h"
#endif
/* SPI driver handle */
static int fd = 0;
static const char *device_name = "/dev/spi1";
/* Main Interface */
int SPI_Init()
{
int rc = -1;
/* *******************************************************************************
* During application mode both SPI0 and SPI1 operate as slaves and, by default,
* configured in mode 1 (CPOL=0, CPHA=1) and for operation at a speed of 10MHz.
* *******************************************************************************/
fd = spi_open(device_name);
if(fd == -1)
{
LOG("spi_open failed, fd=%d\n", fd);
fd = 0;
}
else
{
LOG("spi_open successful, fd=%d\n", fd);
spi_cfg_t cfg;
// need bits_per_word as LSB in spi cfg
cfg.mode = SPI_MODE_BODER_MSB | SPI_MODE_CSHOLD_HIGH | SPI_MODE_CKPHASE_HALF | ((0 << SPI_MODE_DEASSERT_WAIT_SHFT) & SPI_MODE_DEASSERT_WAIT_MASK) | 8;
cfg.clock_rate = 2000000;
LOG("spi_setcfg mode %x, rate %x\n", cfg.mode, cfg.clock_rate);
rc = spi_setcfg(fd, SPI_DEVICE_1, &cfg);
if(rc)
{
LOG("spi_setcfg failed, rc=%d\n", rc);
close(fd);
fd = 0;
}
else
{
LOG("spi_setcfg successful, rc=%d\n", rc);
}
}
return rc;
}
void SPI_Deinit()
{
if(fd)
{
spi_close(fd);
fd = 0;
}
}
/* SPI write functions */
int SPI_Write(uint8_t* buf, uint32_t len)
{
int rc = 0;
if(fd)
{
rc = spi_write(fd, SPI_DEVICE_1, buf, len);
//rc = spi_cmdread(fd, SPI_DEVICE_1, buf, len, NULL, 0);
if(rc != len)
{
LOG("spi_write failed, rc=%d\n", rc);
}
}
else
{
rc = -1;
}
return rc;
}
/* SPI read functions */
int SPI_Read(uint8_t* buf, uint32_t len)
{
int rc = 0;
if(fd)
{
rc = spi_cmdread(fd, SPI_DEVICE_1, NULL, 0, buf, len);
if(rc != len)
{
LOG("spi_read failed, rc=%d\n", rc);
}
}
else
{
rc = -1;
}
return rc;
}
/* SPI write & read function */
int SPI_Write_Read(uint8_t* tx_buf, uint8_t* rx_buf, uint32_t len)
{
int rc = 0;
if( fd )
{
rc = spi_cmdread(fd, SPI_DEVICE_1, tx_buf, len, rx_buf, len);
if( rc != len )
{
LOG("spi_cmdread failed, rc=%d\n", rc);
}
}
else
{
rc = -1;
}
return rc;
}
