Hadoop 3.x(MapReduce)----【MapReduce 框架原理 五】
Hadoop 3.x(MapReduce)----【MapReduce 框架原理 五】
- Join应用
- 1. Reduce Join
- 2. Reduce Join案例实操
- 1. 需求
- 2. 需求分析
- 3. 代码实现
- 4. 测试输出
- 5. 总结
- 3. Map Join
- 1. 使用场景
- 2. 优点
- 3. 具体办法:采用DistributedCache
- 4. Map Join案例实操
- 1. 需求
- 2. 需求分析
- 3. 代码实现
Join应用
1. Reduce Join
Map 端的主要工作:为来自不同表或文件的 key / value 对,打标签以区别不同来源的记录。然后用连接字段作为 key,其余部分和新加的标志作为 value,最后进行输出。
Reduce端的主要工作:在 Reduce 端以连接字段作为 key 的分组已经完成,我们只需要在每一个分组当中将哪些来源与不同文件的记录(在 Map 阶段已经打标志)分开,最后进行合并就 OK 了。
2. Reduce Join案例实操
1. 需求
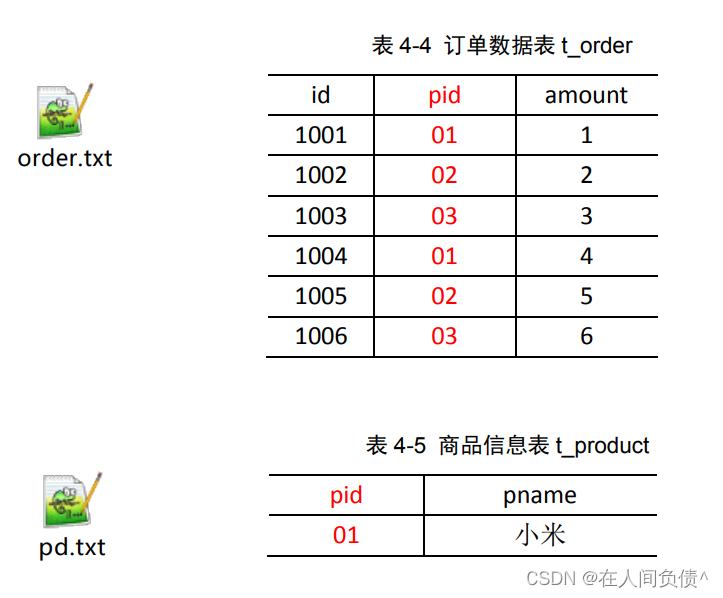
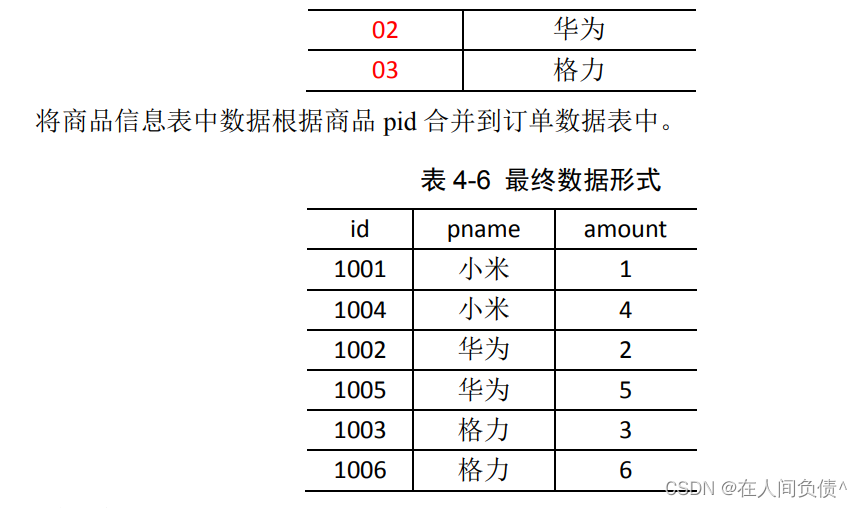
2. 需求分析
通过将关联条件作为 Map 输出的 key,将两表满足 Join 条件的数据并携带数据所来源的文件信息,发往同一个 ReduceTask,在 Reduce 中进行数据的串联。
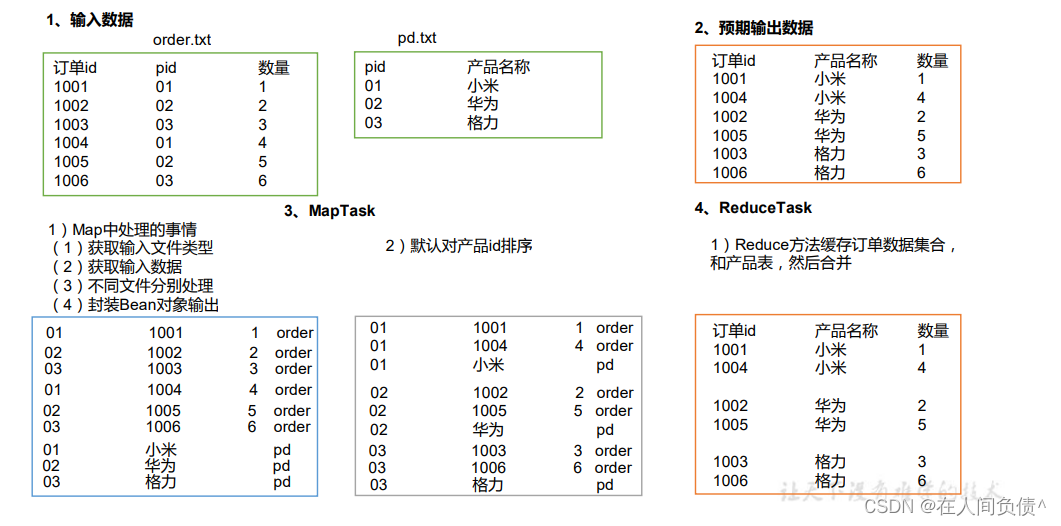
3. 代码实现
- 创建商品和订单合并后的 TableBean 类
package com.fickler.mapreduce.reducejoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author dell
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TableBean implements Writable {
private String id;
private String pid;
private int amount;
private String pname;
private String flag;
public TableBean() {
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPid() {
return pid;
}
public void setPid(String pid) {
this.pid = pid;
}
public int getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(int amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getPname() {
return pname;
}
public void setPname(String pname) {
this.pname = pname;
}
public String getFlag() {
return flag;
}
public void setFlag(String flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + "\t" + pname + "\t" + amount;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeUTF(id);
dataOutput.writeUTF(pid);
dataOutput.writeInt(amount);
dataOutput.writeUTF(pname);
dataOutput.writeUTF(flag);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
this.id = dataInput.readUTF();
this.pid = dataInput.readUTF();
this.amount = dataInput.readInt();
this.pname = dataInput.readUTF();
this.flag = dataInput.readUTF();
}
}
- 编写 TableMapper 类
package com.fickler.mapreduce.reducejoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author dell
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TableMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, TableBean> {
private String filename;
private Text outK = new Text();
private TableBean outV = new TableBean();
@Override
protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, TableBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
InputSplit inputSplit = context.getInputSplit();
FileSplit fileSplit = (FileSplit) inputSplit;
filename = fileSplit.getPath().getName();
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, TableBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
if (filename.contains("order")){
String[] split = line.split("\t");
outK.set(split[1]);
outV.setId(split[0]);
outV.setPid(split[1]);
outV.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(split[2]));
outV.setPname("");
outV.setFlag("order");
} else {
String[] split = line.split("\t");
outK.set(split[0]);
outV.setId("");
outV.setPid(split[0]);
outV.setAmount(0);
outV.setPname(split[1]);
outV.setFlag("pd");
}
context.write(outK, outV);
}
}
- 编写 TableReducer 类
package com.fickler.mapreduce.reducejoin;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @author dell
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TableReduce extends Reducer<Text, TableBean, TableBean, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<TableBean> values, Reducer<Text, TableBean, TableBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
ArrayList<TableBean> orderBeans = new ArrayList<>();
TableBean pdBean = new TableBean();
for (TableBean value : values){
if ("order".equals(value.getFlag())){
TableBean tmpOrderBean = new TableBean();
try {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(tmpOrderBean, value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
orderBeans.add(tmpOrderBean);
} else {
try {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pdBean, value);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
for (TableBean orderBean : orderBeans){
orderBean.setPname(pdBean.getPname());
context.write(orderBean, NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
- 编写 TableDriver 类
package com.fickler.mapreduce.reducejoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author dell
* @version 1.0
*/
public class TableDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setJarByClass(TableDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(TableMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(TableReduce.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(TableBean.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(TableBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\output"));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
}
}
4. 测试输出
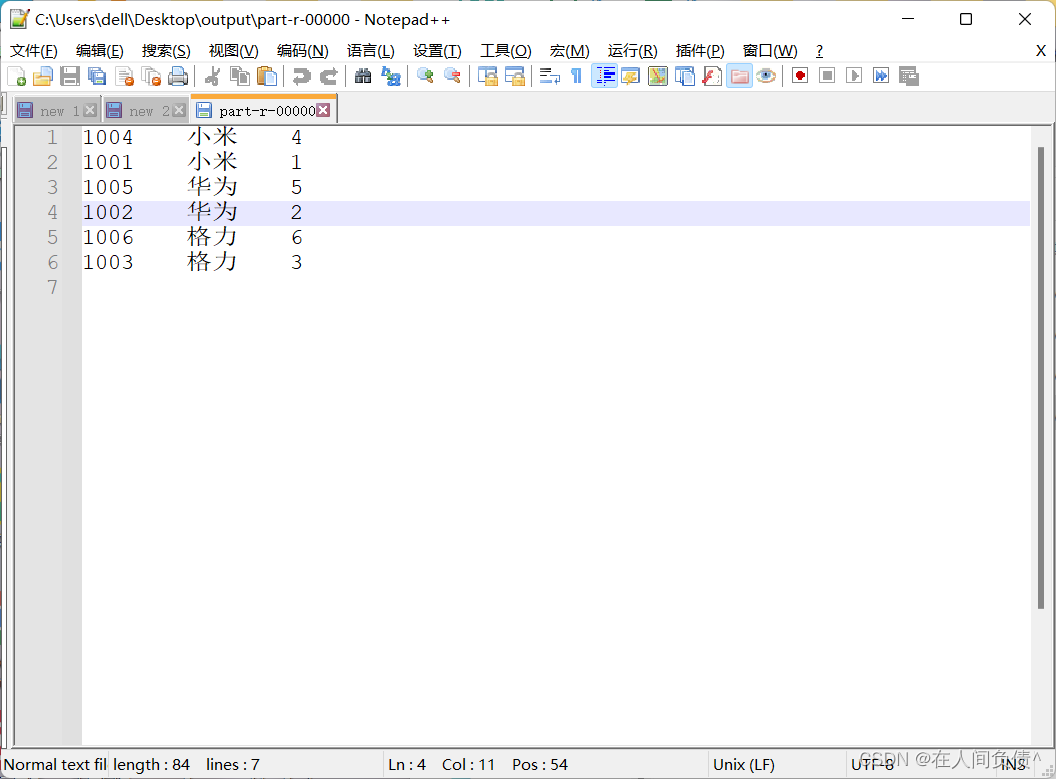
5. 总结
缺点:这种方式中,合并的操作是在 Reduce 阶段完成,Reduce 端的处理压力太大,Map 节点的运算负载则很低,资源利用率不高,且在 Reduce 阶段极易产生数据倾斜。
解决方案:Map 端实现数据合并。
3. Map Join
1. 使用场景
Map Join 适用于一张表十分小、一张表很大的场景。
2. 优点
思考:在 Reduce 端处理过多的表,非常容易产生数据倾斜。怎么办?
在 Map 端缓存多张表,提前处理业务逻辑,这样增加 Map 端业务,减少 Reduce 端数据的压力,尽可能的减少数据倾斜。
3. 具体办法:采用DistributedCache
- 在 Mapper 的 setup 阶段,将文件读取到缓存集合中。
- 在 Driver 驱动类中加载缓存。
//缓存普通文件到 Task 运行节点。
job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///e:/cache/pd.txt"));
//如果是集群运行,需要设置 HDFS 路径
job.addCacheFile(new URI("hdfs://hadoop102:8020/cache/pd.txt"));
4. Map Join案例实操
1. 需求
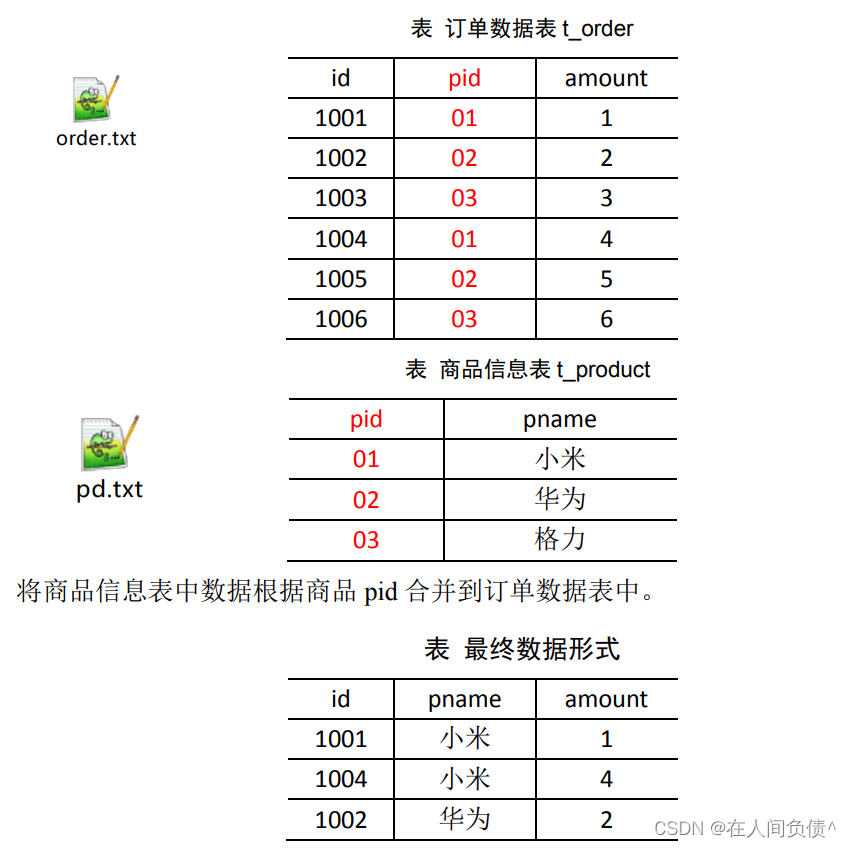

2. 需求分析
MapJoin 适用于关联表中有小表的情形。

3. 代码实现
- 先在 MapJoinDriver 驱动类中添加缓存文件
package com.fickler.mapreduce.mapjoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
/**
* @author dell
* @version 1.0
*/
public class MapJoinDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, URISyntaxException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
job.setJarByClass(MapJoinDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(MapJoinMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///C:/Users/dell/Desktop/tablecache/pd.txt"));
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\input"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\output"));
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
}
}
- 在 MapJoinMapper 类中的 setup 方法中读取缓存文件
package com.fickler.mapreduce.mapjoin;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author dell
* @version 1.0
*/
public class MapJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
private Map<String, String> pdMap = new HashMap<>();
private Text text = new Text();
@Override
protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取缓存文件,并把内容封装到集合 pd.txt 中
URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();
Path path = new Path(cacheFiles[0]);
//获取文件系统对象,并开流
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration());
FSDataInputStream fsDataInputStream = fileSystem.open(path);
//通过包装流转换为reader,方便按行读取
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fsDataInputStream, "UTF-8"));
//逐行读取,按行处理
String line;
while (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line = reader.readLine())){
//切割一行
//01 小米
String[] split = line.split("\t");
pdMap.put(split[0], split[1]);
}
//关流
IOUtils.closeStream(reader);
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//读取大表数据
//1001 01 1
String[] split = value.toString().split("\t");
//通过大表每行的pid,去pdMap里面取出pname
String pname = pdMap.get(split[1]);
//将大表每行数据的pid替换为pname
text.set(split[0] + "\t" + pname + "\t" + split[2]);
//写出
context.write(text, NullWritable.get());
}
}
