再学C语言12:字符串(3)——转换说明
一、转换说明的意义
意义:把存储在计算机中的二进制格式的数值转换成一系列字符(一个字符串)以便于显示;实质上是翻译说明,并不会替代原值
应该使转换说明与要打印的值的类型相匹配
参数传递机制
float n1;
double n2;
long n3, n4;
...
printf("%ld %ld %ld %ld \n", n1, n2, n3, n4);1)该调用告诉计算机把变量n1、n2、n3、n4的值传递给计算机,计算机将其放置在堆栈的一块内存区域中
2)计算机在往堆栈中放置数据时,根据的是变量的类型而非转换说明符:n1在堆栈中占8字节(float被转换为double),n2在堆栈中占8字节,n3和n4在堆栈中占4字节
3)控制转移到printf()函数,从堆栈把值读出来时,根据的是转换说明福而非变量的类型:%ld说明符指出printf()应该读取4个字节,因此虽然n3和n4的说明符都正确,但是因为n1和n2的说明符错误,最终读取到的也是错误的字节
二、printf函数的返回值
printf()函数有一个返回值,即所打印的字符的数目;如果有错误,printf()会返回一个负数
因为printf()函数的功能是打印输出,因此其返回值只是函数的附带功能,很少用到,除非想要检查输出是否有错误
示例代码:
/* test return valve of printf function */
#include <stdio.h>
#define NAME "Forster"
int main(void)
{
int rv;
rv = printf("%s\n", NAME);
printf("The name has %d characters. \n", rv - 1);
return 0;
}运行结果:

三、用printf函数打印较长的字符串
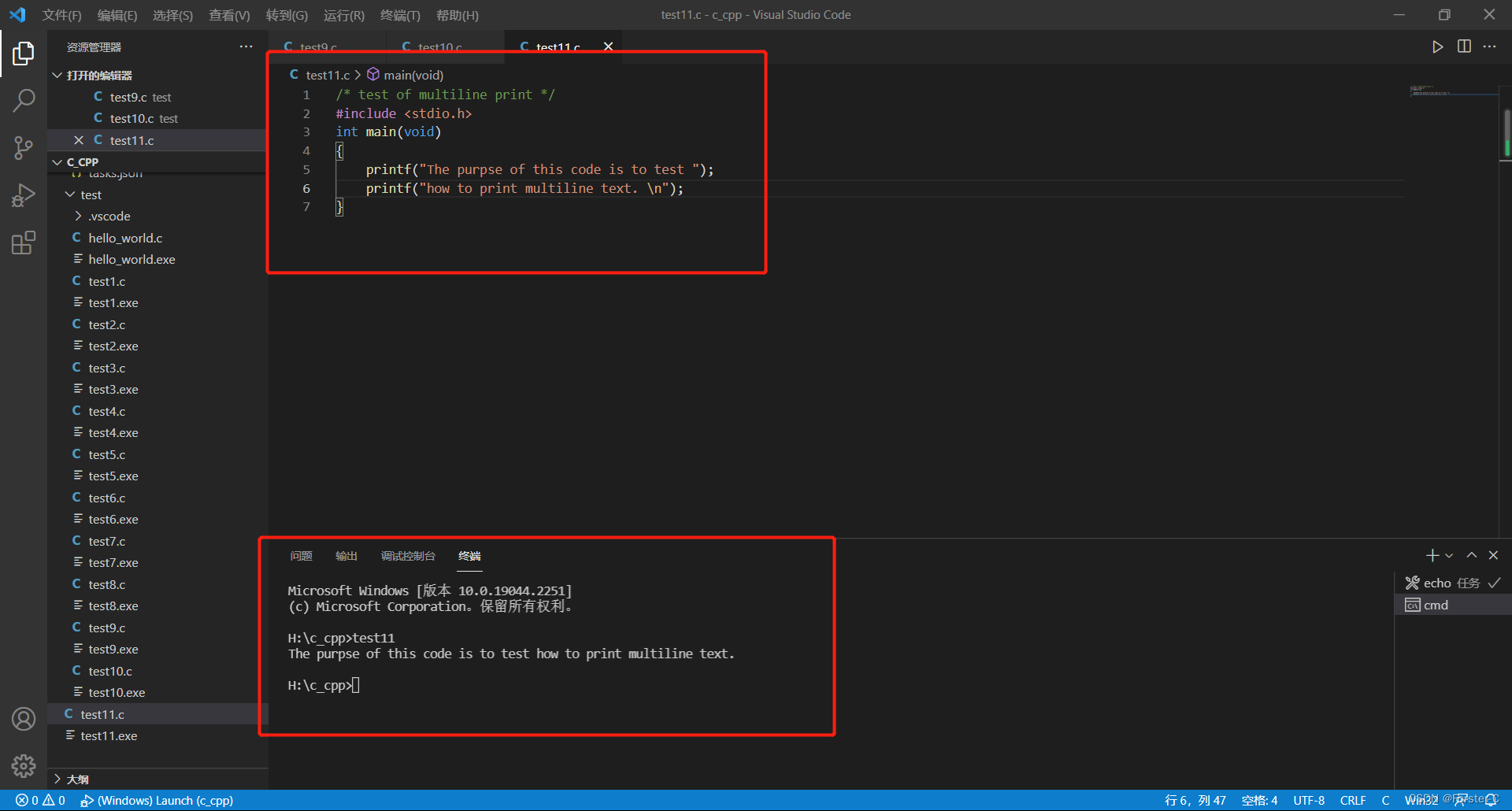
方法一:使用多个printf()语句,只要前面的字符串没有以\n字符结束,后面的字符串会紧跟前面的字符串输出
示例代码:
/* test of multiline print */
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("The purpse of this code is to test ");
printf("how to print multiline text. \n");
return 0;
}运行结果:
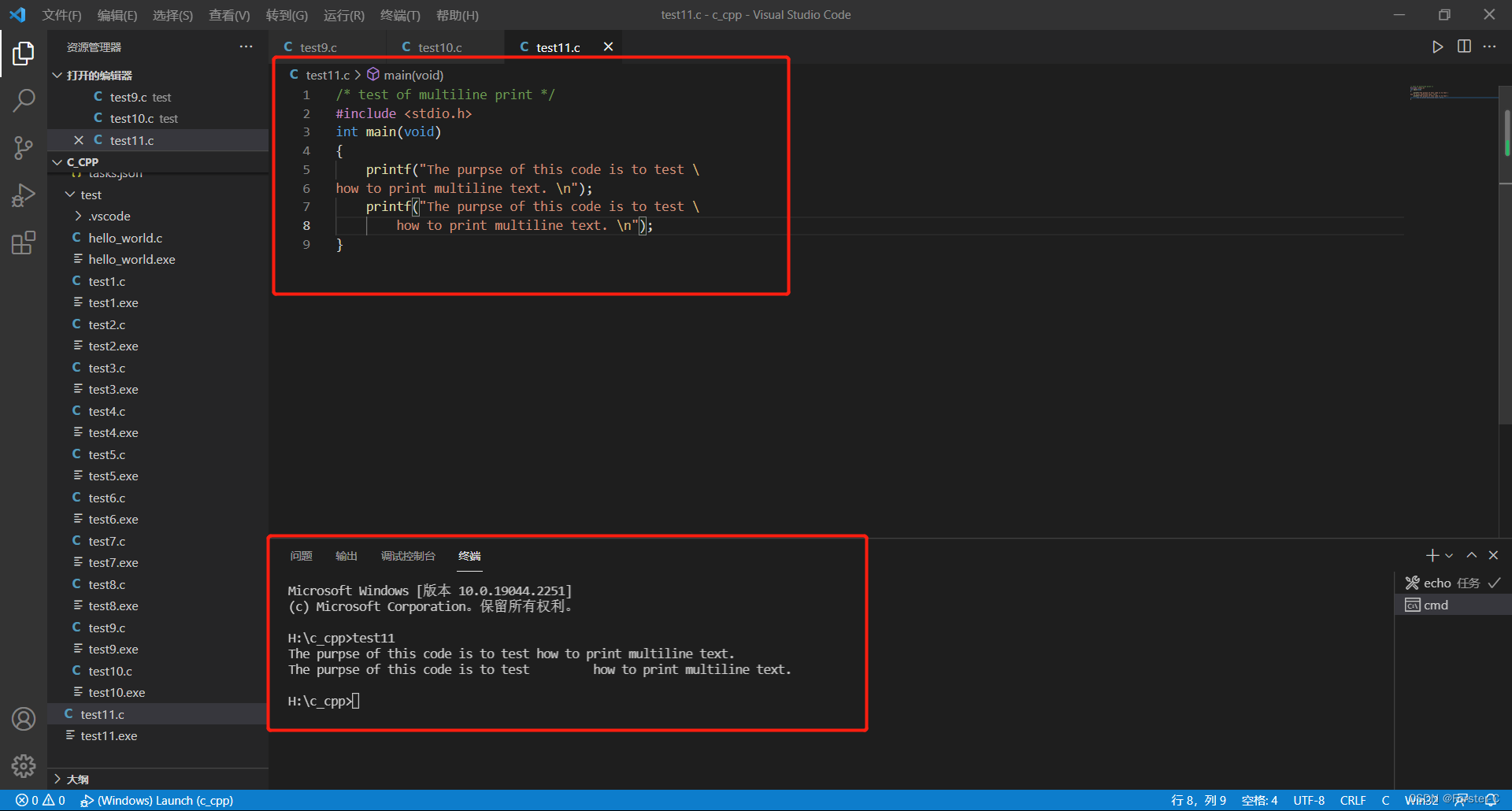
方法二:用反斜线符号(\)和回车键组合,但是要注意在下一行继续该字符串时不能缩进,否则缩进的空格也会变成字符串的一部分
示例代码:
/* test of multiline print */
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("The purpse of this code is to test \
how to print multiline text. \n");
printf("The purpse of this code is to test \
how to print multiline text. \n");
return 0;
}运行结果:
方法三:采用字符串连接的方法,在一个用双引号引起来的字符串后面跟着另一个用双引号引起来的字符串,二者之间禁用空白字符分隔
示例代码:
/* test of multiline print */
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("The purpse of this code is to test"
"how to print multiline text. \n");
return 0;
}运行结果:

